最近很忙,既要外出找工作又要兼顧老板公司的項目。今天在公司,忙裡偷閒,總結一下.NET中的異步調用函數的實現方法,DebugLZQ在寫這篇博文之前自己先動手寫了本文的所有示例代碼,開寫之前是做過功課的,用代碼說話方有說服力。
本文的內容旨在用最簡潔的代碼來把異步調用的方法說清楚,園子裡的高手老鳥可以繞行,不喜勿噴,非誠勿擾~
lz的前一篇文章簡單的說了下異步,主要是從理解上來講;這篇文章主要寫具體的實現方法。實現異步編程有4種方法可供選擇,這4種訪求實際上也對應著4種異步調用的模式,分為“等待”和“回調”兩大類。四種方法,我在代碼中都進行了詳細的注釋,這裡不羅嗦了,直接用代碼說明吧
第一種方法:BeginEnvoke EndEnvoke方法,屬於“等待”類。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 異步調用實現方法匯總
{
/// <summary>
/// 異步調用方法總結:
/// 1.BeginEnvoke EndEnvoke
/// 當使用BeginInvoke異步調用方法時,如果方法未執行完,EndInvoke方法就會一直阻塞,直到被調用的方法執行完畢
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
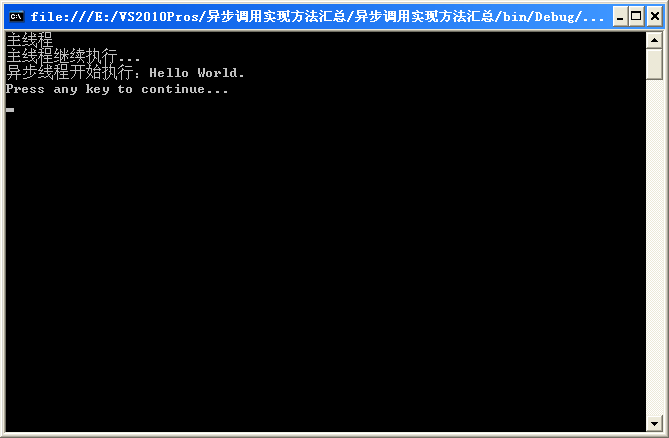
Console.WriteLine("主線程");
IAsyncResult result= printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello World.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主線程繼續執行...");
//當使用BeginInvoke異步調用方法時,如果方法未執行完,EndInvoke方法就會一直阻塞,直到被調用的方法執行完畢
printDelegate.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("異步線程開始執行:"+s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
需要注意的地方,代碼中都有注明了,程序運行結果如下:
第二種方法:WaitOne。同樣屬於“等待”類。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 異步調用實現方法匯總2
{
/// <summary>
/// 異步調用方法總結:
/// 2.WaitOne
/// 可以看到,與EndInvoke類似,只是用WaitOne函數代碼了EndInvoke而已。
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
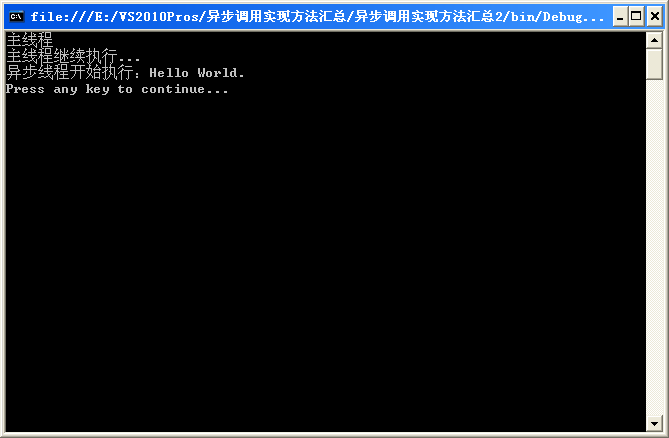
Console.WriteLine("主線程");
IAsyncResult result = printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello World.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主線程繼續執行...");
result.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(-1, false);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("異步線程開始執行:" + s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
需要注意的地方,代碼中都有注明了,程序運行結果如下:
第三種方法:輪詢。也是屬於“等待”類。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 異步調用實現方法匯總3
{
/// <summary>
/// 異步調用方法總結:
/// 3.輪詢
/// 之前提到的兩種方法,只能等下異步方法執行完畢,
/// 在完畢之前沒有任何提示信息,整個程序就像沒有響應一樣,用戶體驗不好,
/// 可以通過檢查IasyncResult類型的IsCompleted屬性來檢查異步調用是否完成,
/// 如果沒有完成,則可以適時地顯示一些提示信息
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
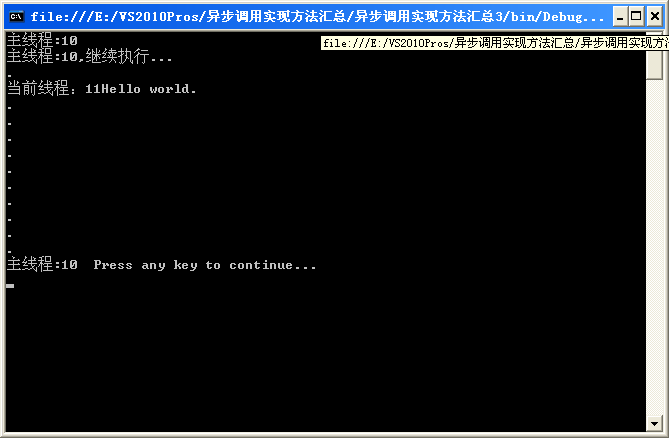
Console.WriteLine("主線程:"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId );
IAsyncResult result = printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello world.", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("主線程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + ",繼續執行...");
while (!result.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine(".");
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
Console.WriteLine("主線程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + " Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("當前線程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId + s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
}
需要注意的地方,代碼中都有注明了,程序運行結果如下:
第四種方法:回調。當然屬於“回調”類。推薦!!!!
之前三種方法者在等待異步方法執行完畢後才能拿到執行的結果,期間主線程均處於等待狀態。回調和它們最大的區別是,在調用BeginInvoke時只要提供了回調方法,那麼主線程就不必要再等待異步線程工作完畢,異步線程在工作結束後會主動調用我們提供的回調方法,並在回調方法中做相應的處理。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace 異步調用實現方法匯總4
{
/// <summary>
/// 異步調用方法總結:
/// 4.回調
/// 之前三種方法者在等待異步方法執行完畢後才能拿到執行的結果,期間主線程均處於等待狀態。
/// 回調和它們最大的區別是,在調用BeginInvoke時只要提供了回調方法,那麼主線程就不必要再等待異步線程工作完畢,
/// 異步線程在工作結束後會主動調用我們提供的回調方法,並在回調方法中做相應的處理,例如顯示異步調用的結果。
/// </summary>
class Program
{
public delegate void PrintDelegate(string s);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintDelegate printDelegate = Print;
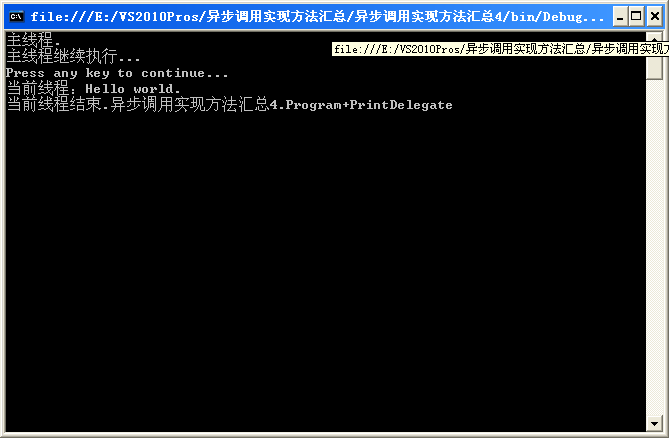
Console.WriteLine("主線程.");
printDelegate.BeginInvoke("Hello world.", PrintComeplete, printDelegate);
Console.WriteLine("主線程繼續執行...");
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue...");
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
public static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("當前線程:"+s);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
//回調方法要求
//1.返回類型為void
//2.只有一個參數IAsyncResult
public static void PrintComeplete(IAsyncResult result)
{
(result.AsyncState as PrintDelegate).EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("當前線程結束." + result.AsyncState.ToString());
}
}
}
需要注意的地方,代碼中都有注明了,程序運行結果如下:
通過EndInvoke方法得到同步函數的返回值。上面的同步方法返回值為void,我們給個例子:
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows;
namespace TestDelegateWrapper
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void ButtonBase_OnClick(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
WrapperSyncMethodAsync("ABC");
Trace.WriteLine("Main thread continue...");
}
private delegate string SyncMethod1Delegate(string str);
private void WrapperSyncMethodAsync(string str)
{
SyncMethod1Delegate syncMethod1Delegate = SyncMethod1;
syncMethod1Delegate.BeginInvoke(str, x =>
{
var result= syncMethod1Delegate.EndInvoke(x);
// using the result to do something
Trace.WriteLine(result);
}, null);
}
private string SyncMethod1(string str)
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
return str;
}
}
}
輸出如下:
Main thread continue...
ABC
以上就是四種實現異步調用函數的四種方法,說的很清楚了,就寫這麼多~希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持幫客之家。