That is, indentation is part of the syntax,
這和C++等其他語言確實很不一樣,
所以要小心 ,
其中python3和python2中print的用法有很多不同,
python3中需要使用括號
縮進要使用4個空格
(這不是必須的,但你最好這麼做),
縮進表示一個代碼塊的開始,
非縮進表示一個代碼的結束.
沒有明確的大括號、中括號、或者關鍵字.
這意味著空白很重要,而且必須要是一致的.
第一個沒有縮進的行標記了代碼塊,
意思是指函數,if 語句、 for 循環、 while 循環等等的結束.
可以直接輸出
>>> print(1)
1
>>> print("Hello World")
Hello World
無論什麼類型,數值,布爾,列表,字典…都可以直接輸出
python學習交流群:660193417###
>>> x = 12
>>> print(x)
12
>>> s = 'Hello'
>>> print(s)
Hello
>>> L = [1,2,'a']
>>> print(L)
[1, 2, 'a']
>>> t = (1,2,'a')
>>> print(t)
(1, 2, 'a')
>>> d = {
'a':1, 'b':2}
>>> print(d)
{
'a': 1, 'b': 2}
類似於C中的 printf
>>> s
'Hello'
>>> x = len(s)
>>> print("The length of %s is %d" % (s,x))
The length of Hello is 5
格式化輸出總結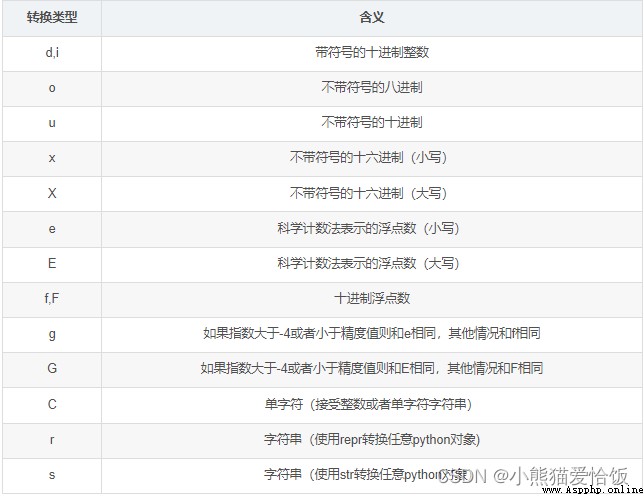
python學習交流群:660193417###
>>> pi = 3.141592653
>>> print('%10.3f' % pi) #字段寬10,精度3
3.142
>>> print("pi = %.*f" % (3,pi)) #用*從後面的元組中讀取字段寬度或精度
pi = 3.142
>>> print('%010.3f' % pi) #用0填充空白
000003.142
>>> print('%-10.3f' % pi) #左對齊
3.142
>>> print('%+f' % pi) #顯示正負號
+3.141593
顯示百分比
num = 0
40 allNum = len(fileNames)
41 while True:
42 queue.get()
43 num += 1
44 copyRate = num/allNum
45 print("\rcopy的進度條是:%.2f%%"%(copyRate*100),end="")
copy的進度條是:100.00%
在Python中總是默認換行的
print(x,end = ‘’ )
>>> "Hello""World"
'HelloWorld'
>>> x = "Hello"
>>> y = "world"
>>> xy
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#10>", line 1, in <module>
xy
NameError: name 'xy' is not defined
>>> x+y
'Helloworld'
# 2**3%5(2的3次冪對5取模)
>>> pow(2,3,5)
3
>>> x = 2
>>> type(x)
<class 'int'>
>>> x = 2.3
>>> type(x)
<class 'float'>
>>> x = [2,3]
>>> type(x)
<class 'list'>
部分函數: