本實例介紹如何在自己的程序中調用指定的Windows程序。
首先啟動一個新的項目,在空白的窗體上添加4個TButton組件。添加組件後的窗體如圖1所示。
圖1 添加組件後的窗體
其中WinExec按鈕用於以WinExec函數來調用指定的Windows程序。ShellExecute按鈕用於以ShellExecute函數來調用指定的Windows程序。CreateProcess按鈕和TerminateProcess按鈕用於實現對被調用程序更全面的操作,前者用於調用指定的Windows程序,而後者則用於終止被調用的Windows程序。
以WinExec函數的方式來調用指定的Windows程序的響應代碼如下:
procedure TForm1.btnWinExecClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
WinExec(’Notepad.exe’,SW_MAXIMIZE);
end;
其中WinExec函數的第1個參數表示了被調用程序的路徑和名稱,第2個參數表示了程序的顯示方式。
以ShellExecute函數的方式來調用指定的Windows程序的響應代碼如下:
procedure TForm1.btnShellExecuteClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
ShellExecute(Application.Handle,’Open’,’NotePad.exe’,PChar(’C:\AutoExec.bat’),nil,SW_SHOWNORMAL);
end;
其中ShellExecute用於打開與指定文件關聯在一起的程序文件。第1個參數用於指定一個窗口的句柄;第2個參數指定了程序運行的類別,如’Open’或’Print’;第3個參數指定了想用關聯程序打印或打開的一個程序名或文件名;如果第3個參數中指定了一個可執行文件,那麼第4個參數就是傳遞給執行程序的參數;第5個參數指定了可執行程序的完整路徑。最後一個參數用於設定程序運行方式。
下面來介紹利用CreateProcess函數和TerminateProcess函數如何實現對被調用程序更全面的操作。
首先定義3個全局變量:
PI:TProcessInformation;
SI:TStartUpInfo;
MyHandle:Thandle;
利用CreateProcess函數調用指定程序的響應代碼如下:
procedure TForm1.btnCreateProcessOpenClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
FillChar(SI,sizeof(SI),#0);
with SI do
begin
cb:=sizeof(SI);
dwFlags:=StartF_UsesTDHandles or STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW;
lptitle:=nil;
wShowWindow:=SW_Show;
end;
CreateProcess(PChar(’C:\WINNT\Notepad.exe’),
nil,nil,nil,true,DETACHED_PROCESS,nil,nil,SI,PI);
end;
調用CreateProcess函數激活C:\WINNT\Notepad.exe程序後,把它的進程信息存儲在變量PI中,然後通過下面的語句來關閉本實例打開的C:\WINNT\Notepad.exe程序:
procedure TForm1.btnCreateProcessCloseClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
MyHandle:=OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE,PI.dwProcessId);
TerminateProcess(MyHandle,0);
end;
程序代碼如下:
unit Unit1;
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms,
Dialogs, StdCtrls, ShellAPI;
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
btnWinExec: TButton;
btnCreateProcessOpen: TButton;
btnCreateProcessClose: TButton;
btnShellExecute: TButton;
procedure btnWinExecClick(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnCreateProcessOpenClick(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnCreateProcessCloseClick(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnShellExecuteClick(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
PI:TProcessInformation;
SI:TStartUpInfo;
MyHandle:Thandle;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
procedure TForm1.btnWinExecClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
WinExec(’Notepad.exe’,SW_MAXIMIZE);
end;
procedure TForm1.btnCreateProcessOpenClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
FillChar(SI,sizeof(SI),#0);
with SI do
begin
cb:=sizeof(SI);
dwFlags:=StartF_UsesTDHandles or STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW;
lptitle:=nil;
wShowWindow:=SW_Show;
end;
CreateProcess(PChar(’C:\WINNT\Notepad.exe’),nil,nil,nil,true,DETACHED_PROCESS,nil,nil,SI,PI);
end;
procedure TForm1.btnCreateProcessCloseClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
MyHandle:=OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE,PI.dwProcessId);
TerminateProcess(MyHandle,0);
//關閉進程
end;
procedure TForm1.btnShellExecuteClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
ShellExecute(Application.Handle,’Open’,’NotePad.exe’,PChar(’C:\AutoExec.bat’),nil,SW_SHOWNORMAL);
end;
end.
保存文件,然後按F9鍵運行程序,程序運行的初始畫面如圖2所示。
圖2 程序運行的初始畫面
單擊窗體上的WinExec按鈕、ShellExecute按鈕和CreateProcess按鈕都可以激活“記事本”程序,而通過CreateProcess按鈕激活的程序可以通過TerminateProcess按鈕來終止。程序運行結果如圖3所示。
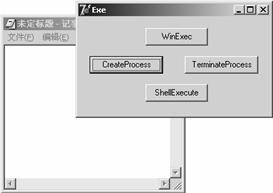
圖3 程序運行結果
本程序介紹了三種調用指定的Windows程序的方法,這樣在大型應用程序中就可以實現各個模塊程序之間的“程序超級鏈接”。