復雜系統的復雜不僅在與架構開發流程本身,還與是否獲得大范圍涉眾的一致同意有關, 涉眾管理的好不能肯定企業架構一定做得好,但是涉眾管理做得不好,企業架構肯定做不好 。在A階段(架構願景)中我們需要進行涉眾管理,交付類似下圖的Stakeholder Map Matrix 。本篇介紹一下涉眾管理。
好處
標識重要的涉眾,能在早期更好的框定架構需求和范圍
通過重要涉眾的支持 ,可以獲取更多的資源
早期頻繁的和涉眾溝通,可以確保更完整的理解架構流程
管理流程
獲取涉眾列表
誰從項目中收益或遭受損失?
誰控制 項目?
誰來設計系統?
誰作出決策?
誰獲得IT系統並決定是否購買?
誰控制資源?
誰有項目要求的專業技能?
誰對項目有影響力?
問 發起人或客戶
檢查組織機構
比較類似項目組
認識涉眾的態度
這個人是否准備好了從當前現狀改變到目標架構上?如故事,准 備怎麼改變?
這個人是否有能力作為一個企業架構發動人和推動者?如果是,他有什 麼能力?
如何參與到企業架構活動中?只是感興趣了解而已,還是需要詳細了解?
對企業架構的開發是否有合約性的承諾?
涉眾分組 涉眾 推動力 當前清楚改變 需要清楚改變 當 前責任義務 需要責任義務 需要支持 CIO 張 三 高 中 高 低 中 高 CFO 李四 中 中 中 低 中 中
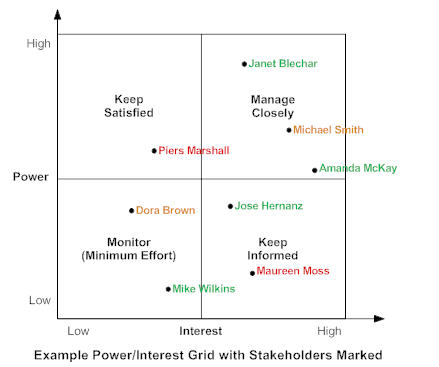
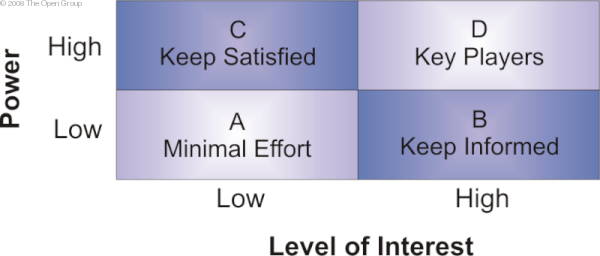
知道關鍵涉眾: Power/Interest
A 不關注他
B 讓他知道
C 使他滿意
D 與他協作
裁剪涉眾相關交付視圖(ViewPoint)
不同項目中自行進行裁剪,在TOGAF文檔中 舉了一個裁剪示例:
涉眾
參與
分類
相 關視圖
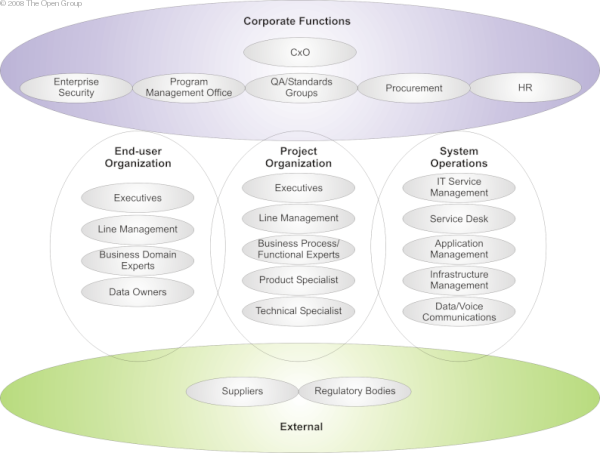
CxO
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., CEO, CFO, CIO, COO
This stakeholder group is interested in the high-level drivers, goals, and objectives of the organization, and howthese are translated into an effective process and IT architecture to advance the business.
KEEP SATISFIED
Business Footprint
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Organization Chart
Program Management Office
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Project Portfolio Managers
This stakeholder group is interested in prioritizing, funding, and aligning change activity. An understanding ofproject content and technical dependencies between projects adds a further dimension of richness to portfolio managementdecision- making.
KEEP SATISFIED
Roadmaps
Business Footprint
Application Communication
Functional Decomposition
Procurement
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Acquirers
Major concerns for these stakeholders are understandingwhat building blocks of the architecture can be bought, andwhat constraints (or rules) exist that are relevant to the purchase.The acquirer will shop with multiple vendors looking for thebest cost solution while adhering to the constraints (or rules) appliedby the architecture, such as standards. The key concern isto make purchasing decisions that fit the architecture, and thereby toreduce the risk of added costs arising from non-compliantcomponents.
KEY PLAYERS
Cost View
Standards View
Human Resources (HR)
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., HR Managers, Training & Development Managers
Key features of the enterprise architecture are the roles and Actors that support the functions, applications, andtechnology of the organization. HR are important stakeholders in ensuring that the correct roles and actors are represented.
KEEP INFORMED
Organization Chart
Organization/Actor/ Location
Enterprise Security
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Corporate Risk Management, Security Officers, IT Security Managers
Major concerns for this group are understanding how to ensure that the information, data, and systems of theorganization are available to only those that have permission, and how to protect the information, data, and systems fromunauthorized tampering.
KEY PLAYERS
Data Security View
Networked Computing Hardware View
Communications View
QA/Standards Group
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Data Owners, Process Owners, Technical Standards Bodies
Major concerns for this group are ensuring the consistent governance of the organization's business, data,application, and technology assets.
KEY PLAYERS
Standards
Guidelines
Specifications
Standards View
Application Portfolio
Technology Portfolio
Technology Standards
Executive
(End User Organization);
e.g., Business Unit Directors, Business Unit CxOs, Business Unit Head of IT/Architecture
This stakeholder group is interested in the high-level drivers, goals, and objectives of the organization, and howthese are translated into an effective process and IT architecture to advance the business.
KEEP SATISFIED
Business Footprint
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Organization Chart
Line Management
(End User Organization);
e.g., Senior Business Managers, Operations Regional Managers, IT Managers
This stakeholder is interested in the top-level functions and processes of the organization, and how the keyapplications of the IT estate support these processes.
KEY PLAYERS
Organization/Actor/ Location
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Cost View
Application & User Location View
Business Domain Experts
(End User Organization);
e.g., Business Process Experts, Business/Process Analyst, Process Architect, Process Designer, Functional Managers, BusinessAnalyst
This stakeholder is interested in the functional aspects of processes and systems. This can cover the human actorsinvolved in the system, the user processes involved in the system, the functions required to support the processes, and theinformation required to flow in support of the processes.
KEY PLAYERS
Process Flow
Use-case
Service/Information Events
Functional Decomposition
Application - Application Communication View
Data Entity/Business Function Matrix
IT Service Management
(Systems Operations);
e.g., Service Delivery Manager
Major concerns for this group are ensuring that IT services provided to the organization meet the service levelsrequired by that organization to succeed in business.
KEEP INFORMED
Standards View
Enterprise Manageability View
IT Operations - Applications
(System Operations);
e.g., Application Architecture, System & Software Engineers
Major concerns for these stakeholders are: Development Approach, Software Modularity and Re-use, PortabilityMigration, and Interoperability.
KEY PLAYERS
Process - System Realization View
Application - Data View
Application Migration Cost View
Software Engineering View
Platform Decomposition View
Networked Computing - Hardware View
Software Distribution View
Data Entities to Application Systems View
IT Operations - Infrastructure
(System Operations);
e.g., Infrastructure Architect, Wintel support, Mid-range support, Operational DBA, Service Desk
Infrastructure stakeholders are typically concerned with location, modifiability, re-usability, and availability ofall components of the system. In general these stakeholders are concerned with ensuring that the appropriate components aredeveloped and deployed within the system in an optimal manner.
KEY PLAYERS
Platform Decomposition View
Standards View
Enterprise Manageability View
Networked Computing - Hardware View
Processing View
Environments & Locations View
IT Operations - Data/Voice Communications
(System Operations);
e.g., Network Management
Communications engineers are typically concerned with location, modifiability, re-usability, and availability ofcommunications and networking services. In general these stakeholders are concerned with ensuring that the appropriatecommunications and networking services are developed and deployed within the system in an optimal manner.
KEY PLAYERS
Communications View
Executive
(Project Organization);
e.g., Sponsor, Program Manager
This stakeholder group is interested in on-time, on- budget delivery of a change initiative that will realizeexpected benefits for the organization.
KEEP INFORMED
Architecture Requirements
Architecture Principles
Architecture Vision
Functional Decomposition
Application & User Location View
Line Management
(Project Organization);
e.g., Project Manager
This stakeholder group is responsible for operationally achieving on-time, on-budget delivery of a changeinitiative with an agreed scope.
KEEP INFORMED
Application - Application Communication View
Functional Decomposition
Environments & Locations View
Business Process/Functional Expert
(Project Organization);
e.g., Financials FICO Functional Consultant, HR Functional Consultant
This stakeholder group will elaborate the functional requirements of a change initiative based on experience andinteraction with business domain experts in the end-user organization.
KEY PLAYERS
Process Flow
Use-case
Service/Information Events
Functional Decomposition
Application - Application Communication View
Product Specialist
(Project Organization);
e.g., Portal Product Specialist
This stakeholder group is responsible for specifying technology product designs in order to meet projectrequirements and comply with the Architecture Vision of the solution.
In a packages and packaged services environment, product expertise can be used to identify product capabilities that can bereadily leveraged and can provide guidance on strategies for product customization.
KEY PLAYERS
Software Engineering View
Application - Data View
Technical Specialist
(Project Organization);
e.g., Application Architect
This stakeholder group is responsible for specifying technology product designs in order to meet projectrequirements and comply with the Architecture Vision of the solution.
KEY PLAYERS
Software Engineering View
Platform Decomposition View
Process System
Realization View
Application - Data View
Application Migration Cost View
Regulatory Bodies
(Outside Services);
e.g., Financial Regulator, Industry Regulator
The main concerns of this group are that they canreceive the information they need in order to regulate the clientorganization, and that their information requirements are beingunderstood and properly satisfied. They are specifically interestedin reporting processes, and the data and applications used to provideregulatory return information.
KEEP SATISFIED
Business Footprint
Application - Application Communication View
Suppliers
(Outside Services);
e.g., Alliance Partners, Key Suppliers
The main concerns of this group are that the information exchange requirements that they have are met in order thatagreed service contracts with the client organizations can be fulfilled.
KEEP SATISFIED
Business Footprint
Service-Information View
Application - Application Communication View
ArchiMate對ViewPoint的分類
ArchiMate架構語言 從視圖的目的和抽象級別來對ViewPoint進行了如下分類:
Viewpoint Purpose
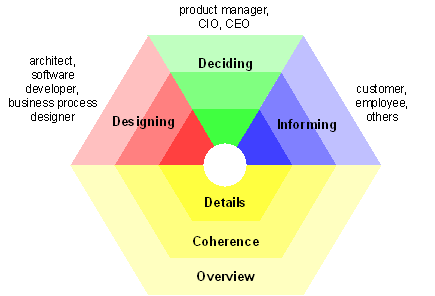
Typical Stakeholders Purpose Examples Designing architect, software developer, business process designer navigate, design, support design decisions, compare alternatives UML diagram, BPMN diagram, flowchart, ER diagram Deciding manager, CIO, CEO decision-making cross-reference table, landscape map, list, report Informing employee, customer, others explain, convince, obtain commitment animation, cartoon, process illustration, char
Viewpoint Abstraction Levels
Typical Stakeholders Purpose Examples Details so ftware engineer, process owner design, manage UML class diagram, BPMN process diagram Coherence operational managers analyze dependencies, impact of-change views expressing relations like “use”, “realize”, and “assign” Overview enterprise architect, CIO, CEO change management landscape map