One 、 introduction
Univariate linear regression : There is only one variable involved
Multiple linear regression : Two or more variables involved
There is a certain error between the predicted result and the real value ( Pictured ):
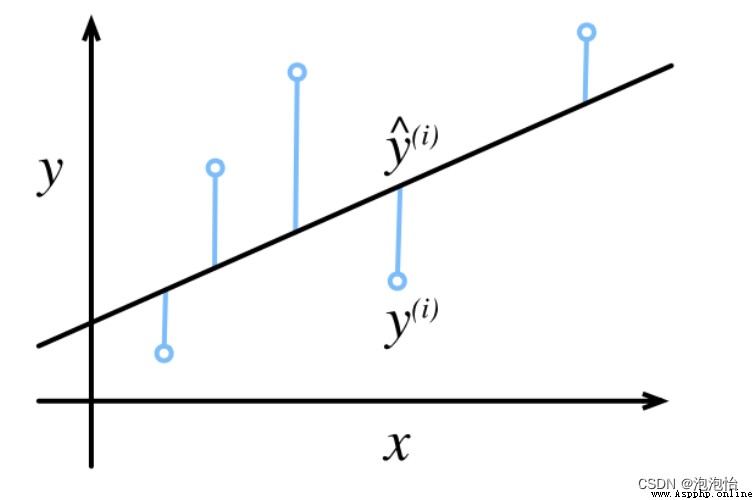
This article takes y=-2x+8 For example , The method of estimating the regression coefficient by using the least square method and python Realization .
Two 、 Formula derivation
1. Least square method :
Suppose you know a series of scatter points (xi,yi)
We will (xi,yi) Plug in y =kx+b have to
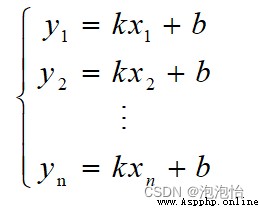
Construct the least squares function :
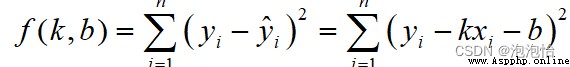
Yes k and b Calculate the partial derivatives respectively to get :
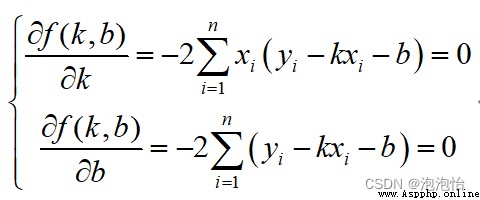
Both ends of the above equations are divided by n have to :
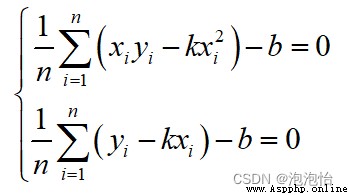
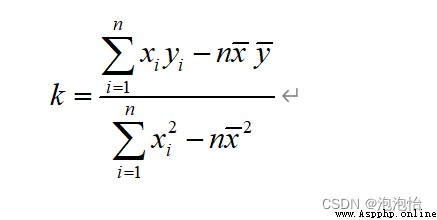
The coefficient can be obtained by substituting it b.
1. Interpret the curve change trend according to the scatter diagram
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
trainX=np.arange(25)
trainY=2*trainX+8+np.random.randn(25)
plt.scatter(trainX, trainY,color='red',marker='+')The result is shown in the figure :
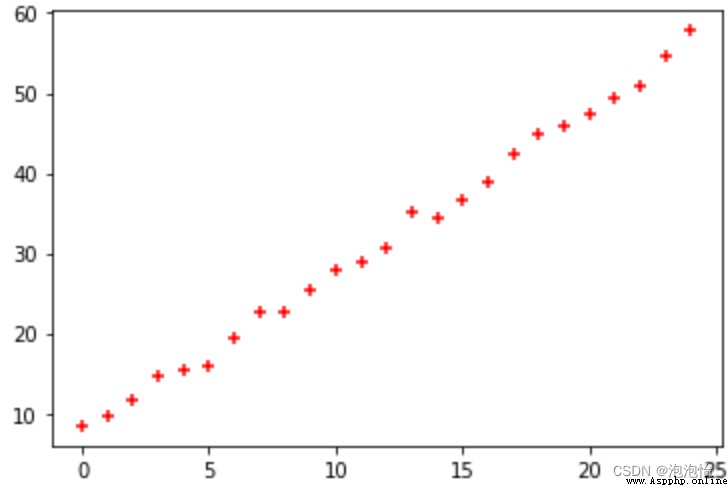
2. The regression coefficient is calculated as follows :
n=25
xu=np.sum(trainX)/n
yu=np.sum(trainY)/n
k1 = sum( trainX * trainY ) - n * xu * yu;
k2 = sum( trainX * trainX ) - n * xu * xu;
k = k1 / k2;
b = yu - k * xu;give the result as follows :k=2.0174825107892924, b=7.508028732222016
3. The complete code is as follows
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
trainX=np.arange(25)
trainY=2*trainX+8+np.random.randn(25)
plt.scatter(trainX, trainY,color='red',marker='+')
n=25
xu=np.sum(trainX)/n
yu=np.sum(trainY)/n
k1 = sum( trainX * trainY ) - n * xu * yu;
k2 = sum( trainX * trainX ) - n * xu * xu;
k = k1 / k2;
b = yu - k * xu;
Y1=k*trainX+b
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(trainX, trainY,color='red',marker='+')
ax.plot(trainX, Y1,color='blue')The result is shown in Fig. :
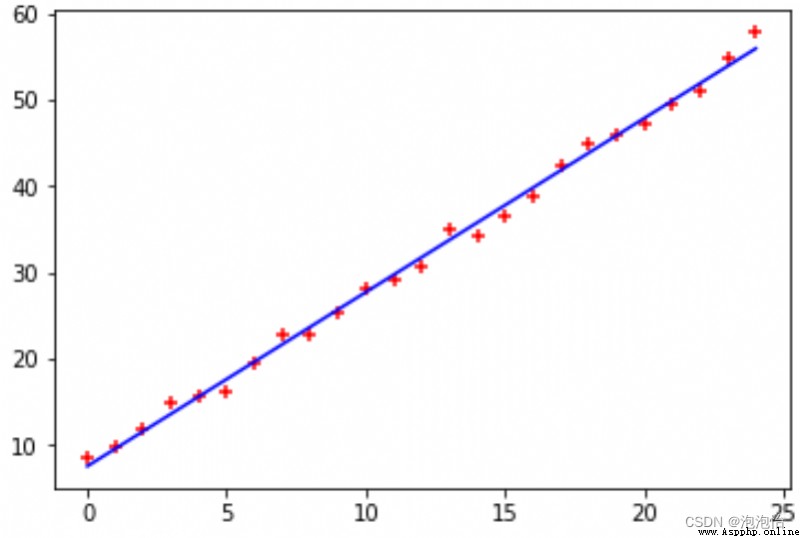
Be careful : Derivation of additional maximum likelihood estimation :
