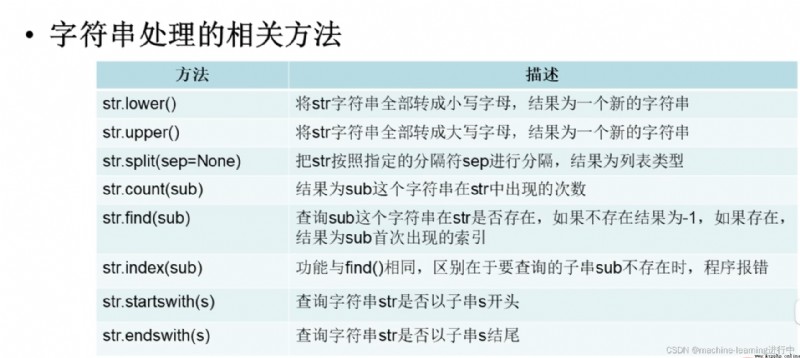
注意是相關方法,不是函數
#大小寫轉換
s1="HelloWorld"
new_s1=s1.lower() #全部轉為小寫,And generate a new string to assignnew_s1
new__s1=s1.upper() #全部轉為大寫,And generate a new string to assignnew__s1
#字符串的分割
s2="[email protected]"
new_s2=s2.split("@") #After the split is the list type
print("郵箱名",new_s2[0],"郵箱域名",new_s2[1])
#Counts the number of substrings in the specified string
print(s1.count("o"))
#檢索操作
print(s1.find("o")) #"o"首次出現的位置索引
print(s1.index("o"))
print(s1.find("p")) #沒找到,故結果為-1
print(s1.find("p")) #該語句會報錯,ValueError,因為沒找到
#Determine prefixes and suffixes
print(s1.startswith("H")) #輸出True
print(s1.startswith("p")) #輸出False
print("demo.py".endswith(".py")) #輸出True
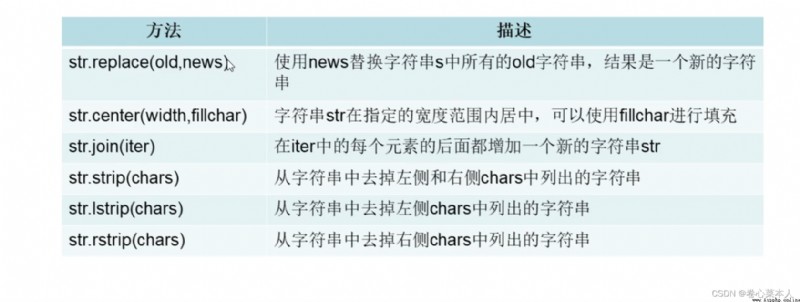
s="HelloWorld"
#替換
new_s=s.replace("0","你好") #Generates a new string after replacement,賦給new_s
#The string is centered within the specified width
print(s.center(20,*))
#去除字符串的左右空格
s1=" Hello World "
print(s.strip()) #默認去除空格,After removal, a new string is generated
print(s.lstrip()) #去除左側空格
print(s.rstrip()) #去除右側空格
#Remove the specified characters,The order of the specified characters is irrelevant
s3="dl-helloworld"
print(s3.strip("ld")) #輸出是"-hellowor",刪除指定的“字符”,與“ld”和“dl”的順序無關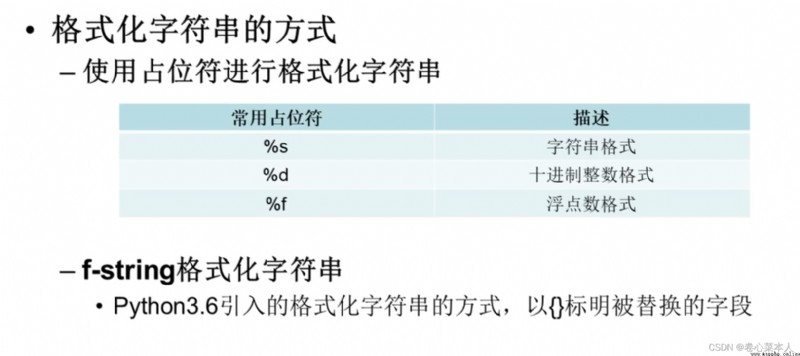

#(1)使用占位符格式化字符串
name="馬冬梅"
age=18
score=98.3
print("姓名:%s,年齡:%d,成績:%f" %(name,age,score)) #注意寫法,後面是%元組形式
print("姓名:%s,年齡:%d,成績:%.2f" %(name,age,score)) #scoreThe output is rounded to two decimal places
#(2)使用f-string格式化字符串
print(f"姓名:{name},年齡:{age},成績:{score}") #""There must be parameters beforef,Otherwise it's a simple string,且以{}Indicates the replaced string
#(3)使用字符串的format()方法
print("姓名:{0},年齡:{1},成績:{2}".format(name,age,score))#Note the preceding curly braces{}中的數字對應format()parameter position in (位置從0開始排),The card slot corresponds to the corresponding position
print("姓名:{2},年齡:{0},成績:{1}".format(age,score,name))
#方法format()的格式控制,The first three control
s="helloworld"
print("{0:*<20}".format(s)) #0對應format()中的s(The corresponding position of the card slot),Then the write is controlled according to the standard format
#Thousand separator in format control,(Only works with integers and floating point numbers)
print("{0:,}".format(9873256)) #輸出9,873,256
print("{0:,}".format(9873256.236)) #輸出9,873,256.236
#The precision of the fractional part of a floating-point number
print("{0:.2f}".format(3.1415926535)) #輸出3.14,are rounding reservations
#Or the maximum display length of the string
print("{0:.5}".format("helloworld")) #輸出hello,輸出寬度為5
#The last bit controls:類型控制
#整數類型
a=425
print("{0:b},{0:c},{0:d},{0:o},{0:x},{0:X}".format(a))#The card slot in the template is0所以format()只需要一個參數
#類型c是對應unicode字符,類型x對應16Radix lowercase characters,類型X對應16Base case characters
#浮點數類型
b=3.141592
print("{0:.2f},{0:.2E},{0:.2e},{0:.2%}".format(b))
#E和e是科學計數法,%It is output as a percentage with decimals


errorsThere are three options:
strictRefers to strict operation,不符合直接報錯
ignoreRefers to ignore errors
replace指替換,If you don't know, replace it with "?" 號
s="偉大的中國"
#編碼
scode=s.encode("gbk")
s_utf-8=s.encode("utf-8")
#解碼
print(bytes.decode(scode,"gbk"))
print(bytes.decode(s_utf-8,"utf-8")) #It must be written this way?,不能寫成scode.decode()嗎?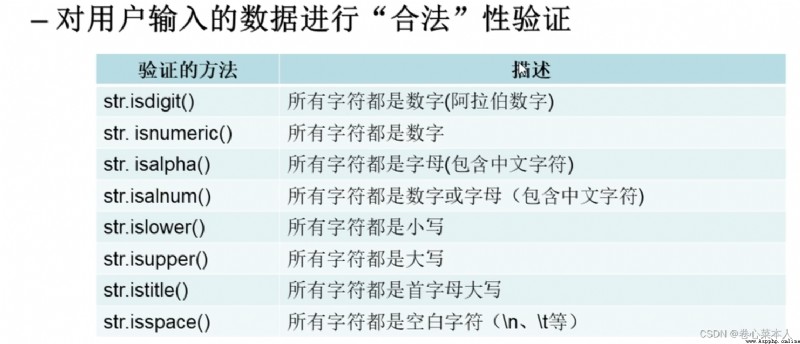
str.isdigit(): Verify that all characters are 十進制的阿拉伯數字
str.isnumeric(): Verify that all characters are numbers,包括阿拉伯數字,羅馬數字,Chinese characters capitalized numbers(壹貳),漢字數字(一二),Binary numbers don't work
str.isalpha(): 判斷所有字符都是字母(包括中文),Chinese numbers are also available,But not Arabic numerals
str.isalnum: Determines that all characters are numbers or letters(包括中文),Chinese numbers are also available,Arabic numerals also work
str.islower(),str.isupper(): Determines whether all characters are uppercase or lowercase,Because Chinese is not case sensitive,Therefore, only uppercase and lowercase letters are judged
str.istitle(): 單詞之間用空格分割,Otherwise considered a word,Because Chinese is not case sensitive,Therefore, only uppercase and lowercase letters are judged
#判斷所有字符都是數字(十進制的阿拉伯數字)
print("123".isdigit()) #True
print("一二三".isdigit()) #False
print("0b1001".isdigit()) #False
print("IIIIII".isdigit()) #False羅馬數字
print("One two three"isdigit()) #False
#判斷所有字符都是數字(羅馬數字,Decimal Arabic,漢字數字(One two three and one two three))
print("123".isnumeric()) #True
print("一二三".isnumeric()) #True
print("0b1001".isnumeric()) #False
print("IIIIII".isnumeric()) #True 羅馬數字
print("One two three"isnumeric()) #True
#判斷都是字母(英文中文)
print("hello你好".isalpha()) #True
print("hello你好123".isalpha()) #False
print("helloHello one two three".isalpha()) #True
print("hello你好IIIIII".isalpha()) #False
#Judging that all characters are numbers and letters(英文和中文)
print("hello你好123".isalnum()) #True
print("hello你好123...".isalnum()) #Falde
print("helloHello one two three".isalnum()) #True
print("helloHello one two three".isalnum()) #True
print("hello你好IIIIII".isalnum()) #True
#判斷首字母大寫
print("Hello".istitle()) #True
print("HelloWorld".istitle()) #False
print("Helloworld".istitle()) #True
print("Hello world".istitle()) #False
print("Hello World".istitle()) #True
print("Hello你好".istitle()) #True
#判斷所有字符都是小寫
print("Hello".islower()) #False
print("hello".islower()) #True
print("hello你好".islower()) #True,Because Chinese has no capitalization,Therefore, only uppercase and lowercase letters are judged
#Similarly, it can be judged that all characters are uppercase
#Determine whether all are blank characters
print("\t".isspace()) #True
print("\n".isspace()) #True
print(" ".isspace()) #True
使用“+”拼接 和 使用join()方法拼接 是最常用的,join()方法 也用於 Concatenation of lists and tuples
s1="hello"
s2="world"
#(1)使用“+”拼接
print(s1+s2)
#(2)使用join()方法拼接,Use lists for stitching
print("".join["hello","world"]) #Use for empty stringsjoin()方法,輸出"hello world"
#join()This is done by adding a symbol to each string in the list to concatenate them together
print("*".join["hello","world","php"]) #輸出“hello*world*php”,The first string has no symbol
#(3)直接拼接
print("hello""world")
#(4)Concatenate using format strings
print("%s%s" %(s1,s2)) #輸出“helloworld”
print(f"{s1}{s2}") #輸出“helloworld”
print("{0}{1}".format(s1,s2)) #輸出“helloworld”s="alknvlakgakdvnpawirugsagkj"
#(1)使用for循環和not in方法去重
new_s1=""
for item in s:
if item not in new_s1: #判斷s中的字符是否在new_s1中存在(Or repeat)
new_s1+=item #因為s和new_s1都是字符串,所以“+”進行拼接操作
print(new_s1)
#(2)使用索引,range()函數,for循環,not in
new_s2=""
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] not in new_s2: #The index element is judged
new_s2+=s[i]
print(new_s2)
#(3)通過集合去重+列表排序+join()方法拼接
new_s3=set(s) #new_s3是集合類型
lst=list(new_s3) #轉為列表
lst.sort(key=s.index) #sort()方法排序,使用參數key(Specifies the key for the comparison sort)
print("".join(lst)) #join()方法拼接lst=["金星","木星","水星","火星","土星","金星","木星","水星","火星","土星"]
new_lst=[]
#(1)用for循環遍歷+ not in
for item in lst:
if item not in new_lst:
new_lst.append(item) #添加item到new_lst中
#(2)for+range()+not in
new_lst2=[]
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i] not in new_lst2:
new_lst2.append(lst[i])
#(3)利用集合去重,Switch to list sorting(用key參數)
s_lst=set(lst)
new_lst3=list(s_lst)
new_lst3.sort(key=lst.index)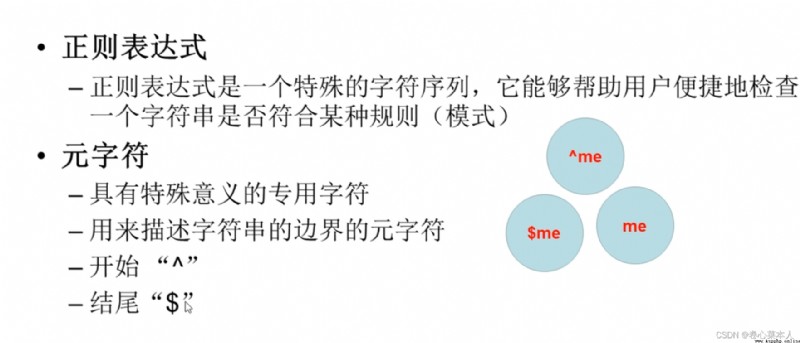
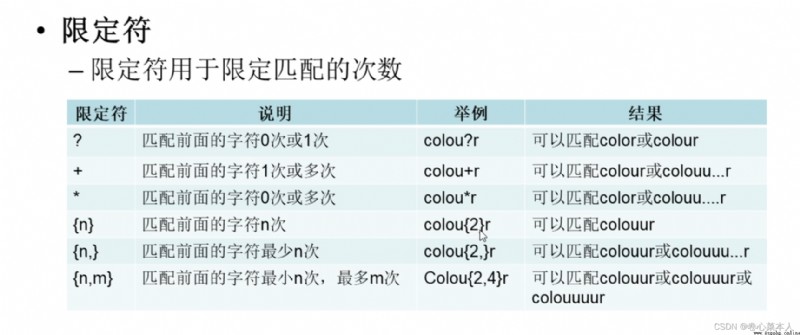

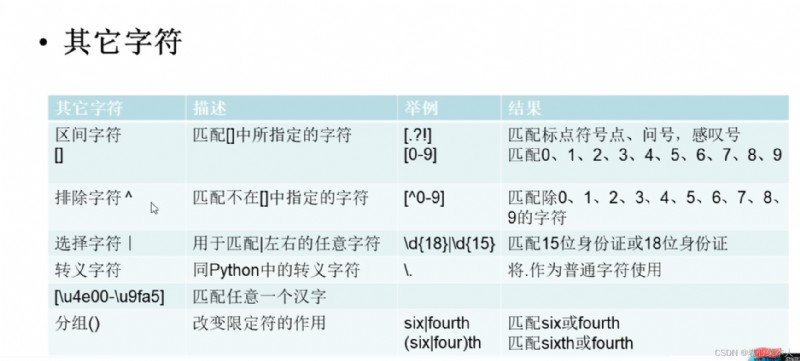

①pattern是模式字符串,也可以說 匹配規則,string是待匹配的字符串,flag是標志位(控制匹配的方式,例如是否區分大小寫,Whether to utilize multiline mode)
②用前面的 pattern匹配string,是否滿足規則
③pattern 是 Follow the previous regular expression的格式書寫
#re模塊的使用,導入re模塊
import re
pattern=r"\d\.\d+" #r表示元字符,指pythonEscape characters in
s="i study python everyday"
match=re.match(pattern,s,re.I)#參數re.I是忽略大小寫
print(match) #輸出是None
s2="3.10python i study"
match2=re.match(pattern,s2,re.I)
print(match2) #輸出<re.match.object>
print("匹配的起始位置",match2.start()) #輸出0
print("匹配的結束位置",match2.end()) #輸出4,because of the location4沒匹配到,it ends
print("matching location interval",match2.span) #輸出(0.4)
print("待匹配的字符串",match2.string) #輸出3.10python i study,即match方法中的string
print("匹配的數據",match2.group()) #輸出3.10
findall()The result of the method is a list,If there is no match the result is an empty list
import re
pattern=r"\d\.\d+"
s="i study python 3.10 every day python2.1 i love u"
s2="4.10python i study"
s3="i study python every day"
match=re.search(pattern.s) #3.10
match2=re.search(pattern.s2) #4.10
match3=re.search(pattern.s3) #None
lst1=re.findall(pattern,s) #["3.10","2.1"]
lst2=re.findall(pattern,s2) #["4.10"]
lst3=re.findall(pattern,s3) #[]是空列表

re.sub()方法 的結果是 字符串, re.split方法的結果是 列表
import re
pattern="黑客|破解|反爬"
s="我想學python,like crackVIP視頻,pythonInfinite back climb"
new_s=re.sub(pattern,"***",s) #The result of the replacement is a string
print(new_s) #s中符合pattern的替換為***
s2="https://www.baidu/s?wd=cij&ie=utf-8&tn=baidu"
pattern2="[?|&]"
lst=re.split(pattern2,s2)
print(lst) #結果是列表#車牌歸屬地
lst=["京A446262","粵C562394","津B123965"]
for item in lst:
s=item[0:1]
print(item,"歸屬地",s)#統計字符串中出現指定字符的次數,Only count characters but not strings
s="Hellopython,Hellojava,hellophp"
word=input("要統計的字符")
print("{0}在{1}中出現的次數{2}".format(word,s,s.upper().count(word))#格式化輸出商品的名稱和單價
lst=[
["01","電風扇","美的",500],
["02","洗衣機","TCL",1000],
["03","微波爐","老板",400]
]
print("編號\t\t名稱\t\t品牌\t\t價格")
for item in lst:
for i in item:
print(i,end="\t\t")
print()
#Format the output for the list contents
for item in lst:
item[0]="000"+item[0]
item[3]="${:.2f}".format(item[3])#Regular expressions to extract valid data
import re
s="akjfbakjsfkx cjefsdncskdjnjnskdjf"#In short, it is a large string of characters copied from the Internet,will contain website information
pattern="https://img\d{1}.baidu.com/it/u=\d*,\d*&fm=\d*&fmt=auto"
lst=re.findall(pattern,s) #結果是列表
for item in lst:
print(item)