Immutable data types :Number、String、Tuple
Variable data :List、Dictionary、Setumber
Catalog
data type
1. Number
1.1 Integers
1.2 Floating point numbers
1.3 character string
1.3.1 ' It is also a character
1.3.2 Escape character
1.4 Boolean value
1.4.1 Boolean values can be used and、or and not operation .
1.5 Add
1.5.1 Null value
1.5.2 matters needing attention
2. String
3. List( list )
3.1 List functions
4.Tuple( Tuples )
5.dict(dictionary)
5.1 Dictionary function
5.2dict What can't be found
6.set( aggregate )
6.1 Set function
Number It can be divided into :int( Integers )、float( Floating point numbers are decimals )、String( character string )、bool( Boolean value )
Python Can handle integers of any size , Including, of course, negative integers , The expression method is consistent with the mathematical writing .
Allow... In the middle of numbers _ Separate
10_000_000_000 and 10000000000
Floating point numbers are decimals , It's called floating point number , Because according to the scientific notation , The decimal position of a floating point number is variable . Floating point numbers can be written mathematically , Such as 1.23,-9.01 wait .
stay Python in In scientific counting method 10 use e replace .
Strings are in single quotes ' Or double quotes " Any text enclosed .
use "" Cover up

Escape character \ Can escape many characters , such as \n Means line break ,\t Represents a tab , character \ We need to escape ourselves , therefore \\ The character is \ .
When the string is Both ' Contain, ", Use escape characters
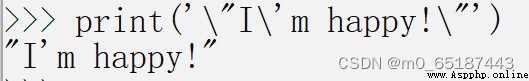
special case :
use r'' Express '' The internal string is not escape
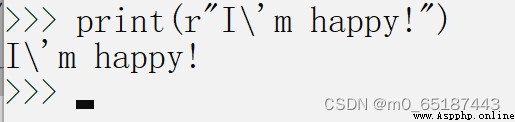
use '''...''' The format of represents multiline content

stay Python in , It can be used directly True、False Represents a Boolean value ( Please pay attention to the case )
and Operation is with operation , Only for True,and The result is True

or Operation is or is , As long as one of them is True,or The result is True

not Operation is not operation , It's a monocular operator , hold True become False,False become True

None It can't be understood as 0, because 0 It makes sense , and None Is a special null value .
Python The grammar of : Indent mode ( There is no rule whether the indentation is a few spaces or Tab, The Convention is 4 A space Indentation )
Python Case sensitive .
List It's an orderly collection , Can appear as a comma separated value in square brackets .List The data types of the elements inside can also be different , You can add and remove elements at any time .List The element can also be another List( But the other List Only one element , It can be understood as a two-dimensional array ).
List None of the elements in , It's just an empty list, Its length is 0
Format :List=['a','b','c']
len(list) # get list Number of elements
list.append(obj) # Add a new object at the end of the list
list.count(obj) # Count the number of times an element appears in a list
list.extend(seq) # Appends multiple values from another sequence at once at the end of the list ( Extend the original list with the new list )
list.index(obj) # Find the index position of the first match of a value in the list
list.pop() # Removes an element from the list ( Default last element ), And returns the value of that element
list.remove() # Removes the first match of a value in the list
list.reverse() # Reverse list of elements
list.sort(key=None,reverse=False) # Sort the original list ,True Descending ,False Ascending ( Default )
list.clear() # clear list
list.copy() # Copy list tuple And list Very similar , however Once initialized, it cannot be modified .
Other ways to get elements and list It's the same , But it can't be assigned to another element .
Only 1 An element of tuple A comma must be added to the definition ,Python In the display, only 1 An element of tuple when , A comma will also be added ,, In case you misunderstand it as a bracket in the sense of mathematical calculation .
tuple So-called “ unchanged ” Is said ,tuple Each element of , Direction never changes .
Python Built in dictionary :dict Support for ,dict Full name dictionary, Also known in other languages as map, Use the key - value (key-value) Storage , With extremely fast search speed .
d = {key1 : value1, key2 : value2 }
principle : First in the index table of the dictionary ( For example, the radical list ) Look up the page number of this word , Then go straight to the page , Find the word .
Be careful :dict The order of internal storage and key It doesn't matter in what order
radiansdict.clear() # Delete all elements in the dictionary
pop(key[,default]) # Delete dictionary given key key The corresponding value , Return the deleted value .key Value must be given . otherwise , return default value When you can't find it, an error will be reported , So there are two ways to avoid reporting errors .
One is to pass. in Judge key Whether there is :'' in list
Two is through dict Provided get() Method , If key non-existent , Can return None, Or as you specify value
A set is an unordered sequence of distinct elements , You can use braces { } perhaps set() Function to create a collection
set and dict similar , It's also a group. key Set , But no storage. value. because key Can't repeat , therefore , stay set in , No repeat key.
Be careful : To create an empty set, you must use set() instead of { }, because { } Is used to create an empty dictionary
Repeating elements in set Automatically filtered
s.add() # Add an element to the collection
s.clear() # Remove all elements from the collection
s.copy() # Copy a collection
s.remove() # Remove elements