Catalog
Previous review :
Content overview of this issue :
The content of this issue :
Three mesh operation :
Logical operations :
And logic and:
Or logic or:
Illogical not:
Summary :
Last time we learned if Use :if Later, the judgment expression , Pay attention to adding colons and indents ;else Use :else Not to be used alone , Followed by a colon , There is no judgement ;elif Use :elif I can only follow you if Back , Not alone ; use : Judgement statements are basic statements , It's something we have to master .
In this issue, we will study Three mesh operation as well as Logical operations These two things .
Last issue The conventional if Judge , But some are very simple if Judge whether there is a simple way to write ?
Speaking of simple writing is our three eye operation , Let's see !!!
Normal writing :
# The normal way of writing is as follows :
# assignment a yes 6
a =6
# Judgment statement :
# If a Greater than 5 Output True
if a > 5:
print(True)
# Otherwise output False
else:
print(False)
Three eye operation :
These lines of code shown above are our normal judgment statements , Next, let's look at the ternary operation corresponding to the above string of judgment statements .
# Three eye operation :
# assignment a yes 6
a = 6
# Judge ( Ternary operation grammar )
print(True if a > 5 else False)Code parsing :
I believe you can understand the first picture above , Maybe the second one is a little hard , But don't worry , Now let's analyze the code :
Let's take down the code first , Then I make a comment and explanation directly in the code , Then I use multi line annotation here , This is more convenient and intuitive
# Three eye operation :
# assignment a yes 6
a = 6
# Judge ( Ternary operation grammar )
print(True if a > 5 else False)
'''
Explanation of three eye operation :
True by The result returned when it is true That is to say if The print results inside
a > 5 by Judgmental That is, the conditional sentence of judgment
False by The result returned when it is false That is to say else Print results inside
Grammatical construction :
The value returned when it is true if Judgmental else Data returned when false
'''Although the latter is also a judgment , And it should be quite concise , This can save a lot of code , Make the code look simpler, but Be careful : It's just simple if Judgment can be used , Don't use too complex judgments , That will affect the readability of the code .
Last time we introduced if You can follow it with a judgment statement , What if we need to judge multiple conditions at the same time ?
Let's look at it first Python Common judgment symbols in :
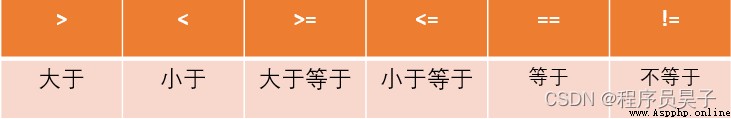 When it is necessary to judge multiple contents at the same time , have access to And 、 or 、 Not Wait for logic to judge multiple conditions at the same time .
When it is necessary to judge multiple contents at the same time , have access to And 、 or 、 Not Wait for logic to judge multiple conditions at the same time .
# assignment a yes 6
a = 6
# Judgment statement
if a > 3 and a < 9:
print('OK')
else:
print('NO')
and Express “ also ” perhaps “ and ” It means , Only when and When both sides are true , Will return really , Commonly used in other languages & To express and.
# assignment a yes 6
a = 6
# Judgment statement
if a > 8 or a < 2:
print('OK')
else:
print('NO')or Express “ perhaps ” It means , As long as one of the two sides is true , Will return to true , All false will return false , Commonly used in other languages | To express or.
# a The value of is False
a = False
# Judgment statement
if not a:
print('OK')
else:
print('NO')not Express “ Take the opposite ” It means , That is, true will become false , False will become true , Commonly used in other languages ! To express not.
In this issue, we understand and learn the three eye operation , And in logical operations and;or;not.