The excel to be imported is: 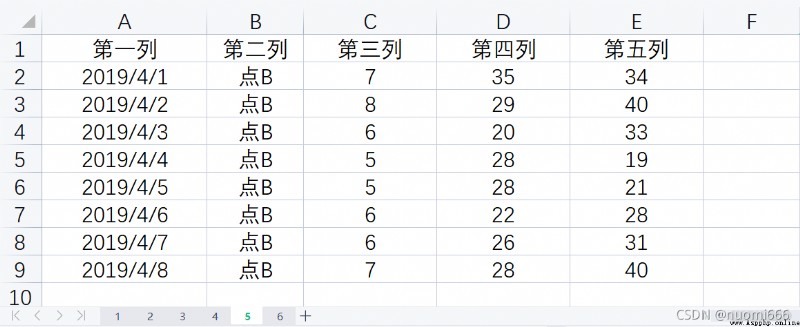
You can use the read_excel function of pandas, the specific code is as follows:
import pandas as pdgetdata=pd.read_excel(r'C:/folder index/filename.xlsx',sheet_name='name of worksheet sheet')If sheet_name does not set parameters, it will default to the first worksheet. At the same time, the position of the worksheet can also be set. When reading the fifth worksheet, it can be set to =4.
If you want to get one or more columns in the worksheet, you can use the usecols parameter. For example, to read the 2nd to 5th columns of the 5th worksheet, you can use the following code:
import pandas as pdgetdata=pd.read_excel(r'C:/folder index/filename.xlsx',sheet_name='name of worksheet sheet',sheet_name=4,usecols=[i for i in range (1,6)])The usecols parameter can also be set to the index letter of the column, such as usecols="B, D:E", you can get the 1st and 3rd to 5th columns, and set the parameter index_col=1 at the same time, take the second column as the index,The code and output result are:
getdata=pd.read_excel(r'C:/folder index/filename.xlsx',sheet_name='name of worksheet sheet',sheet_name=4,usecols="A,C:E",index_col=1)print(Getdata)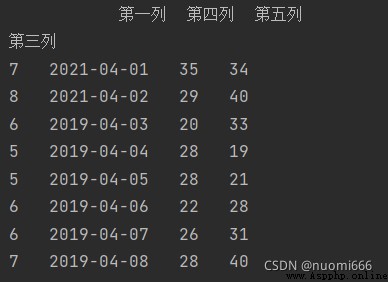
If you don't want to get all the rows, you can set the parameter nrows=5 to get the first 5 rows, and skip the 2nd to 4th rows at the same time, you can set the parameter skiprows=[i for i in range(2,5)], or skiprows=[2,3,4], code and output:
getdata=pd.read_excel(r'C:/folder index/filename.xlsx',sheet_name='name of worksheet sheet',skiprows=[2,3,4],nrows=5)print(Getdata)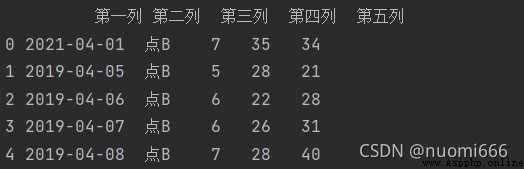
It should be noted here that the set nrows is the total number of rows to be acquired. If skiprows is set to skip a certain number of rows, it will continue to be acquired in the following rows until the number of rows to be acquired by nrows is made up.
The first article I wrote may not be exhaustive and will be supplemented later