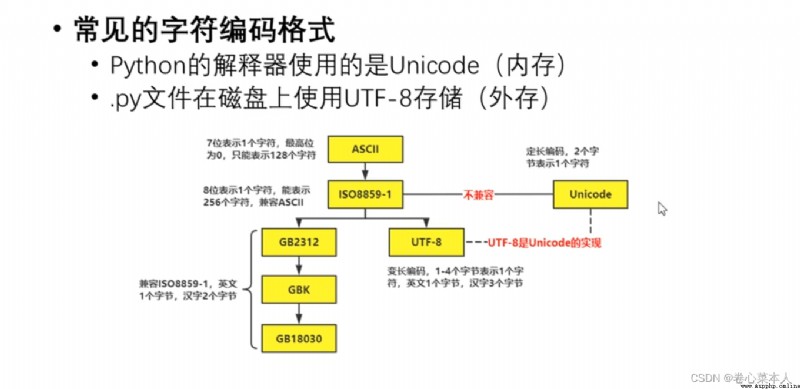
修改py文件的編碼格式:In the first line to write program #encoding=gbk 修改為gbk編碼格式
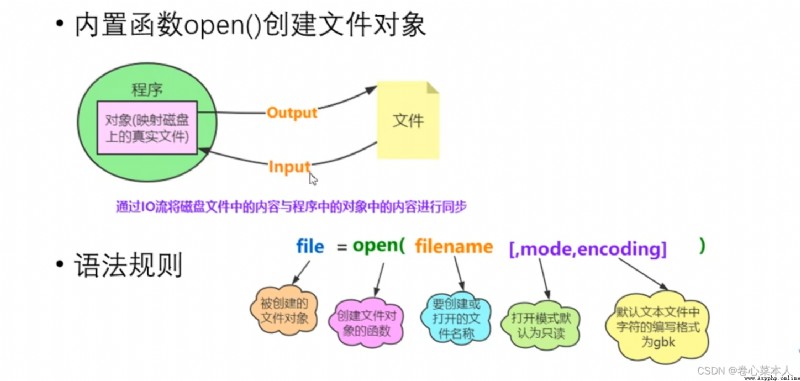
file=open("a.txt","r") #"r"表示read
print(file.readlines()) #readlines()The contents of the text file will be read and in the form of a list to show
file.close()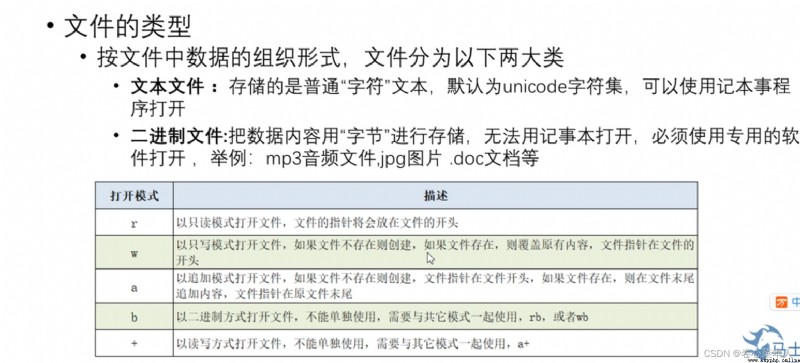
source_file=open("logo.png",rb) #Source files in read mode of binary read
target_file=open("copy.png",wb) #The target file to write the binary file,目標文件是copy.png
target_file.write(source_file.read())
source_file.close()
target_file.close()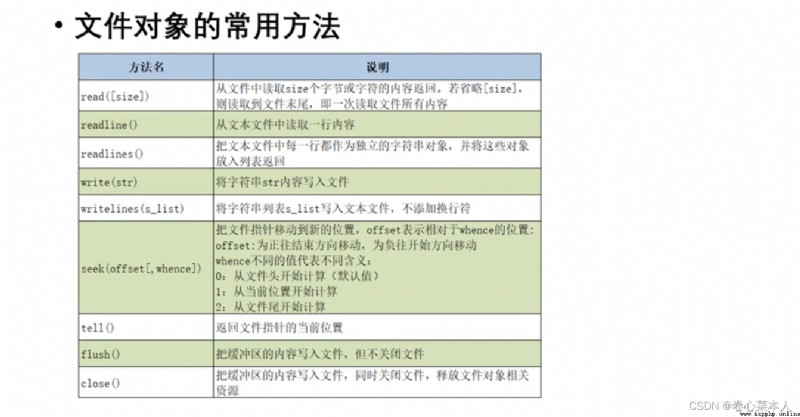
file=open('a.txt','r')
print(file.read())
print(file.readline())
print(file.readlines())#作為列表返回tell()Method Pointers position from0開始算
flush()Methods after can still to write content file(Because there is no close the file),但close()Methods after not
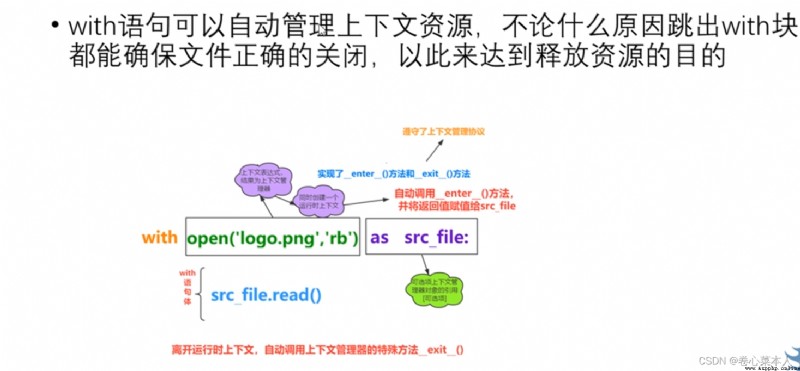
①If a class implements the special method__enter__()和__exit__(),The class has complied with the context management agreement,An instance of this class object is called context manager
②離開運行時上下文,Automatically invocation context manager's special methods__exit__()進行退出
with open("c.txt","r") as file: #相當於file=open("c.txt","r")
print(file.read()) #不用再寫file.close(),因為離開withBlock automatically shut off when the file resources#with語句實現文件的復制
with open("a.png","rb") as source_file:
with open("b.png","wb") as target_file:
target_file.write(source_file.read())
import os
os.system("notepad.exe") #打開記事本,也可在WIN中輸入notepad
os.system("calc.exe") #打開計算器,也可在WIN中輸入
#osModules can also be called directly executable file 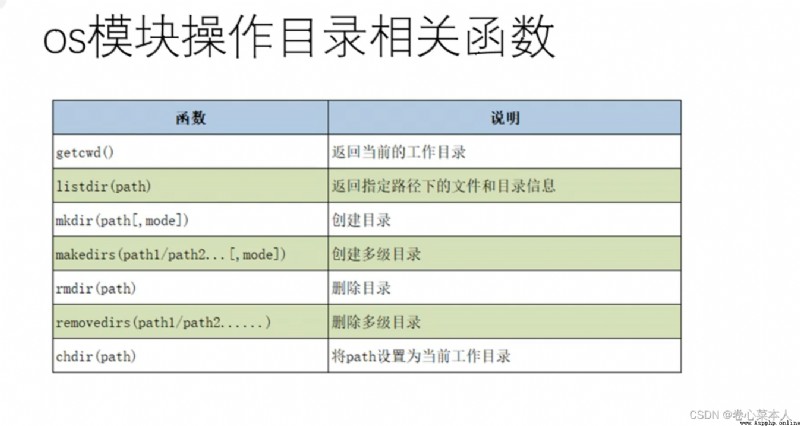
The part and functionubuntuThe system of the terminal command similar again
This part of the generally used in辦公自動化
import os
print(os.getcwd())
lst=os.listdir("../chap15") #listdir()函數返回列表,".."表示上一級目錄
print(lst)
os.mkdir(newdir) #創建目錄
os.makedirs("/a/b/c") #創建多級目錄
os.rmdir(newdir) #刪除目錄
os.removedirs("a/b/c") #刪除多級目錄
import os.path
print(os.path.abspath('demo3.py'))#獲取demo3.py文件的絕對路徑
print(os.path.exists('demo13.py'),os.path.exists('12.txt'))#結果返回True/False
print(os.path.join('E:\\python','demo6.py')) #Before and after for Mosaic isE:\python\demo6.py
print(os.path.split('E:\\vippython\\chapter11\\demo.py'))#Separate file path and file name is('E:\\vippython\\chapter11','demo.py')
print(os.path.splitext('demo4.py'))#輸出{'demo4','.py'}
print(os.path.basename('E:\\vippython\\chapter11\\demo.py'))#輸出demo.py,從路徑中提取文件名
print(os.path.dirname('E:\\vippython\\chapter11\\demo.py'))#輸出E:\vippython\chapter11,Extracted from path directory,不包括文件名
print(os.path.isdir('E:\\vippython\\chapter11\\demo.py'))#輸出False,因為demo.py不是路徑名在 辦公自動化 Just started to learn is 文件處理
#列出指定目錄下的所有.py文件
import os
path=os.getcwd() #獲取當前路徑,Of course you can also specify the corresponding path
lst=os.listdir(path)
for filename in lst:
if filename.endswith('.py'):
print(filename)
#Successive home directory and subdirectory corresponding directory path,目錄名,文件名
import os
path=os.getcwd()#獲取當前路徑,也可以指定路徑
lst_files=os.walk(path)
for dirpath,dirname,filename in lst_files: #Will step by step a successive visit home directory and subdirectory paths,目錄名,文件名
print(dirpath) #Output current directory path
print(dirname) #The output of the current directory subdirectory name
print(filename) #The output file name is not a subdirectory of the current directory第二個代碼塊中,用到了 osAn important method in modulewalk(), 該方法可以Recursive traversal of the home directory and neutron directory home directory file