主要內容
1.概述
2.使用Validation
3.如何擴展
4.深入分析驗證
一.概述
在錄入數據時,對數據有效性的驗證是必不可少的,很多時候我們在UI層上就會做一層驗證,但有時也需要在底層做一些必要的處理,這就要用到ActiveRecord中的數據有效性的驗證。ActiveRecord為我們提供了如下幾個驗證:
n ValidateEmail
n ValidateIsUnique
n ValidateRegExp
n ValidateNotEmpty
n ValidateConfirmation
二.如何使用
為了使用上面這些驗證,我們必須用ActiveRecordValidationBase來代替ActiveRecordBase,即實體類必須繼承於ActiveRecordValidationBase。
[ActiveRecord("Customs")]
public class Custom : ActiveRecordValidationBase
{
//
}
ActiveRecordValidationBase類為我們提供了如下一個方法和屬性:
方法|屬性 說明
IsValid() 返回驗證是否通過
ValidationErrorMessages 獲取驗證錯誤信息數組
下面看一個完整的例子代碼,在這個程序中我們需要驗證用戶名不能為空,Email地址、郵政編碼、電話號碼的格式是否正確
[ActiveRecord("Customs")]
public class Custom : ActiveRecordValidationBase
{
private int _id;
private string _name;
private string _email;
private string _address;
private string _post;
private string _phone;
[PrimaryKey(PrimaryKeyType.Native)]
public int ID
{
get { return this._id; }
set { this._id = value; }
}
[Property,ValidateNotEmpty]
public string Name
{
get { return this._name; }
set { this._name = value; }
}
[Property,ValidateEmail]
public string Email
{
get { return this._email; }
set { this._email = value; }
}
[Property]
public string Address
{
get { return this._address; }
set { this._address = value; }
}
[Property,ValidateRegExp(@"\d{6}")]
public string Post
{
get { return this._post; }
set { this._post = value; }
}
[Property,ValidateRegExp(@"(\(\d{3,4}\)|\d{3,4}-)?\d{8}")]
public string Phone
{
get { return this._phone; }
set { this._phone = value; }
}
public static void DeleteAll()
{
ActiveRecordBase.DeleteAll(typeof(Custom));
}
public static Custom[] FindAll()
{
return ((Custom[])(ActiveRecordBase.FindAll(typeof(Custom))));
}
}
編寫一些簡單的測試代碼,大家有興趣可以看一下:
[Test]
public void TestNameValidation()
{
//姓名為空
Custom custom = new Custom();
custom.Address = "TianJin";
custom.Email = "lhj_cauc@hotmail.com";
custom.Phone = "022-24096356";
custom.Post = "300192";
//錯誤消息數
int expectedError = 1;
Assert.IsFalse(custom.IsValid());
Assert.AreEqual(expectedError,custom.ValidationErrorMessages.Length);
}
[Test]
public void TestPostValidation()
{
//郵政編碼錯誤、Email錯誤
Custom custom = new Custom();
custom.Name = "Terry Lee";
custom.Email = "lhj_cauc#hotmail.com";
custom.Phone = "022-24096356";
custom.Post = "222t";
custom.Address = "Tianjin";
//錯誤消息數
int expectedError = 2;
Assert.IsFalse(custom.IsValid());
Assert.AreEqual(expectedError,custom.ValidationErrorMessages.Length);
}
[Test]
public void TestAllValidation()
{
//全部正確
Custom custom = new Custom();
custom.Name = "Terry Lee";
custom.Email = "lhj_cauc@hotmail.com";
custom.Phone = "022-24096335";
custom.Address = "TianJin";
custom.Post = "300192";
//錯誤消息數
int expectedError = 0;
Assert.IsTrue(custom.IsValid());
Assert.AreEqual(expectedError,custom.ValidationErrorMessages.Length);
}
三.如何擴展
上面這些驗證已經能夠滿足我們絕大多數的需求,但是我們也可以去添加自己的驗證。來看看ActiveRecord中的Validation的類結構圖(只畫出了部分)
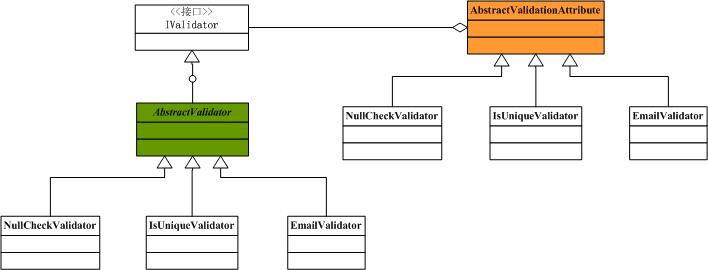
通過上圖可以看到,如果想添加自己的驗證,需要有一個繼承AbstractValidator和繼承於AbstractValidationAttribute的類就可以了,具體可以參考ActiveRecord的代碼。
四.深入分析驗證
通過上面的分析我們都知道所有的實體類都繼承於ActiveRecordValidationBase基類,那麼ActiveRecord是如何通過特性來進行驗證的呢?下面我們結合源碼進一步分析一下。
我們在屬性上加上了驗證, Attribute並不做任何實質性的工作,它只是調用驗證器進行驗證,先來看一下ValidateNotEmptyAttribute的代碼:
[Serializable]
public class ValidateNotEmptyAttribute : AbstractValidationAttribute
{
public ValidateNotEmptyAttribute() : base(new NullCheckValidator())
{
}
public ValidateNotEmptyAttribute(String errorMessage) : base(new NullCheckValidator(), errorMessage)
{
}
}
所有驗證工作都是在Validator中進行的,以NullCheckValidator為例來看它做了什麼操作:
[Serializable]
public class NullCheckValidator : AbstractValidator
{
public NullCheckValidator()
{
}
public override bool Perform(object instance, object fieldValue)
{
return fieldValue != null && fieldValue.ToString().Length != 0;
}
protected override string BuildErrorMessage()
{
return String.Format("{0} is not optional.", Property.Name);
}
}
這個類其實很簡單,但我們注意到有一個Perform的方法,正是這個方法完成了驗證工作,拿這個例子來說,如果字段的值為空或長度等於零就返回false,否則為true。對於正則驗證等其他的也都是在這個方法中完成。回到ActiveRecordValidationBase中去,看這個類初始化的時候做了什麼操作?
/**//// <summary>
/// Constructs an ActiveRecordValidationBase
/// </summary>
public ActiveRecordValidationBase()
{
CollectValidators( this.GetType() );
}
/**//// <summary>
/// Collect the validations applied to this class properties.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetType"></param>
private void CollectValidators( Type targetType )
{
ActiveRecordModel model = GetModel( targetType );
if (model == null)
{
throw new ActiveRecordException("Seems that the framework wasn't initialized properly. (ActiveRecordModel could not obtained)");
}
__validators.AddRange( model.Validators );
while( model.Parent != null )
{
__validators.AddRange( model.Parent.Validators );
model = model.Parent;
}
}
在初始化的時候,通過ActiveRecordModel獲取到當前實體所有屬性對應的Validator,並放在了一個ArrayList中去,然後在IsValid()方法中再逐一調用Validator的Perform()方法來判斷驗證是否通過,因為所有的驗證器都實現了Ivalidator。如果有驗證發生錯誤,則把錯誤信息保存再一個字符數組中,可以通過屬性ValidationErrorMessages來獲取錯誤信息。
public bool IsValid()
{
ArrayList errorlist = new ArrayList();
__failedProperties = new Hashtable();
foreach(IValidator validator in __validators)
{
if (!validator.Perform(this))
{
String errorMessage = validator.ErrorMessage;
errorlist.Add( errorMessage );
ArrayList items = null;
if (__failedProperties.Contains(validator.Property))
{
items = (ArrayList) __failedProperties[validator.Property];
}
else
{
items = new ArrayList();
__failedProperties[validator.Property] = items;
}
items.Add(errorMessage);
}
}
_errorMessages = (String[]) errorlist.ToArray( typeof(String) );
return errorlist.Count == 0;
}
在ActiveRecord中的數據有效性驗證就介紹到這兒了,下篇我會介紹ActiveRecord常用的一些技巧。[非常感謝idior大哥提出的意見]