Description
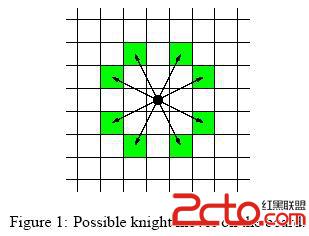
Input
The input begins with the number n of scenarios on a single line by itself.Output
For each scenario of the input you have to calculate the minimal amount of knight moves which are necessary to move from the starting point to the ending point. If starting point and ending point are equal,distance is zero. The distance must be written on a single line.Sample Input
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 8 0 0 7 0 100 0 0 30 50 10 1 1 1 1Sample Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 5 28 0 <strong>題意:給一個N*N的棋盤,並給出起點終點的x y坐標 球起點到終點的最小步數。</strong> 雙向BFS代碼: <pre class="brush:java;">#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<queue> #include<cstring> #define qq 330 using namespace std; int vis1[qq][qq]; //既標記路徑 也統計步數 int vis2[qq][qq]; int fx1[8]={2,2,-2,-2,1,1,-1,-1}; int fx2[8]={1,-1,1,-1,2,-2,2,-2}; struct node { int x,y; }start,end; //雙向BFS的兩端起點 int sx,sy,ex,ey; int m; bool inside(int xx,int yy) //判斷越界 { if(xx>=0&&yy>=0&&xx<m&&yy<m) return="" true;="" else="" false;="" }="" void="" dbfs()="" {="" int="" i,tq,tw;="" queue<node="">q,w; //兩個隊列 start.x=sx;start.y=sy; end.x=ex;end.y=ey; q.push(start); w.push(end); vis1[sx][sy]=0; //後面的步數是從0開始加的 vis2[ex][ey]=0; while(!q.empty()&&!w.empty()) { node now,next; tq=q.size(); //為了先將一個隊列的全部判斷完 while(tq--) { now=q.front(); q.pop(); if(inside(now.x,now.y)&&vis2[now.x][now.y]!=-1) //兩端開始的都經過這一點。。 { printf("%dn",vis1[now.x][now.y]+vis2[now.x][now.y]); return; } for(i=0;i<8;i++) { next.x=now.x+fx1[i]; next.y=now.y+fx2[i]; if(inside(next.x,next.y)&&vis2[next.x][next.y]!=-1) //重要,,因為奇數步時。。。 { printf("%dn",vis1[now.x][now.y]+1+vis2[next.x][next.y]); return; } if(inside(next.x,next.y)&&vis1[next.x][next.y]==-1) { vis1[next.x][next.y]=vis1[now.x][now.y]+1; q.push(next); } } } tw=w.size(); while(tw--) //同上 { now=w.front(); w.pop(); if(inside(now.x,now.y)&&vis1[now.x][now.y]!=-1) { printf("%dn",vis1[now.x][now.y]+vis2[now.x][now.y]); return; } for(i=0;i<8;i++) { next.x=now.x+fx1[i]; next.y=now.y+fx2[i]; if(inside(next.x,next.y)&&vis1[next.x][next.y]!=-1) { printf("%dn",vis2[now.x][now.y]+1+vis1[next.x][next.y]); return; } if(inside(next.x,next.y)&&vis2[next.x][next.y]==-1) { vis2[next.x][next.y]=vis2[now.x][now.y]+1; w.push(next); } } } } } int main() { int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&m); scanf("%d%d%d%d",&sx,&sy,&ex,&ey); memset(vis1,-1,sizeof(vis1)); //標記為未走過 memset(vis2,-1,sizeof(vis2)); dbfs(); } return 0; } </m&&yy<m)></cstring></queue></cstdio></iostream></pre><br>雙向BFS的精髓在於從起點終點同時開始搜索 當找到一點同時兩端都經過時 即找到最短路徑。。<br><br>