這篇文章主要介紹了PythonKnowledge of file-related operations and method instance analysis,內容詳細易懂,操作簡單快捷,具有一定借鑒價值,相信大家閱讀完這篇PythonDocument related operations and method case analysis articles will be beneficial,下面我們一起來看看吧.
前言:
PythonThere are several built-in modules for manipulating files and directories(os、os.path、shutil、pathlib等等).
os.path模塊主要用於獲取文件的屬性,Contains the following common methods:
路徑操作:
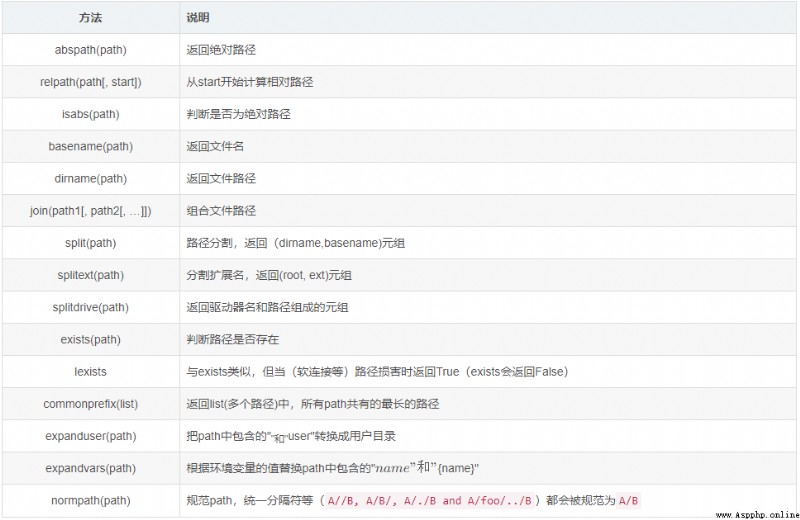
print(os.path.splitext('.info')) # ('.info', '')print(os.path.splitext('test.txt')) # ('test', '.txt')print(os.path.splitext(r'c:\tmp\test.txt')) # ('c:\\tmp\\test', '.txt')屬性操作:
文件類型判斷:
PythonReading and writing files is very simple,只需通過openThe function is opened in the appropriate way,Then it works.
with open('data.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: data = f.read() print('contents: {}'.format(data))open()用於打開一個文件,並返回文件對象(Open failure will be thrown OSError異常);When the file object is no longer in use,一定要關閉(可用withStatement is guaranteed to close automatically).
open(file, mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None)
參數說明:
file: 文件路徑(相對或者絕對路徑)或文件句柄(interger).
mode: 文件打開模式(默認是r).
buffering: 設置緩沖(0:關閉緩沖;1:Only valid for text files,Set line buffering;其他:Sets the number of bytes to buffer).
encoding: Set the codec mode(只對文本模式有效,如’utf-8’).
errors: Set the error level of the codec:
strict:默認,When the codec error occurs,拋出ValueError異常;
ignore:Codec errors are ignored(可能會丟失數據);
replace:Use alternate IDs(如’?')Substitute invalid data;
surrogateescape:Use private area encoding(U+DC80 to U+DCFF)to replace the error byte;Valid when dealing with files of unknown encoding;
xmlcharrefreplace:Writing the file works;Error bytes are replaced with XML字符(&#nnn;);
backslashreplace:使用Python’s backslashed escape sequences替換錯誤字節;
namereplace: Writing the file works;Error bytes are replaced with \N{...};
newline: Text files are valid,如何處理換行符
closefd: When using file handles,是否關閉;When using file paths,必須為True;
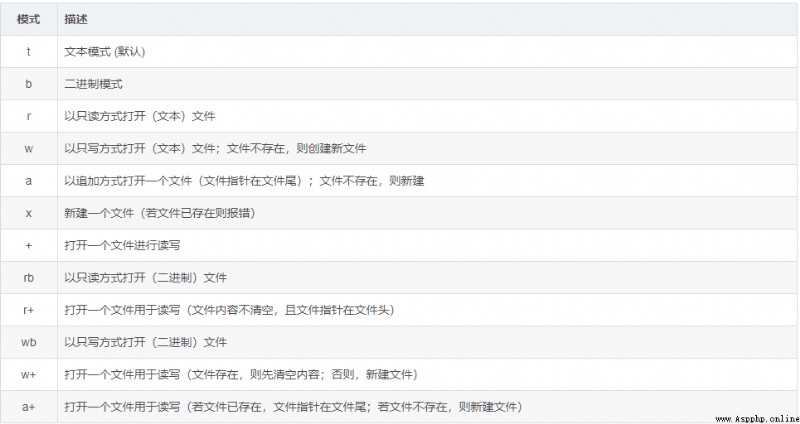
打開模式Mode(t:文本;b:二進制):
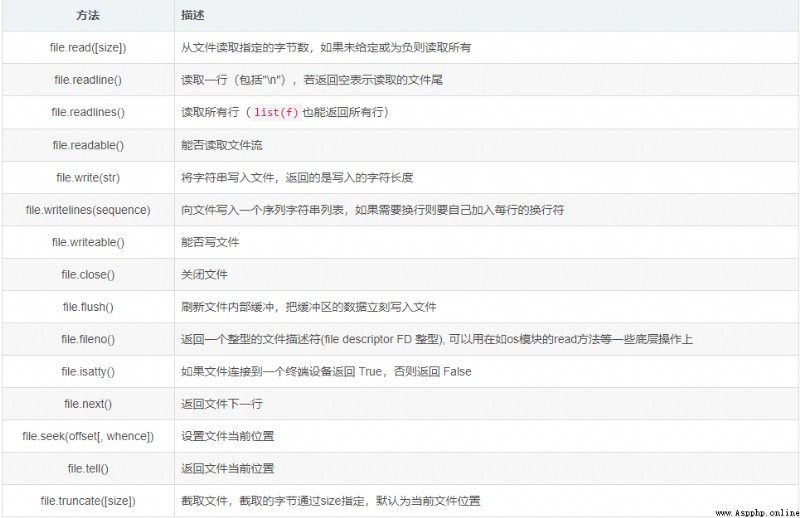
Manipulation functions for file objects:
Deleting files is OK:
os.remove()/os.unlink()
pathlib.Path.unlink()If passed is not a file,則會拋出OSError異常.
復制文件:
shutil.copy(src, dst):把文件src復制到dst中指定的位置(若dst是文件,則該文件的內容將替換為src的內容;若dst是目錄,則src將被復制到該目錄中);
shutil.copy2():File details are preserved;
移動文件:
os.rename(src, dst):重命名文件;
shutil.move(src,dst):Move the file to the specified location.
There are multiple ways to create a directory:
os.makedirs(name, mode=0o777, exist_ok=False)
If the directory already exists,則拋出FileExistsError異常;
傳遞exist_ok=True,then the directory exists,不報錯.
There is the following function to delete a directory:
rmdirThe directory is not empty,則引發OSError異常.
shutil.copytree()復制整個目錄及其子文件、目錄.
shutil.move(src,dst):Move a file or directory to the specified location.
os.rename(src, dst):重命名文件或目錄;
Windows下,若dst存在則拋出FileExistsError異常;
Unix下,若src與dstNot thrown for files or directories at the same timeIsADirectoryError/NotADirectoryError異常;重命名目錄時,若dst非空,則拋出OSError異常. 枚舉目錄
列表,可通過:
os.scandir():推薦方法;返回一個包含DirEntry迭代器;
pathlib.Path()對象的iterdir()方法:Returns an iterator containing directory objects;
os.listdir():遺留方法;Returns an included subfile(夾)list of names;
with os.scandir('/tmp') as entries: for en in entries: if en.is_file(): print(en.name)DirEntry屬性與方法:
name:文件名
path:完整路徑名
is_dir():是文件夾,返回
True;is_file():是文件,返回
True;is_symlink():是symbolic link,返回True;
stat():Returns file attribute informationstat_result;
os.walk()Used to output filenames in directories by walking the directory tree:os.walk(top[, topdown=True[, onerror=None[, followlinks=False]]])
top:The top-level directory to start traversing;
topdown:True,優先遍歷top目錄;False,Traverse subdirectories first;
onerror:當walk出錯時,調用的callable函數;
followlinks:Whether to traverse soft links;Returned as a triple(root,dirs,files):
root:The folder currently being traversed(路徑)
dirs:A list of all directory names in the current directory;
files:A list of all file names in the current directory;
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(r"D:\temp"): print(root, files)# D:\temp ['add.log', 'out.yml']# D:\temp\picture ['1.jpeg']# D:\temp\result\log ['1.log', '2.log']
After getting the directory listing,To search for files matching a specific pattern:
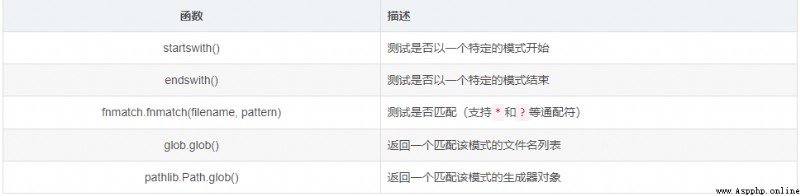
nmatch模塊主要用於文件名稱的匹配,More powerful than simple string matching,But slightly weaker than regular expressions.

fnmatchThe following wildcards are supported:
*:可匹配0或多個任意字符.
?:可匹配一個任意字符.
[字符序列]:Matches any character in a sequence of characters;Line drawing notation is supported,如 [a-c]表示a、b和c字符中任意一個.
[!字符序列]:Matches any character that is not in the character sequence.
for name in os.listdir('/tmp'): if fnmatch.fnmatch(name, 'log-*.txt'): print(name)glob模塊中的glob()返回所有匹配的文件路徑列表;iglob()與glob基本相同,It just returns an iterator(非列表).glob.glob(pathname, *, recursive=False)
參數說明:
pathname:is the path to matchpattern,可支持通配符* ? [];
recursive:若為True,則pattern中的**Will match zero or more levels of directories and subdirectories.
Such as get all the current directory and its subdirectoriespy文件:
# files = glob.iglob(r"D:\temp\**\*.log", recursive=True)files = glob.iglob(r"**\*.py", recursive=True)for f in files: print(f)## Returns files containing matching paths;# log的返回為: # D:\temp\add.log # D:\temp\result\result.log # D:\temp\result\log\test2022.log# py的返回為 # main.py # files\file_handle.py
tempfile模塊用於創建臨時文件和目錄(These temporary files are automatically deleted when the program stops running),The creation locations are in order:
Windows下:C:\TEMP,C:\TMP,當前目錄;
其他系統:/tmp,/var/tmp,/usr/tmp,當前目錄;
with tempfile.TemporaryFile('w+t') as fp: fp.write('Hello world!') fp.seek(0) fp.read()# 此處,文件已被刪除tmp = ''with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir: print('Created temporary directory ', tmpdir) tmp = tmpdir print(os.path.exists(tmpdir))# 此處,目錄已被刪除關於“PythonFile-related operations and method instance analysis”這篇文章的內容就介紹到這裡,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家對“PythonFile-related operations and method instance analysis”知識都有一定的了解,大家如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速雲行業資訊頻道.