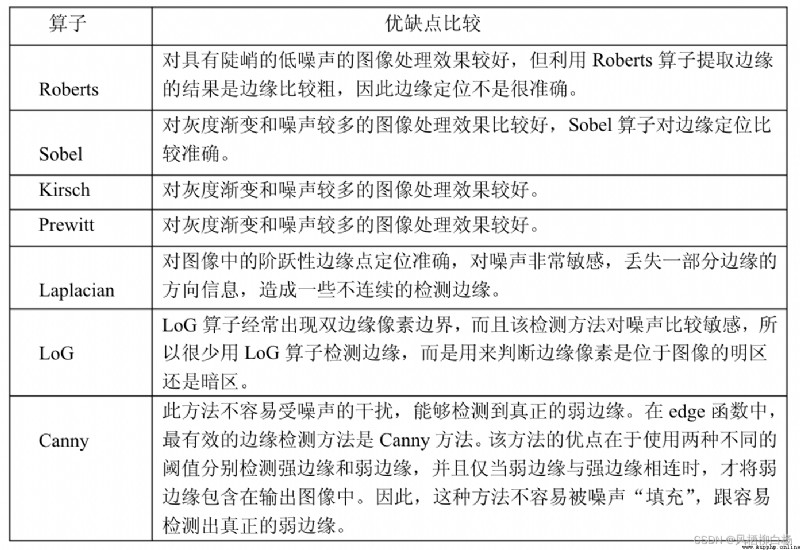
Edge detection is a basic problem of image processing and computer vision,Its purpose is to represent Numbers in the image brightness change obvious point.圖像屬性中的顯著變化通常反映了屬性的重要事件和變化.Edge detection of the form as shown in the figure below: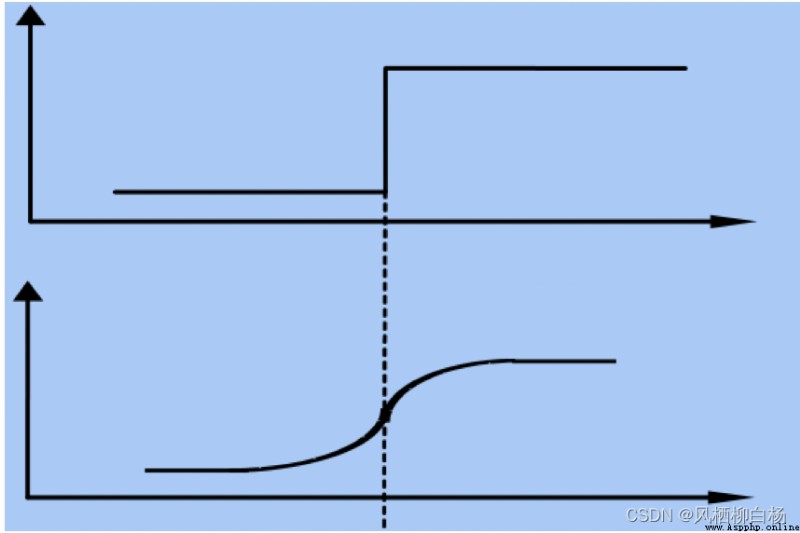
Image edge detection significantly reduces the amount of data,並且剔除了可以認為不相關的信息,保留了圖像重要的結構屬性.有許多方法用於邊緣檢測,Most of them can be divided into two types of:基於搜索、基於零穿越
By the first derivative of the image to find the maximum value to detect the boundary,然後利用計算結果估計On the edge of the local direction,通常采用梯度的方向,And use the find local gradient in the direction of the模的最大值,代表算法有Sobel算子和Scharr算子.
(1)A maximum of image first derivative -->
.
(2)On the edge of the local direction(General gradient direction) -->
.
(3)The local gradient modulus maximum
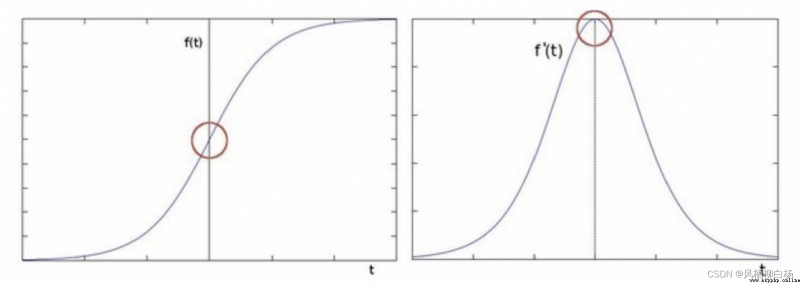
通過尋找圖像二階導數零穿越來尋找邊界,On behalf of the operator islaplacian算子.
Zero is refers to the function andy軸的交點.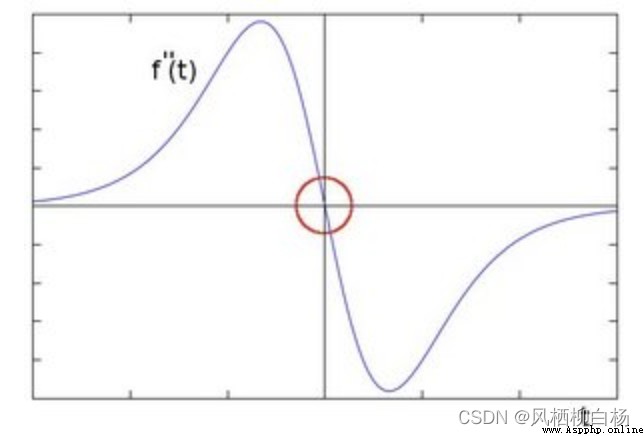
Sobel邊緣檢測算法比較簡單,In the practical application efficiency thancanny邊緣檢測效果高.但是邊緣不如canny檢測的准確,But with a lot of practical application of the occasion,SobelOperator is the preferred.
Sobel算子是高斯平滑與微分操作的結合體,所以其Ability to resist noise is very strong,用途較多.尤其是效率要求較高,For detailed textures don't care.
對於不連續的函數,一階導數可以寫作:
或者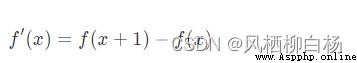
所以有: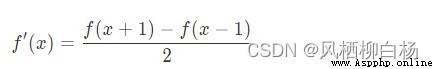
假設要處理的圖像為I,在兩個方向求導
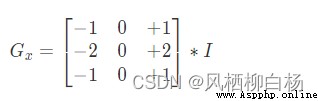
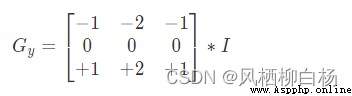
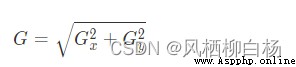

利用OpenCV進行Sobel邊緣檢測的API是:
Sobel_x_or_y =
cv2.Sobel(src, ddepth, dx, dy, dst, ksize, scale, delta, borderType)
參數:
Sobel函數求完導數後會有負值,There will be greater than255的值.而原圖像是uint8,即8為無符號數,所以Sobel建立的圖像位數不夠,會有截斷.因此要使用16位有符號的數據類型,即cv2.CV_16s.處理完圖像後,再使用cv2.convertScaleAbs()函數將其轉回原來的uint8類型,否則圖像無法顯示.
Sobel算子是在兩個方向計算的,最後還需要用cv2.addWeighted()函數將其組合起來
Scale_abs = cv2.convertScaleAbs(x) # 格式轉換函數
result = cv2.addWeighted(src1, alpha, src2, beta) # 圖像混合
代碼示例:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 1 讀取圖像
img = cv.imread('./image/horse.jpg',0)
# 2 計算Sobel卷積結果
x = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0)
y = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1)
# 3 將數據進行轉換
Scale_absX = cv.convertScaleAbs(x) # convert 轉換 scale 縮放
Scale_absY = cv.convertScaleAbs(y)
# 4 結果合成
result = cv.addWeighted(Scale_absX, 0.5, Scale_absY, 0.5, 0)
# 5 圖像顯示
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8),dpi=100)
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap=plt.cm.gray),plt.title('原圖')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(result,cmap = plt.cm.gray),plt.title('Sobel濾波後結果')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()

將上述代碼中計算SobelOperator partksize設為-1,就是利用scharr進行邊緣檢測.
x = cv2.Sobel(img, cv2.CV_16S, 1, 0, ksize=-1)
y = cv2.Sobel(img, cv2.CV_16S, 0, 1, ksize=-1)

可以看出,使用Scharr算子,Detection effect thanSobelOperator is a little better.
LaplacianEdge detection method by using second derivative to detect.因為圖像是“2維”,So we need in two direction derivative,如下式所示: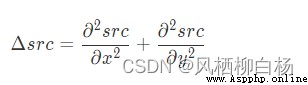
Then the discrete second derivative is: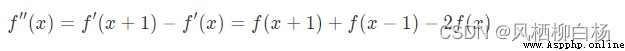
Then using convolution kernels is:
API:
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(src, ddepth[, dst[, ksize[, scale[, delta[, borderType]]]]])
參數:
代碼示例:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 1 讀取圖像
img = cv.imread('./image/horse.jpg',0)
# 2 laplacian轉換
result = cv.Laplacian(img,cv.CV_16S)
Scale_abs = cv.convertScaleAbs(result)
# 3 圖像展示
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8),dpi=100)
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap=plt.cm.gray),plt.title('原圖')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(Scale_abs,cmap = plt.cm.gray),plt.title('Laplacian檢測後結果')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()

canny邊緣檢測算法是一種非常流行的邊緣檢測算法,是John F.Canny與1986年提出的,Edge detection algorithm is considered to be the best.
CannyEdge detection algorithm by the4步構成,分別介紹如下:
Due to the edge detection is susceptible to noise interference,Therefore the first to use gaussian filter to remove noise.(Gaussian filter mentioned in the image smooth,You can go through)
對平滑後的圖像使用Sobel算子計算水平方向和垂直方向的一階導數(Gx和Gy).根據得到的這兩幅梯度圖(Gx和Gy)找到邊界的梯度和方向,公式如下:
如果某個像素點是邊緣,It always and edge direction vertical gradient direction.梯度方向被歸為四類:垂直、水平,和兩個對角線方向.
After get the gradient direction and size,對整幅圖像進行掃描,去除那些非邊界上的點.Inspection on each pixel,看這個點的梯度是不是周圍具有相同梯度方向的點中最大的.如下圖所示:
A點位於圖像的邊緣,在其梯度變化方向,選擇像素點B和C,用來檢驗A點的梯度是否為極大值,若為極大值,則進行保留,否則A點被抑制,最終的結果是具有“細邊”的二進制圖像.
現在要確定真正的邊界. 我們設置兩個阈值: minVal 和 maxVal. 當圖像的灰度梯度高於 maxVal 時被認為是真的邊界, 低於 minVal 的邊界會被拋棄.如果介於兩者之間的話,就要看這個點是否與某個被確定為真正的邊界點相連,如果是就認為它也是邊界點,如果不是就拋棄.如下圖:
如上圖所示,A 高於阈值 maxVal 所以是真正的邊界點,C 雖然低於 maxVal 但高於 minVal 並且與 A 相連,所以也被認為是真正的邊界點.而 B 就會被拋棄,因為低於 maxVal 而且不與真正的邊界點相連.所以選擇合適的 maxVal 和 minVal 對於能否得到好的結果非常重要.
在opencvTraditional Chinese medicine (TCM) implementationcanny檢測使用的API:
canny = cv2.Canny(image, threshold1, threshold2)
參數:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 1 圖像讀取
img = cv.imread('./image/horse.jpg',0)
# 2 Canny邊緣檢測
lowThreshold = 0
max_lowThreshold = 100
canny = cv.Canny(img, lowThreshold, max_lowThreshold)
# 3 圖像展示
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8),dpi=100)
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap=plt.cm.gray),plt.title('原圖')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(canny,cmap = plt.cm.gray),plt.title('Canny檢測後結果')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()