目錄
一、requests包
1.1 安裝
1.2 get方法請求
1.2.1 使用get方法獲取請求結果
1.2.2 在get請求中使用參數
1.2.3 在get請求中使用列表參數
1.3 post方法請求
1.4 其他方法
1.5 獲取json的返回結果
1.6 定制請求頭
1.7 狀態碼
1.7.1 獲取狀態碼
1.7.2 判斷狀態碼
1.7.3 非200時候拋出異常代碼
1.8 獲取響應頭
1.10 請求超時
1.11 重定向
1.11.1 獲取重定向的 url
1.11.2 禁止重定向
1.12 session
1.12.1 跨請求保存參數的方法
1.12.2 會話也可用來為請求方法提供缺省數據
二、爬蟲
2.1 Urllib
URL 編碼
URL 參數拼接及 get、post 請求
服務器返回結果
帶有 header 發送數據
異常處理
設定超時時間
服務返回結果保存為 html
下載一張圖片
2.2 bs4
安裝
創建 beautifulsoup 對象
輸出 beautifulsoup 對象及解析
四大對象種類分析
html 結構化分析
遍歷文檔結構查詢
CSS 選擇器
三、實戰練習
3.1 抓取搜狐網頁連接並做分析
py -3 -m pip install requests
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('https://www.sohu.com/')
print(r) #返回<Response [200]>
print(r.status_code) #返回請求的Http狀態碼
print(r.url) #獲取請求的url
print(r.text[:200]) #獲取請求的返回內容,str類型,直接可以編程用
print(type(r.text[:200]))
print(r.encoding) #獲取請求的編碼
print(r.content[:10]) #以字節方式獲取影響結果,返回byte類型字符串
print(type(r.content[:10]))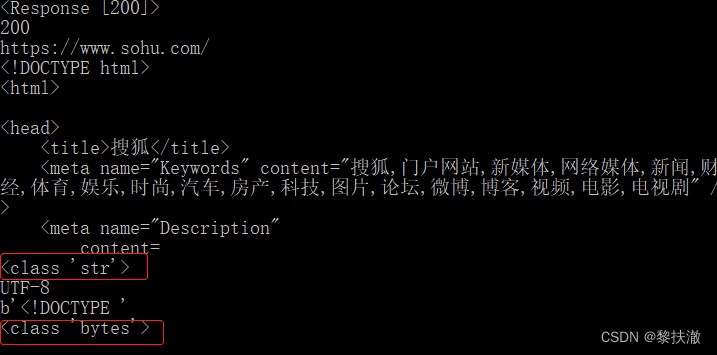
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
r = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get", params=payload)
print(r.url)
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': ['value2', 'value3']}
r = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get", params=payload)
print(r.url)
簡單的post請求例子,發送的數據類似提交表單(form)數據:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data = {'key':'value'})
print(r.text)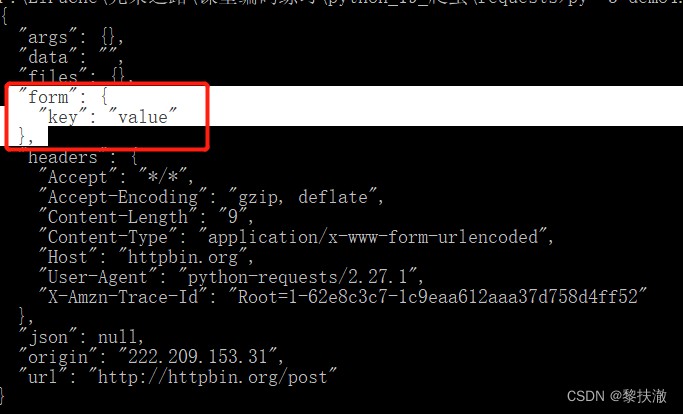
復雜的post請求例子,發送一個元組:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
payload = (('key1', 'value1'), ('key1', 'value2'), ('key2', 'value3'))
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data=payload)
print(r.text)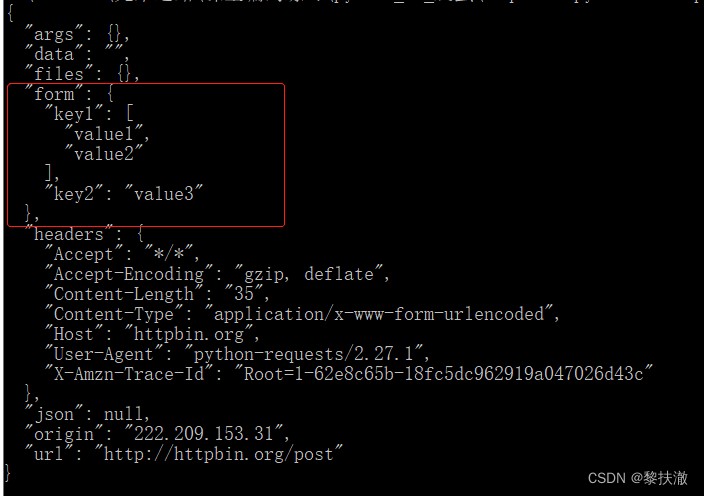
發送一個非表單數據的Post,發送一個json字符串的post請求:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
import json
payload = {'some':'data'}
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data=json.dumps(payload))
# r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', json=payload) #這種方式也可以
print(r.text)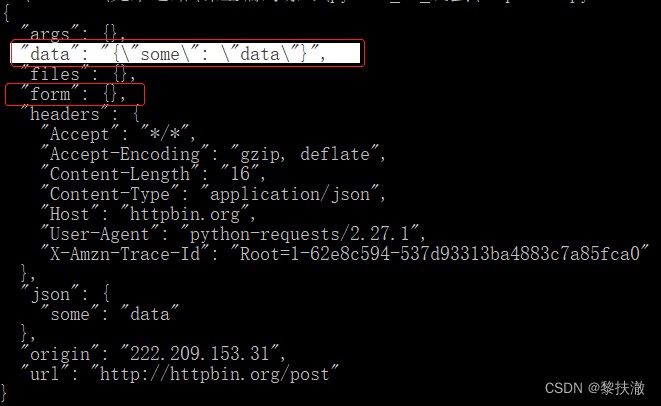
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
import json
payload = "fine,I am ok."
r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', json=payload)
print(r.text)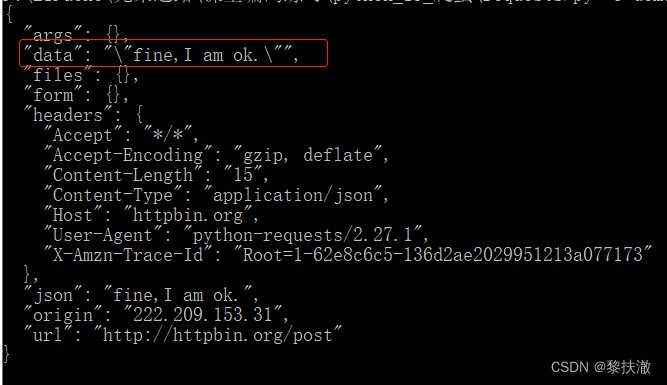
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.put('http://httpbin.org/put', data = {'key':'value'})
print("put:",r.text)
r = requests.delete('http://httpbin.org/delete')
print("delete:",r.text)
r = requests.head('http://httpbin.org/head')
print("head:",r.text)
r = requests.options('http://httpbin.org/get')
print("options:",r.text)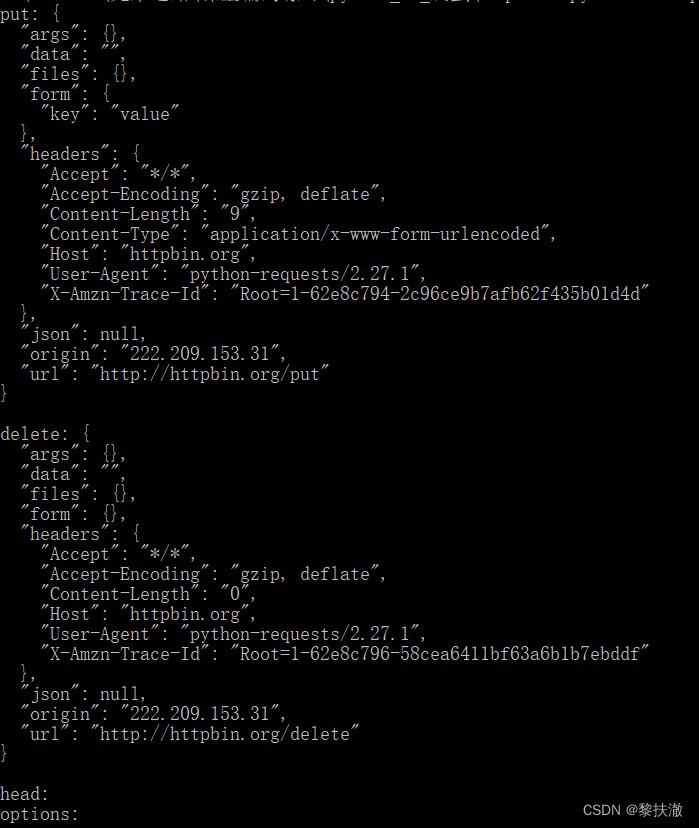
證書取消驗證
#coding:utf-8
import requests
from requests.packages import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings() #從 urllib3 中消除警告
response = requests.get('https://www.12306.cn',verify=False) #證書驗證設為FALSE
print(response.status_code)#輸出:200#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')
print(r.json())#自動將返回的json串,轉換為字典
print(type(r.json()))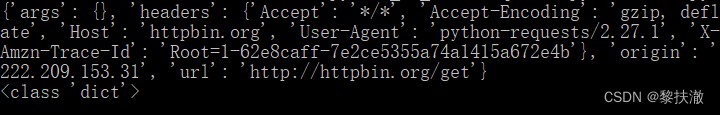
簡單的服務器端程序:
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/success/<name>')
def success(name):
return 'welcome %s' % name
@app.route('/login',methods = ['POST', 'GET',"DELETE"])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
return '{"key":"i am a boy!"}'
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
return "how are you?"
else:
return "you are a girl!"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)測試程序:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/login')
print(r.json())#自動將返回的json串,轉換為字典
print(type(r.json()))
r = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/login')
print(r.text)
r = requests.delete('http://127.0.0.1:5000/login')
print(r.text)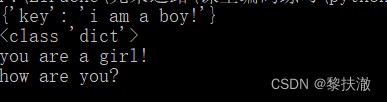
服務端:
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/success/<name>')
def success(name):
return 'welcome %s' % name
@app.route('/login',methods = ['POST', 'GET',"DELETE"])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
browser_type = request.headers.get("user-agent")
return 'your header is :' + browser_type
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
return "how are you?"
else:
return "you are a girl!"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)請求程序:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
headers = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}
r = requests.post(url, headers=headers)
print(r.text)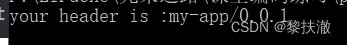
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')
print(r.status_code)#輸出:200#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')
print(r.status_code)
print(r.status_code == requests.codes.ok)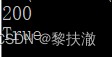
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
bad_r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/404')
print(bad_r.status_code)
print(bad_r.raise_for_status())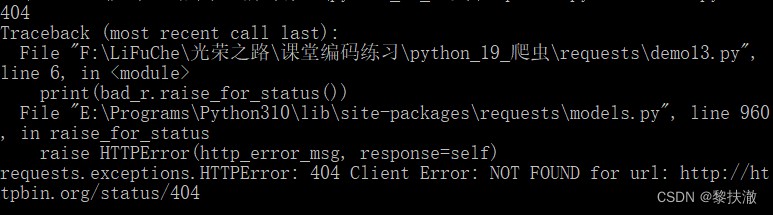
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('https://sohu.com')
print(r.headers)
print(r.headers['Content-Type'])
print(r.headers.get('content-type'))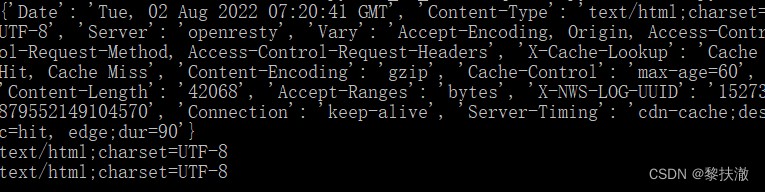
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
url = 'http://iciba.com'
r = requests.get(url)
print(r.cookies['iciba_u_rand'])todo:我這裡得到的結果是[] ,原因未知
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'
cookies = dict(cookies_are='working')
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies)
print(r.text)
服務端:
from flask import Flask, redirect, url_for, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/success/<name>')
def success(name):
return 'welcome %s' % name
@app.route('/login',methods = ['POST', 'GET',"DELETE"])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
cookie = request.cookies.get("cookies_are")
return '你提交的cookie是:' + cookie
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
return "how are you?"
else:
return "you are a girl!"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)請求程序:
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
cookies = dict(cookies_are='working')
r = requests.post(url, cookies=cookies)
print(r.text)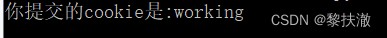
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
jar = requests.cookies.RequestsCookieJar()
jar.set('tasty_cookie', 'yum', domain='httpbin.org', path='/cookies')
jar.set('gross_cookie', 'blech', domain='httpbin.org', path='/elsewhere')
url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'
r = requests.get(url, cookies=jar)
print(r.text)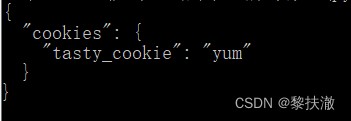
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
requests.get('http://github.com', timeout=0.5)#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.head('http://github.com', allow_redirects=True)
print(r.url)#'https://github.com/'
print(r.history[0].url)#http://github.com/
print(r.history)
解釋:
r.history返回的結果是一個列表,裡面記錄每個重定向後的響應對象,通過r.history[0].url可以獲取每次重定向後的url是什麼
#encoding=utf-8
import requests
r = requests.get('http://github.com', allow_redirects=False)
print(r.status_code)
print(r.history)
會話對象讓你能夠跨請求保持某些參數。它也會在同一個 Session 實例發出的所有請求之間保持 cookie
#coding=utf-8
import requests
s = requests.Session()
s.get('http://httpbin.org/cookies/set/sessioncookie/123456789')
r = s.get("http://httpbin.org/cookies")
print(r.text)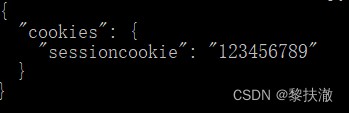
這是通過為會話對象的屬性提供數據來實現的:
#coding=utf-8
import requests
s = requests.Session()
s.auth = ('user', 'pass')
s.headers.update({'x-test': 'true'})
# both 'x-test' and 'x-test2' are sent
r=s.get('http://httpbin.org/headers', headers={'x-test2': 'true'})
print(r.text)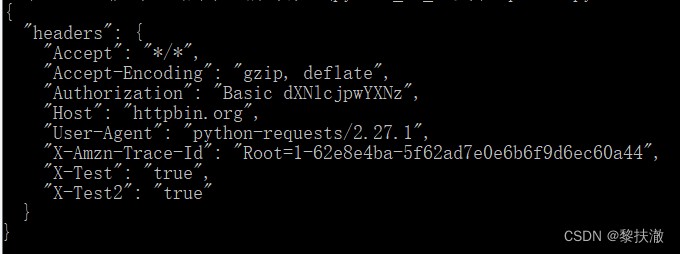
什麼是爬蟲
是一種按照一定的規則,自動地抓取萬維網信息的程序或者腳本。
實現流程
自動提取網頁的程序,它為搜索引擎從萬維網上下載網頁,是搜索引擎的重要組成。傳統爬
蟲從一個或若干初始網頁的 URL 開始,獲得初始網頁上的 URL,在抓取網頁的過程中,不斷
從當前頁面上抽取新的 URL 放入隊列,直到滿足系統的一定停止條件。聚焦爬蟲的工作流程
較為復雜,需要根據一定的網頁分析算法過濾與主題無關的鏈接,保留有用的鏈接並將其放
入等待抓取的 URL 隊列。然後,它將根據一定的搜索策略從隊列中選擇下一步要抓取的網頁
URL,並重復上述過程,直到達到系統的某一條件時停止。另外,所有被爬蟲抓取的網頁將
會被系統存貯,進行一定的分析、過濾,並建立索引,以便之後的查詢和檢索;對於聚焦爬
蟲來說,這一過程所得到的分析結果還可能對以後的抓取過程給出反饋和指導。
爬蟲目的
從網上抓取出來大量你想獲取類型的數據,然後用來分析大量數據的類似點或者其他信息來
對你所進行的工作提供幫助
#coding:utf-8
from urllib import parse
print (parse.quote('http://www.baidu.com')) #未編碼斜槓
print (parse.quote_plus('http://www.baidu.com')) #編碼斜槓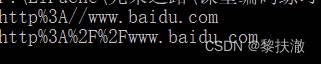
#coding:utf-8
import urllib
import urllib.parse
import urllib.request
param={'spam':1,'eggs':2,'bacon':0}
print ("初始參數")
print (param)
params= urllib.parse.urlencode(param)
print ("編碼後的參數")
print (params)
url="http://python.org/query?%s" % params
print ("最終 get 請求")
print ('urllib.request.urlopen("http://python.org/query?%s" % params)')
print ("最終 post 請求方式")
print ('urllib.request.urlopen("http://python.org/query",parmas)')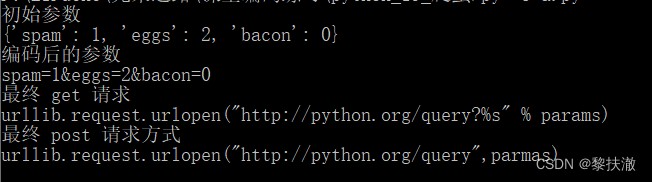
# coding: utf-8
import urllib
import urllib.request
response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.baidu.com')
print (response.getcode()) #打印狀態碼信息 其方法和 response.getcode() 一樣都是打印當前 response 的狀態碼
print (response.headers) #打印出響應的頭部信息,內容有服務器類型,時間、文本內容、連接狀態等等
print (response.headers['Server']) #這種拿到響應頭的方式需要加上參數,指定你想要獲取的頭部中那一條數據
print (response.geturl()) #獲取響應的 url
# print (response.readline()) #讀取 html 頁面第一行
print (response.fileno()) #文件描述符
# print (response.read()) #使用 read()方法得到響應體內容,這時是一個字節流bytes,看到明文還需要 decode 為 charset 格式帶有 header 發送數據
import urllib.parse
import urllib.request
url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
user_agent = 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.5; Windows NT)'
values = { 'act' : 'login', 'login[email]' : '[email protected]',
'login[password]' : '123456' }
headers = { 'User-Agent' : user_agent }
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(values)
req = urllib.request.Request(url, data.encode("utf-8"), headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(req)
the_page = response.read()
print(the_page.decode("utf8"))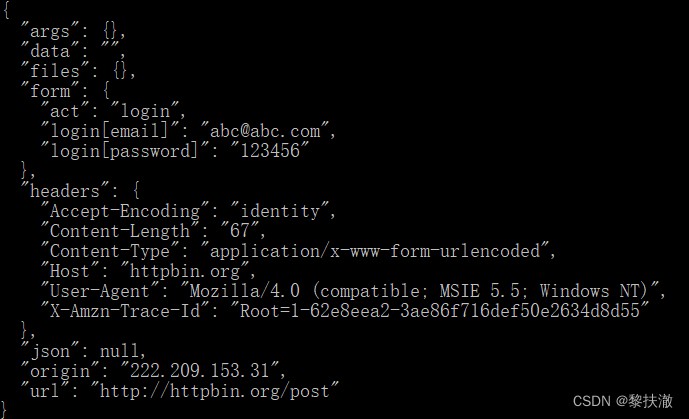
from urllib.request import Request, urlopen
from urllib.error import URLError, HTTPError
req = Request('http://www.python.org/')
try:
response = urlopen(req)
except HTTPError as e:
print('The (www.python.org)server couldn\'t fulfill the request.')
print('Error code: ', e.code)
except URLError as e:
print('We failed to reach a server.')
print('Reason: ', e.reason)
else:
print("good!")
print(response.read().decode("utf8"))import socket
import urllib.request
# timeout in seconds
timeout = 2
socket.setdefaulttimeout(timeout)
# this call to urllib.request.urlopen now uses the default timeout
# we have set in the socket module
req = urllib.request.Request('http://www.python.org/')
a = urllib.request.urlopen(req).read()# coding: utf-8
import urllib
import urllib.request
result=urllib.request.urlretrieve('https://www.w3cschool.cn/flask/flask_http_methods.html',filename=r"F:\python_19_爬蟲\flask.html")
print (u"網頁保存文件地址地址: ",result[0])
print (u"網頁內容: ",result[1])
urllib.request.urlcleanup() #清除 urllib.urlretrieve 產生的緩存from urllib.request import urlretrieve
urlretrieve("http://pic1.win4000.com/pic/b/20/b42b4ca4c5_250_350.jpg",
r"F:\python_19_爬蟲\1.jpg")方法 2:
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import urllib
imgPath="http://pic1.win4000.com/pic/7/8a/1e81de5511_250_350.jpg"
pic_content = (urllib.request.urlopen(imgPath)).read()
f = open(r'F:\python_19_爬蟲\img2.jpg', 'wb')
f.write(pic_content)
f.close()Beautiful Soup 是一個可以從HTML或XML文件中提取數據的Python庫。它能夠通過你喜歡的轉換器實現慣用的文檔導航、查找、修改
py -3 -m pip install bs4
將一段文檔傳入BeautifulSoup 的構造方法,就能得到一個文檔的對象, 可以傳入一段字符串或一個文件句柄.
# coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html=requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
html.encoding='utf-8'
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.text,"html.parser")#html可以是html 內容
print(soup.title)
# soup = BeautifulSoup(open(r'F:\python_19_爬蟲\flask.html',encoding="utf-8"),"html.parser")#也通過直接打開 html 文件獲得
print (type(soup))
# coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html=requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
html.encoding='utf-8'
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.text,"html.parser")#html可以是html 內容
print (soup.prettify()[0:100])#格式化輸出 html 內容Beautiful Soup將復雜HTML文檔轉換成一個復雜的樹形結構,每個節點都是Python對象,所有對象可以歸納為4種: Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSoup , Comment .
Tag 對象與XML或HTML原生文檔中的tag相同 # coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html=requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
html.encoding='utf-8'
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.text,"html.parser")
print (soup.title)#第一個 title 標簽的內容
print (soup.head)#第一個 head 標簽的內容
print (soup.p)#第一個 p 標簽的內容
print (soup.a) #第一個 a 標簽的內容
print ("標簽對象: ")
print (type(soup.a))
print (soup.a.name)#第一個 a 標簽本身名稱
print (soup.a.attrs)#打印所有的屬性
print (soup.a["name"])#獲取屬性值
print (soup.a.get("name"))#同上
soup.a["name"]="test"
print ("修改 a 標簽對應 name 屬性值: ")
print (soup.a)
del soup.a["name"]
print ("刪除 a 標簽對應 name 屬性值")
print (soup.a)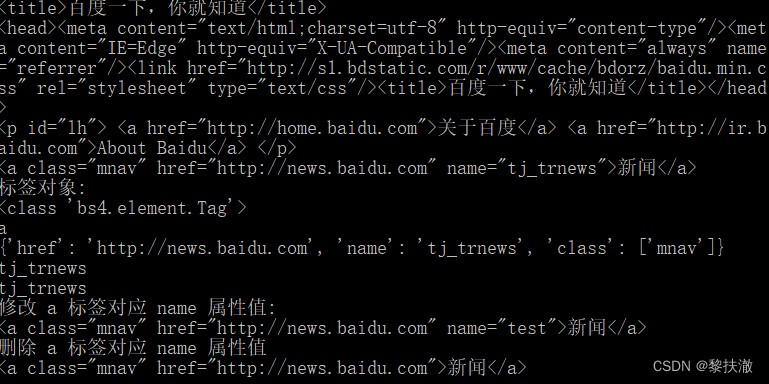
NavigableString(標簽內容)
字符串常被包含在tag內.Beautiful Soup用 NavigableString 類來包裝tag中的字符串
# coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html=requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
html.encoding='utf-8'
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.text,"html.parser")
print (soup.title.string) #打印第一個 title 標簽的內容
soup.title.string="neirong"#修改第一個 title 標簽的內容,無內容時打印為 None
print ("tile 標簽對應內容對象類型: ")
print (type(soup.title.string))
Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSoup 幾乎覆蓋了html和xml中的所有內容,但是還有一些特殊對象.容易讓人擔心的內容是 文檔的注釋部分。 Comment 對象是一個特殊類型的 NavigableString 對象。 # coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their
names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie -
-></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")#html 可以是 html 內容
print (soup.a.string)#打印第一個 a 標簽的內容
print ("特殊類型 NavigableString 對象: ")
print (type(soup.a.string))
# coding: utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their
names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie - -></a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")print (soup.head.contents)# tag的 .contents屬性可以將tag的子節點以列表的方式輸出
print ("子節點內容類型: ")
print (type(soup.head.contents))
print ("生成器方式存儲子節點: ")
print (soup.head.children)#Tag的 .children生成器,可以對tag的子節點進行循環
子孫節點
.descendants 屬性可以對所有tag的子孫節點進行遞歸循環
for i in soup.body.descendants:#生成結果也是生成器的方式
print (i)#結果也是一層一層向內部解析輸出,對比結果體會節點內容及多個節點內容
print (soup.body.string) #包含多個節點,所以無法確定打印哪個節點內容,所以結果為 None
print (soup.body.a.string)
print (soup.body.strings) #獲取所有子節點內容
print (list(soup.body.strings))
print (soup.body.stripped_strings) #對內容中存在空行做處理
for i in soup.body.stripped_strings:
print(i)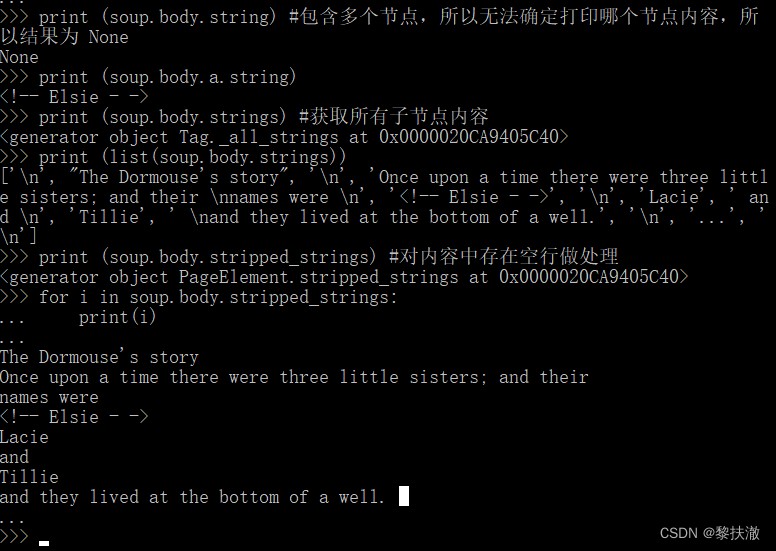
父節點
.parent 屬性來獲取某個元素的父節點
.parents 屬性可以遞歸得到元素的所有父輩節點
print(soup.body.parent)
content = soup.head.title.string #獲取一個 NavigableString 對象
print(content.parent.parent) #獲取父節點的父節點並打印
#content.parents#遞歸獲取元素所有的父輩節點然後存成一個生成器,通過遍歷可以輸出
for i in content.parents:
print(i.name).next_sibling 和 .previous_sibling 屬性來查詢兄弟節點 .next_siblings 和 .previous_siblings 屬性可以對當前節點的兄弟節點迭代輸出 print (soup.a.next_sibling) #此節點的下一個兄弟節點
print (soup.p.previous_sibling) #此節點的上一個兄弟節點
print (soup.a.next_siblings) #此節點的下一個兄弟節點,存儲結果為生成器
print (list(soup.a.next_siblings))
print (soup.p.previous_siblings) #此節點的上一個兄弟節點,存儲結果為生成器
for i in soup.a.next_siblings:#遍歷所有下面兄弟節點
print (i)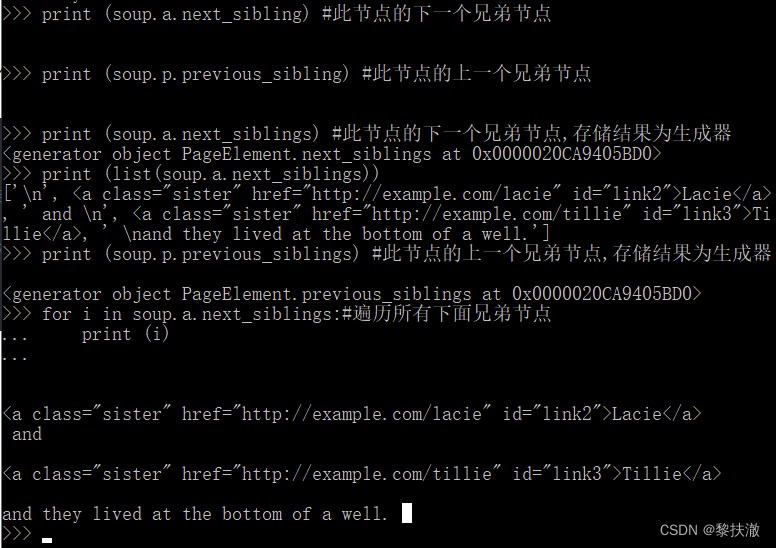
前後節點
.next_element 屬性指向解析過程中下一個被解析的對象(字符串或tag),結果可能與 .next_sibling 相同,但通常是不一樣的.
.previous_element 屬性剛好與 .next_element 相反,它指向當前被解析的對象的前一個解析對象
print (soup.a.next_element) #針對於所有節點中後的一個結點
print (soup.a.previous_element) #針對於所有節點中前一個節點
print (soup.a.next_elements) #針對於所有節點中所有後節點
print (soup.a.previous_elements) #針對於所有節點中所有前節點from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their
names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie - -></a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")name 的tag,字符串對象會被自動忽略掉string 參數:可以搜索文檔中的字符串內容recursive 參數:調用tag的 find_all() 方法時,Beautiful Soup會檢索當前tag的所有子孫節點,如果只想搜索tag的直接子節點,可以使用參數 recursive=Falselimit參數:限制返回結果的數量print (soup.find_all('a'))
print (soup.find_all('a')[-1])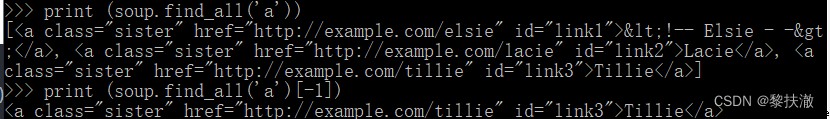 正則表達式
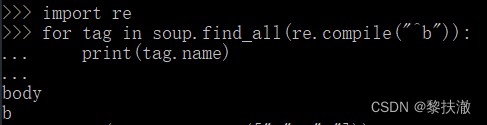
正則表達式 import re
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")): #找出所有以b開頭的標簽
print(tag.name)
傳列表
如果傳入列表參數,Beautiful Soup會將與列表中任一元素匹配的內容返回.下面代碼找到文檔中所有<a>標簽和<b>標簽:
print (soup.find_all(["a", "b"]))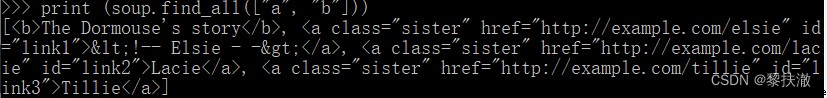
傳方法
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')#此方法符合條件輸出True 類似filter
print (soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id))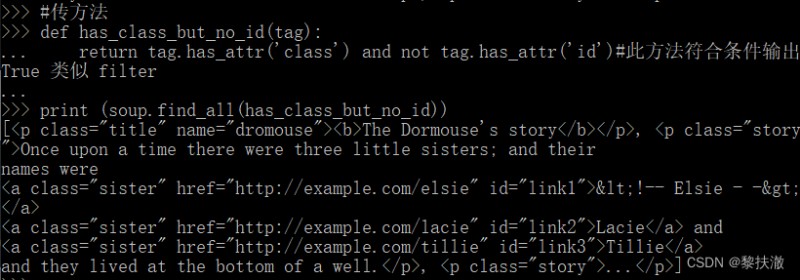
說明:結果中包含a標簽是因為返回的p標簽中包含3個a標簽
傳屬性參數篩選import re
print (soup.find_all(id='link2'))#搜索有 id 屬性並且對應值為 link2
print (soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie")))#搜索有 href 屬性並且符合正則表達式值得結果
print (soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"), id='link1')) #同時滿足兩個條件得結果
print (soup.find_all("a", class_="sister")) #對於類似 class 需要後面加上_
print (soup.find_all(attrs={"class": "title"})) #attrs 傳鍵值對條件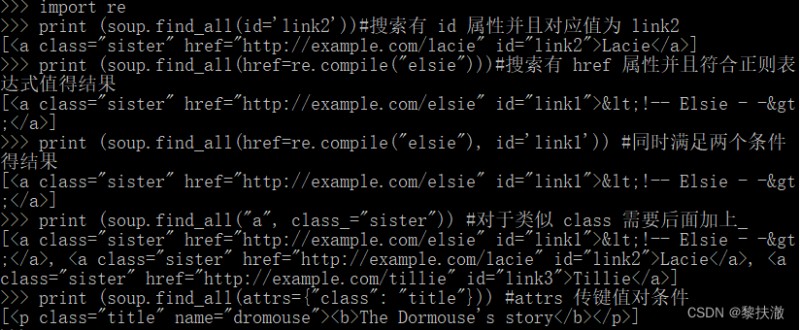
說明:
按照CSS類名搜索tag的功能非常實用,但標識CSS類名的關鍵字 class 在Python中是保留字,使用 class 做參數會導致語法錯誤,可以通過 class_ 參數搜索有指定CSS類名的tag。
print (soup.find_all(text="Lacie")) #搜索一個內容
print (soup.find_all(text=["Tillie", "Elsie", "Lacie"])) #一次搜索三個內容
print (soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse"))) #根據正則表達式搜索內容
print (soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse"))[1].parent)
limit 參數限制返回結果的數量. print (soup.find_all("a", limit=2))#對篩選結果篩選兩個內容嗎,限定返回個數find_all() 方法時,Beautiful Soup會檢索當前tag的所有子孫節點,如果只想搜索tag的直接子節點,可以使用參數 recursive=Falseprint (soup.html.find_all("b")) #默認搜索結果范圍是子孫節點
print (soup.html.find_all("b", recursive=False)) #設置 recursive 此參數後搜索結果范圍只為子節點在 Tag 或 BeautifulSoup 對象的 .select() 方法中傳入字符串參數, 即可使用CSS選擇器的語法找到tag.
print (soup.select('title')) #直接原值表示標簽名通過類名查找
print (soup.select('.sister')) #.加值代表類名通過 id 查找
print (soup.select('#link1')) ##字符代表 id組合查找
print (soup.select('p #link1')) #p 標簽下且 id 為 link1 的對象
print (soup.select("head > title")) #head 標簽下的 title 標簽
print (soup.select('p a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')) #p 標簽下 a的屬性href的值為XXX的標簽import requests
import re
# 獲取網頁源碼
r = requests.get("http://www.sohu.com")
# print(r.text)
#所有網頁url
links = re.findall(r'href="(.*?)"',r.text)
# print(links)
# print(len(links))
# for link in links:
# print(link)
#過濾url,只保留網頁的url,去除圖片、css、js等
valid_link = []
for link in links:
if "sohu" not in link:
continue
if re.search(r'\.jpg|\.png|\.css|\.ico|\.tif|\.gif|\.mailto',link):
continue
if link.startswith("//"):
valid_link.append("http:"+link)
else:
valid_link.append(link.strip())
print(len(valid_link))
#爬取所有的網頁url,判斷內容是否包含籃球二字,如果包含則保存到本地
no=1
for link in valid_link:
lr = requests.get(link)
if "籃球" in lr.text:
with open("F:\LiFuChe\光榮之路\課堂編碼練習\python_19_爬蟲\p1\%s.html"%no,"w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(lr.text)
no += 1
方法2:用bs4取url鏈接
import requests
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 獲取網頁源碼
r = requests.get("http://www.sohu.com")
# print(r.text)
#所有網頁url
# links = re.findall(r'href="(.*?)"',r.text)
#用bs4去取
def have_href(tag):
return tag.has_attr('href')
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text,"html.parser")
links = [i.get('href') for i in soup.find_all(have_href)]
print(links)
print(len(links))
# for link in links:
# print(link)
#過濾url,只保留網頁的url,去除圖片、css、js等
valid_link = []
for link in links:
if "sohu" not in link:
continue
if re.search(r'\.jpg|\.png|\.css|\.ico|\.tif|\.gif|\.mailto',link):
continue
if link.startswith("//"):
valid_link.append("http:"+link)
else:
valid_link.append(link.strip())
print(len(valid_link))
#爬取所有的網頁url,判斷內容是否包含籃球二字,如果包含則保存到本地
no=1
for link in valid_link:
lr = requests.get(link)
if "籃球" in lr.text:
with open("F:\LiFuChe\光榮之路\課堂編碼練習\python_19_爬蟲\p1\%s.html"%no,"w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(lr.text)
no += 1