Example 1. It is known that the coordinates of the four corners of a surface are ( 0.1, 0.1 ), ( 0.1, 1.2 ), ( 1.1, 0.1 ), ( 1.1, 1.2 ), and the surface is completed by bilinear interpolationInterpolate, draw the patch after interpolation.
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dfig=plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))ax=plt.gca(projection='3d')x=np.array([0.1,0.1,1.1,1.1,0.1])y=np.array([0.1,1.2,0.1,1.2,0.1])z=np.array([1,0.3,1.9,0.6,1])figure=ax.plot(x[0:2],y[0:2],z[0:2],c='r')figure=ax.plot(x[1:3],y[1:3],z[1:3],c='y')figure=ax.plot(x[2:4],y[2:4],z[2:4],c='b')figure=ax.plot(x[3:5],y[3:5],z[3:5],c='g')plt.show()The results are as follows:
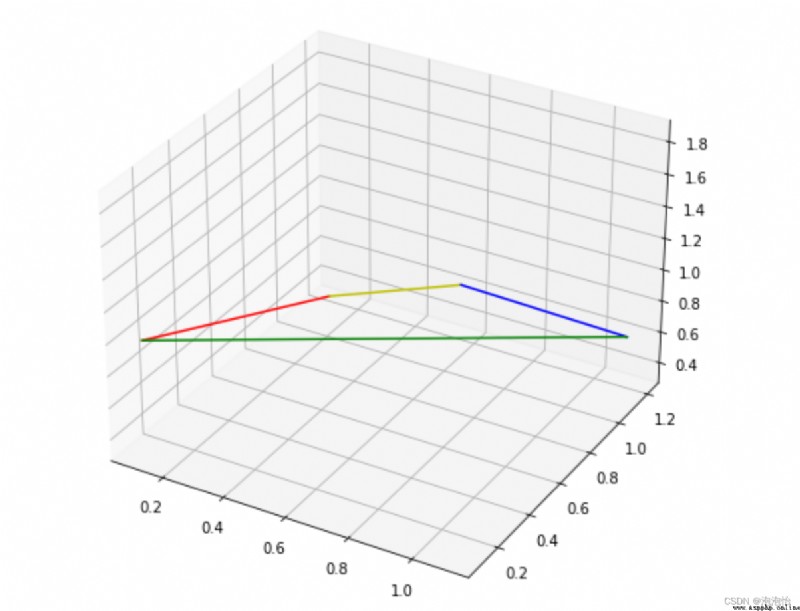
2) Draw the mesh patch generated by the interpolation points inside the patch
x_=np.arange(0,1.3,0.1)y_=np.arange(0,1.3,0.1)X,Y=np.meshgrid(x_,y_)x1=x[0]x2=x[2]y1=y[0]y2=y[1]z1=z[0]z2=z[2]z3=z[1]z4=z[3]x2_1=x2-x1y2_1=y2-y1Y_1=Y-y1X_1=X-x1Z=(Y_1*X_1*(z1-z2-z3+z4))/(x2_1*y2_1)+(Y_1*(z3-z1))/y2_1+(X_1*(z2-z1))/x2_1+z1fig=plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))ax=fig.gca(projection='3d')ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z)ax.view_init(15,-25)ax.set_xlabel('x')ax.set_ylabel('y')ax.set_xlim(-3,3)ax.set_ylim(-1,1.5)plt.show()Running result: 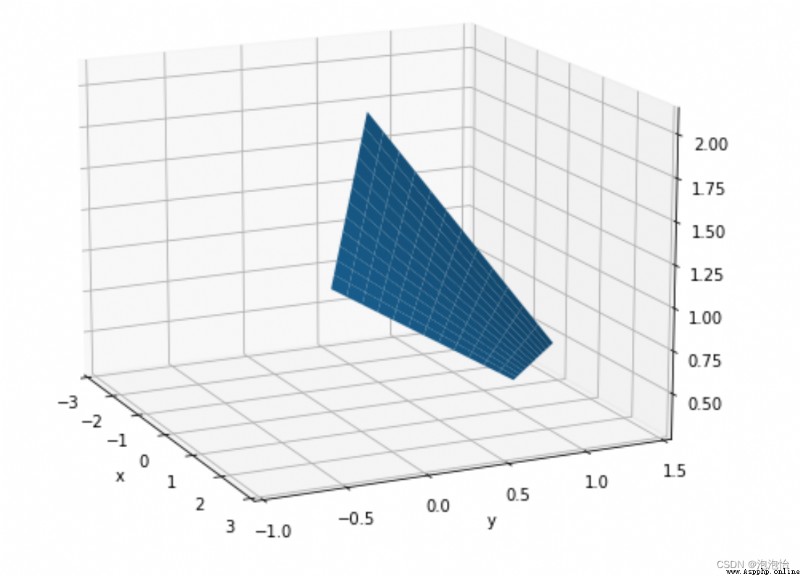
3) The interpolation surface obtained after adding external interpolation points
x_=np.arange(-0.6,1.6,0.1)y_=np.arange(-0.6,1.6,0.1)X,Y=np.meshgrid(x_,y_)x1=x[0]x2=x[2]y1=y[0]y2=y[1]z1=z[0]z2=z[2]z3=z[1]z4=z[3]x2_1=x2-x1y2_1=y2-y1Y_1=Y-y1X_1=X-x1Z=(Y_1*X_1*(z1-z2-z3+z4))/(x2_1*y2_1)+(Y_1*(z3-z1))/y2_1+(X_1*(z2-z1))/x2_1+z1fig=plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))ax=fig.gca(projection='3d')ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z)ax.view_init(15,-25)ax.set_xlabel('x')ax.set_ylabel('y')ax.set_xlim(-3,3)ax.set_ylim(-1,1.5)plt.show()plt.show()Running result:
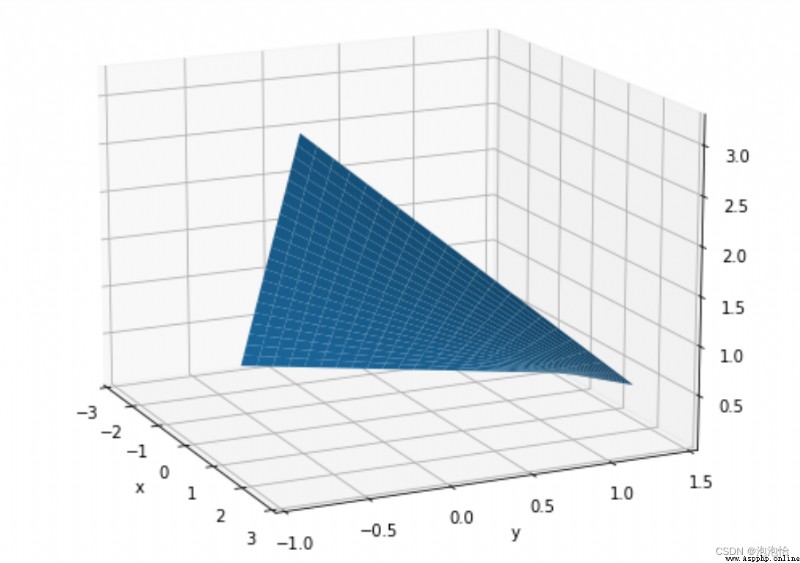
Happy Qixi Festival everyone!!quack quack