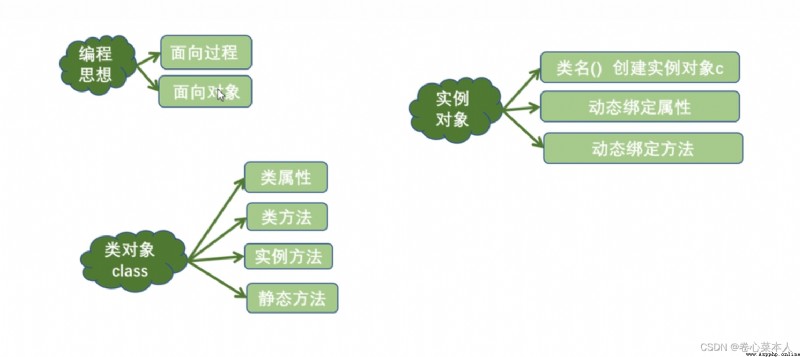

Student是類的名稱(簡稱類名),類名由一個或多個單詞組成,The first letter of each word is capitalized and the rest are lowercase (python中的規范)
對象本身具有內存空間,數據類型,數值
class Student: #類名由一個或多個單詞組成,The first letter of each word is capitalized and the rest are lowercase (python中的規范)
native_place="abc" #直接寫在類裡的變量,是類屬性
#初始化方法
def __init__(self,name,age): #()中的self是實例對象,name、age是局部變量
self.name=name #self.name稱為實例屬性,賦值操作,將局部變量name的值賦給實例屬性
self.age=age
#實例方法
def eat(self): #定義類的實例方法,Similar to function definitions,Instance methods to writeself,即實例對象
print("吃飯")
#靜態方法
@staticmethod #Used before static [email protected]修飾
def method(): #靜態方法中不能寫self
print("使用靜態方法")
#類方法
@classmethod #Used before class [email protected]修飾
def cm(cls): #class method to writecls,即類對象
print("類方法")①直接寫在 Inside the class but outside the method 的變量 稱為 類屬性
②初始化方法__init__(self,name,age)有默認參數self(指實例對象),See the code comments above for details
③def在 類裡面 是類的實例方法,在 Outside the class are functions
④靜態方法 要 用@staticmethod修飾,類方法 要 用@classmethod修飾
⑤實例方法()內必須是self對象(實例對象,默認參數),靜態方法()must not writeself,類方法()要寫cls(類對象,默認參數)
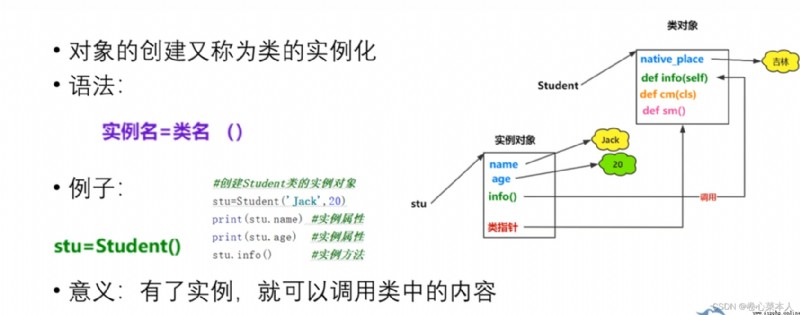
The instance object in the above figure isstu, 類對象是Student
class Student: #類名由一個或多個單詞組成,The first letter of each word is capitalized and the rest are lowercase (python中的規范)
native_place="abc" #直接寫在類裡的變量,是類屬性
#初始化方法
def __init__(self,name,age): #()中的name,age是局部變量
self.name=name #self.name稱為實例屬性,賦值操作,將局部變量name的值賦給實例屬性
self.age=age
#實例方法
def eat(self): #定義類的實例方法,Similar to function definitions,Instance methods to writeself
print("吃飯")
#靜態方法
@staticmethod #Used before static [email protected]修飾
def method(): #靜態方法中不能寫self
print("使用靜態方法")
#類方法
@classmethod #Used before class [email protected]修飾
def cm(cls):
print("類方法")
stu=Student("abc",20) #Because the initialization method in the class hasname和age兩個局部變量,因此用"abc",20初始化
#調用實例方法,Since the instance method is passed isself對象,Therefore, the instance method can be called directly by the object
stu.eat() #輸出"吃飯"
print(stu.name) #輸出"abc"
ptint(stu.age) #輸出20
由於實例方法傳遞的是self對象,故可Instance methods are called directly by the object

class Student: #類名由一個或多個單詞組成,The first letter of each word is capitalized and the rest are lowercase (python中的規范)
native_place="abc" #直接寫在類裡的變量,是類屬性
#初始化方法
def __init__(self,name,age): #()中的name,age是局部變量
self.name=name #self.name稱為實例屬性(實例變量),賦值操作,將局部變量name的值賦給實例屬性
self.age=age
#實例方法
def eat(self): #定義類的實例方法,Similar to function definitions,Instance methods to writeself
print("吃飯")
#靜態方法
@staticmethod #Used before static [email protected]修飾
def method(): #靜態方法中不能寫self
print("使用靜態方法")
#類方法
@classmethod #Used before class [email protected]修飾
def cm(cls):
print("類方法")
#類屬性的調用,Class attributes are shared by all instance objects of that class
stu1=Student("abc","18")
stu2=Student("wsx","20")
print(stu1.native_place) #輸出“abc”
print(stu2.native_place) #和上面一樣
Student.native_place="tyu"
print(stu1.native_place) #輸出“tyu”
print(stu2.native_place) #和上面一樣
#類方法的調用,Since the class method is passed isclsAn object is a class object,So use the class name to call the class method
Student.cm #直接輸出"類方法"
#靜態方法的使用方式,由於沒有默認參數,So use the class name to call the method
Student.method #輸出"使用靜態方法"
class Student: #類名由一個或多個單詞組成,The first letter of each word is capitalized and the rest are lowercase (python中的規范)
native_place="abc" #直接寫在類裡的變量,是類屬性
#初始化方法
def __init__(self,name,age): #()中的name,age是局部變量
self.name=name #self.name稱為實例屬性(實例變量),賦值操作,將局部變量name的值賦給實例屬性
self.age=age
#實例方法
def eat(self): #定義類的實例方法,Similar to function definitions,Instance methods to writeself
print("吃飯")
stu1=Student("張三",20)
stu2=Student("李四",30)
#動態綁定屬性
stu2.gender="女"
print(stu2.name,stu2.age,stu2.gender)
print(stu1.name,stu1.age,stu1.gender)#報錯,因為stu1沒有gender屬性
def show:
print("Outside of classes are functions")
#動態綁定方法
stu1.show=show
print(stu1.show) #輸出"Outside of classes are functions"
print(stu2.show) #報錯,因為stu2沒有綁定show方法