Ncurses是一個能提供基於文本終端窗口功能的動態庫. Ncurses可以:
Ncurses可以在任何遵循ANSI/POSIX標准的Unix/Linux系統上運行,除此之外,它還可以從系統數據庫中檢測終端的屬性,,並且自動進行調整,提供一個不受終端約束的接口。因此,Ncurses可以在不同的系統平台和不同的終端上工作的非常好。
mc工具集就是一個用ncurses寫的很好的例子,而且在終端上系統核心配置的界面同樣是用ncurses編寫的. 下面就是它們的截圖:
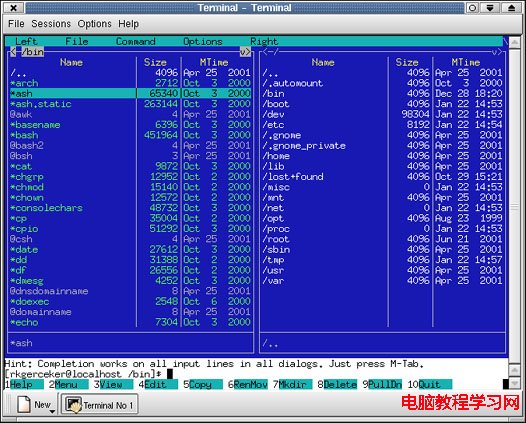
當然,在我們這篇文章中,我們不會教你怎麼寫NCurses程序,我們只是想告訴你如何用Python來寫Ncurses的程序,示例會非常簡單,點到為止。
在此之前,我們先簡單的回顧一下如何使用Python的一些簡單的語法。
先看看一個最簡單的Python程序:
print "How easy is this?" x = 1 y = 2 z = x + y print "Result of x + y is", z
程序很簡單,我就不多說,把這個文件存成test.py,然後在命令行下調用python test.py就可以看到輸出了。
下面我們再來看一個Python的函數定義——還是很簡單,我也不用多說了。
def saystuff(mystring):
print "You said:", mystring
saystuff("Bach rules")
saystuff("So does Telemann")
好,言歸正傳,讓我們來看一下,如何在Python中使用NCurses,下面是一個小例程:
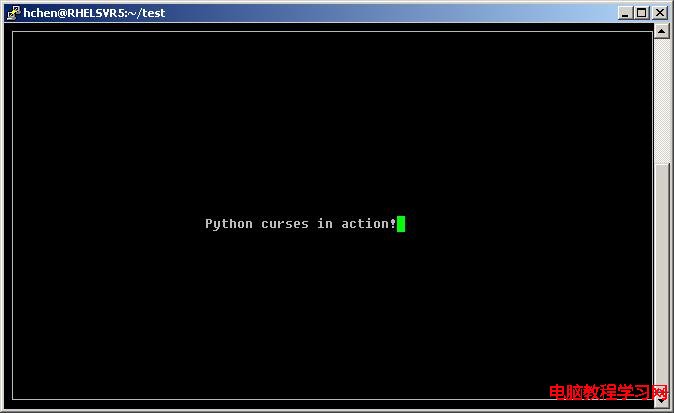
import curses myscreen = curses.initscr() myscreen.border(0) myscreen.addstr(12, 25, "Python curses in action!") myscreen.refresh() myscreen.getch() curses.endwin()
注意這個示例中的第一行import curses,表明使用curses庫,然後這個示像在屏幕中間輸出“Python curses in action!”字樣,其中坐標為12, 25,注意,在字符界面下,80 x 25是屏幕大小,其用的是字符,而不是像素。下面是運行後的抓屏:
最後,我們再來看一個數字菜單的示例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from os import system
import curses
def get_param(prompt_string):
screen.clear()
screen.border(0)
screen.addstr(2, 2, prompt_string)
screen.refresh()
input = screen.getstr(10, 10, 60)
return input
def execute_cmd(cmd_string):
system("clear")
a = system(cmd_string)
print ""
if a == 0:
print "Command executed correctly"
else:
print "Command terminated with error"
raw_input("Press enter")
print ""
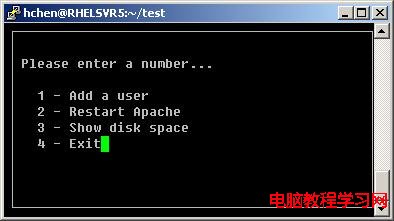
x = 0
while x != ord('4'):
screen = curses.initscr()
screen.clear()
screen.border(0)
screen.addstr(2, 2, "Please enter a number...")
screen.addstr(4, 4, "1 - Add a user")
screen.addstr(5, 4, "2 - Restart Apache")
screen.addstr(6, 4, "3 - Show disk space")
screen.addstr(7, 4, "4 - Exit")
screen.refresh()
x = screen.getch()
if x == ord('1'):
username = get_param("Enter the username")
homedir = get_param("Enter the home directory, eg /home/nate")
groups = get_param("Enter comma-separated groups, eg adm,dialout,cdrom")
shell = get_param("Enter the shell, eg /bin/bash:")
curses.endwin()
execute_cmd("useradd -d " + homedir + " -g 1000 -G " + groups + " -m -s " + shell + " " + username)
if x == ord('2'):
curses.endwin()
execute_cmd("apachectl restart")
if x == ord('3'):
curses.endwin()
execute_cmd("df -h")
curses.endwin()
下面是運行時的顯示:
如果你你了解NCurses編程,你可以看看相關的Linux HOW-TO的文章,鏈接在這裡:Linux Documentation Project’s NCURSES Programming How To