本文導讀:
C#的預處理器指令從來不會轉化為可執行代碼的命令,但是會影響編譯過程的各個方面,常用的預處理器指令有#define、#undef、#if,#elif,#else和#endif等等,下面介紹C#中使用#define進行條件編譯的實例。
C#中條件編譯指令用於按條件包含或排除源文件中的某些部分。在Visual Studio中,會看到被排除的代碼顯示為灰色。
一、#define可以用來做什麼
1、當計劃發布兩個版本的代碼的時候。即基本版和擁有更多版本的企業版,就可以用到條件編譯指令;
2、例如同一個文件給silverlight、wpf、winform等使用,並且還考慮Debug和Release等,有大部分代碼是一樣的;
3、指定函數和屬性是否編譯到最終產品中去。
二、#define用法
語法:#define 名稱
注意:這裡名稱取Debug,你也可以取其他名稱如Dragon
1 #define Debug
說明:
1、Debug可以看做是聲明的一個變量,但此變量沒有真正的值,存在時#if Debug結果為true,否則為false;
2、#define單獨用沒什麼意義,一般是和#if或者Conditional特性結合使用;
3、#define必須定義在所有using命名空間前面;
4、Debug與DEBUG是不同的,C#區分大小寫。
三、#define條件編譯實例
方式一、使用#if
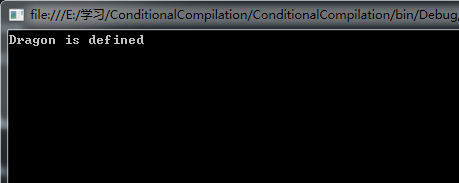
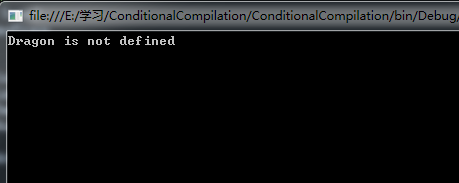
1 #define Dragon
2 using System;
3 using System.Collections.Generic;
4 using System.Linq;
5 using System.Text;
6 using System.Diagnostics;
7
8 namespace ConditionalCompilation
9 {
10 class Program
11 {
12 static void Main(string[] args)
13 {
14 #if Dragon
15 Console.WriteLine("Dragon is defined");
16 #else
17 Console.WriteLine("Dragon is not defined");
18 #endif
19 Console.ReadKey();
20 }
21 }
22 }
輸出結果如下:
如果注釋掉 //#define Dragon ,輸出結果為:
方式二、使用Conditional特性
我們可以將一些函數隔離出來,使得它們只有在定義了某些環境變量或者設置了某個值之後才能發揮作用,使用Conditional特性的隔離策略要比#if/#endif不容易出錯。
1 #define Debug
2 #define Trace
3 #if (Debug && Trace)
4 #define DebugAndTrace
5 #endif
6 using System;
7 using System.Collections.Generic;
8 using System.Linq;
9 using System.Text;
10 using System.Diagnostics;
11
12 namespace ConditionalCompilation
13 {
14 class Program
15 {
16 static void Main(string[] args)
17 {
18 Print0();
19 Print1();
20 Print2();
21 Print3();
22 Console.ReadKey();
23 }
24
25 [Conditional("DEBUG")]
26 static void Print0()
27 {
28 Console.WriteLine("DEBUG is defined");
29 }
30
31 [Conditional("Debug")]
32 static void Print1()
33 {
34 Console.WriteLine("Debug is defined");
35 }
36
37 //定義了Debug或者Trace後才會執行此方法
38 //或者的關系
39 [Conditional("Debug"), Conditional("Trace")]
40 static void Print2()
41 {
42 Console.WriteLine("Debug or Trace is defined");
43 }
44
45 //只有定義了Debug和Trace後才會執行此方法
46 //並且的關系
47 [Conditional("DebugAndTrace")]
48 static void Print3()
49 {
50 Console.WriteLine("Debug and Trace is defined");
51 }
52 }
53 }
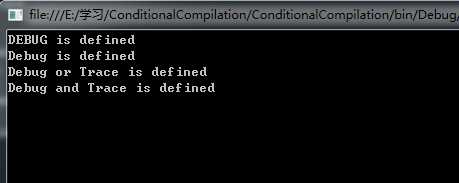
輸出結果如下:
說明:
1、代碼中沒有定義DEBUG,卻輸出了DEBUG,是因為DEBUG版本,自動定義了DEBUG。“項目——右鍵——屬性——生成選項卡——常規欄”下的定義 DEBUG 常量(U)前面的復選框被選中。當然你可以去掉其選中狀態,這樣就不會輸出DEBUG了。
2、如果Debug和Trace均沒有定義,則不會輸出Debug or Trace;只有Debug和Trace均定義了,才會輸出Debug and Trace。
3、可以給Conditional增加多個屬性如示例代碼 [Conditional("Debug"), Conditional("Trace")] ,不過多個屬性之間的關系是或的關系,即“Debug”或者“Trace”任意一個被定義了,那麼對應方法就會被執行。
4、如果需要增加多個與的屬性,直接用Conditional是無法實現的,需要借助#if/#endif間接來完成,如示例代碼中的組合操作
1 #if (Debug && Trace) 2 #define DebugAndTrace 3 #endif
使用Conditional屬性的方法受到以下限制:
1、條件方法必須是類聲明或結構聲明中的方法。如果在接口聲明中的方法上指定Conditional屬性,將出現編譯時錯誤;
2、條件方法不能是接口方法的實現。否則將發生編譯時錯誤;
3、條件方法必須具有void返回類型;
4、不能用override修飾符標記條件方法。但是,可以用virtual修飾符標記條件方法。此類方法的重寫方法隱含為有條件的方法,而且不能用Conditional屬性顯式標記。
環境變量(或條件編譯符號)的設置方法有三:
1)用#define定義以及#undef取消定義,在所有using命名空間前面定義;
2)用編譯器命令行選項(例如,/define:DEBUG),在“項目——右鍵——屬性——生成選項卡——常規欄”下的條件編譯符號(Y)中設置(如果多個,可以用英文逗號隔開)。DEBUG版本下,系統默認設置了DEBUG和TRACE;
3)用操作系統外殼程序中的環境變量(例如,set DEBUG=1)。
參考鏈接①:http://www.studyofnet.com/news/1240.html
參考鏈接②:http://blog.csdn.net/teng_s2000/article/details/5510420
參考鏈接③:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.diagnostics.conditionalattribute.aspx