1. Definition : An algorithm is an accurate and complete description of the solution . The algorithm is a set of feasible algorithms for model analysis , Definite and finite rules .
2. features :
a) Fineness (Finiteness): The algorithm must be able to terminate after a limited number of steps .
b) Accuracy (Definiteness): Every step of the algorithm must be defined exactly .
c) Input item (Input): The algorithms are 0 One or more inputs , To describe the initial situation of the operation object .
d) Output item (Output): The algorithm has one or more outputs , To reflect the result of processing the input data . Algorithms without output make no sense ;
e) The feasibility of (Effectiveness): Any calculation step in the algorithm can be decomposed into basic executable operation steps , That is, each calculation step can be completed in a limited time ( It's also called validity ).
3. elements
a) Operations and operations on data objects : Arithmetic operations 、 Logical operations 、 Relationship between operation 、 The data transfer .
b) The control structure of the algorithm : Execution order of algorithm ( The order 、 choice 、 loop )
4. Complexity
a) Time complexity : It refers to the amount of computation required to execute the algorithm , It can be measured by the number of basic operations performed by the algorithm .
b) Spatial complexity : It refers to the memory space required to execute the algorithm . Including algorithm program 、 The initial data entered and the additional space required during the execution of the algorithm .
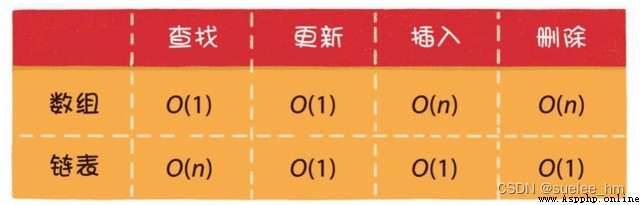
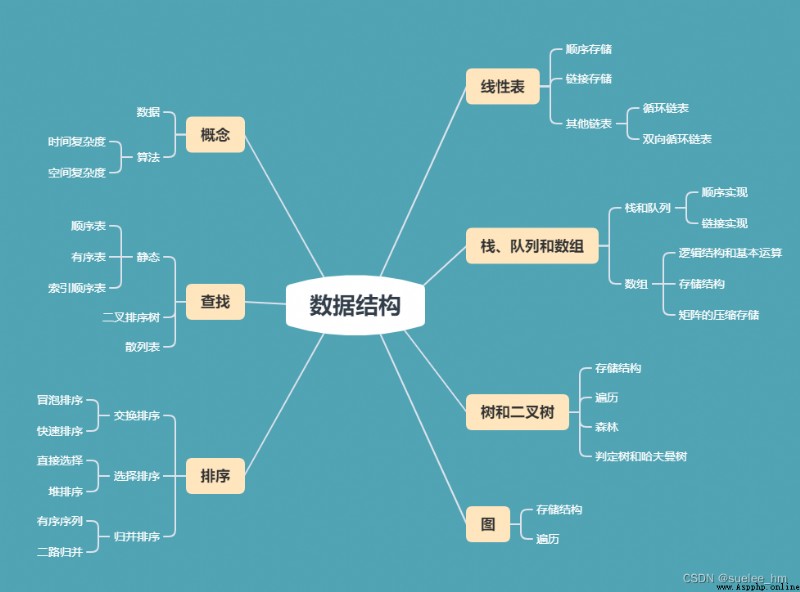
1. Array
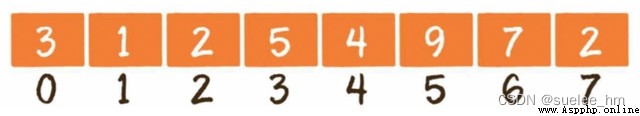
Basic operation : Read O(1)、 to update O(1)、 Insert O(n)、 Delete O(n)、 Capacity expansion O(n).
2. Linked list
Each node of the unidirectional linked list contains two parts , Part of it is the variables that hold the data data, The other part is a pointer to the next node next.

Basic operation : Read O(n)、 to update O(1)、 Insert O(1)、 Delete O(1).
Array and list comparison
Array : It's suitable for reading more 、 Insert and delete less scenes .
Linked list : It is suitable for inserting and deleting many 、 Reading less scenes
3. Stack
A stack is a linear logical data structure , Stack elements can only be LIFO . The location where the first elements entered is called the bottom of the stack , The location of the last entered element is called the top of the stack . The stack can only be accessed from one end .
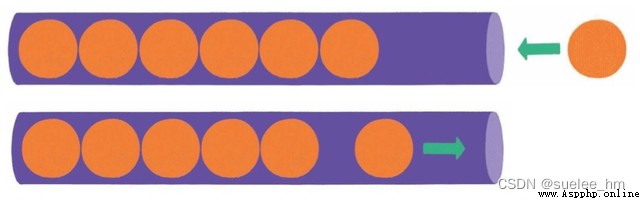
Basic operation : Push O(1)、 Out of the stack O(1).
4. queue
Queue is a linear logical data structure , The elements of the queue can only be in and out . The exit end of the queue is called the leader of the queue , The entry end of the queue is called the tail of the queue . Head in , On the other end .

Basic operation : The team O(1)、 Out of the team O(1).
5. Hashtable
A logical data structure , Key provided (key) And the value (value) The mapping relation of .
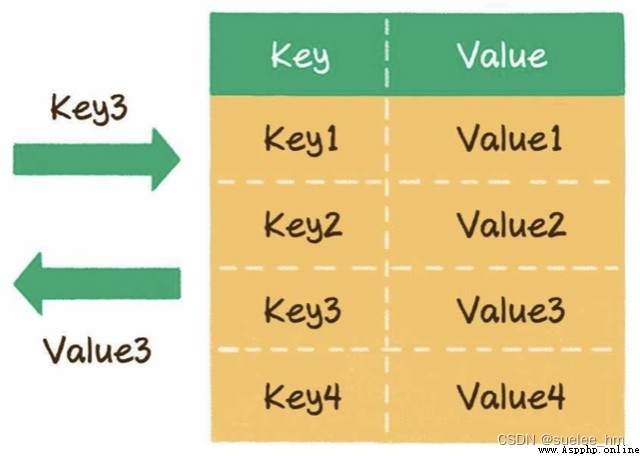
Basic operation : write in :O(1)、 Read :O(1)、 Capacity expansion O(n).
6. Trees
A tree is composed of root nodes and several subtrees . A tree is made up of a set and a relationship defined on that set . The elements in the set are called the nodes of the tree , The defined relationship is called parent-child relationship . The parent-child relationship establishes a hierarchy between the nodes of the tree . In this hierarchy, a node has a special position , This node is called the root node of the tree , Or root .
To put it simply , Algorithm is the process of solving problems by computer . In the process , Whether it is to form a solution or to write a program , They're all implementing some kind of algorithm . The former is the logical form of Algorithm , The latter is the code form of the algorithm .
Such as : seek 1+2+3+...998+999+1000=?
Algorithm 1: Add... In turn : Loop processing --- Handle 999 Time
Algorithm 2: Gauss solution : Add head and tail *500 (1+1000)*1000/2 --- Handle 3 Time
Algorithm 3: Use recursion to implement --- Handle 100 Time
sum(100) = sum(99)+100
sum(99) = sum(98)+99
.....
sum(2) = sum(1)+2
sum(1) = 1
The basis for evaluating the algorithm : Complexity ( Time complexity and space complexity )
The most important computer resources are time and space resources , So complexity is divided into time and space complexity , Time complexity refers to the amount of computation required to execute the algorithm , Space complexity refers to the memory space required to execute this algorithm .
1. Time complexity (Time Complexity)
The time spent by an algorithm is proportional to the number of times the statements in the algorithm are executed , Which algorithm has more statements executed , It takes more time . The number of statements executed in an algorithm is called statement frequency or time frequency .
2. Spatial complexity (Space Complexity)
Space complexity is a measure of the amount of storage space temporarily occupied by an algorithm during operation .
Algorithm complexity is divided into time complexity and space complexity . Its role : Time complexity refers to the amount of computation required to execute the algorithm ; And space complexity is the memory space needed to execute this algorithm .
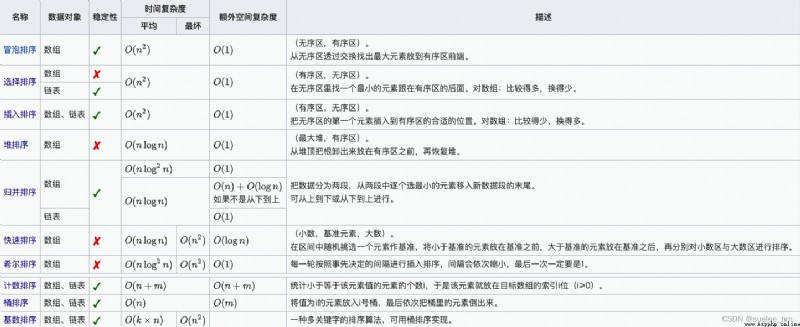
Sort (sorting) The function of is to convert an arbitrary sequence of data elements , Rearrange into a keyword ordered sequence .
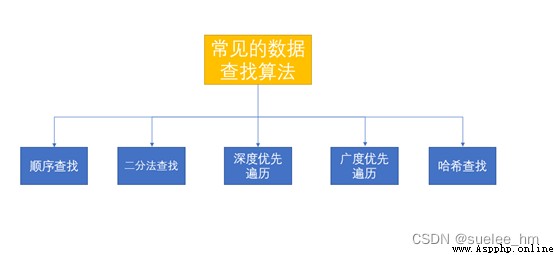
Find the required data from a large amount of data .
[1]: Baidu security verification