I have java Based on learning python It's quite fast , I really feel that java You can do it python. It can be that it is still in the basic stage . Write it down and see what I learned today Python grammar
Look at Python Of hello world. I'm getting started hahahaha
# My introduction
print("hello world");Running results
Take a look at the variables I learned , I feel Python Automatically type your variables , It's very convenient , You don't need to deliberately define data types .
grammar Variable name = A variable's value
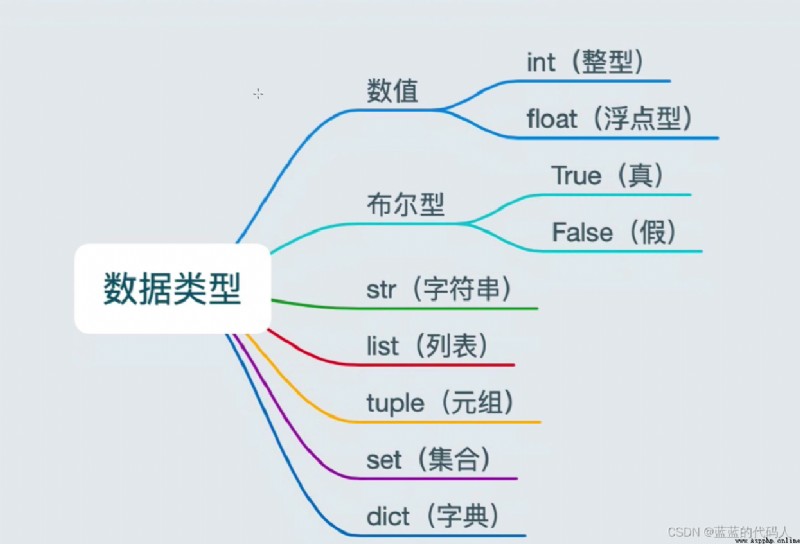
# Understanding variables
lanLan = ' Blue code man !!!'
print(lanLan)
# str type
blogName='csdn'
print(type(blogName))
print(blogName)
# plastic and floating-point
zhengXing=18
fuDianXing=9.9
print(type(zhengXing))
print(type(fuDianXing))
print(" I this year "+str(zhengXing)+" year ")
print(" I have a "+str(fuDianXing)+" RMB ")
#bool-- Boolean type
b = False
print(type(b))
# list aggregate
lan = [1,2,3,4,5]
print(type(lan))
# tuple-- Tuples
e = (1,2,3,4)
print(type(e))
# set-- aggregate
e = {1,2,3,4}
print(type(e))
# Dictionaries --dict
lans = {'name':'tom','age':18}
print(type(e))Introduce to you :type This object
type( Variable name ) In this way, you can show what type of data this data is

There are two ways, one is equivalent to jdbc A placeholder for
One is f{} The object is as shown in the figure
Here and java It's a big difference
# String splicing exercise
# Create concatenated string data
age = 18
name = ' Lazy coder '
socreNum = 90.123
stu =90
print(' I this year %d Year old ' % age)
print(' My name is %s'% name)
print(' My weight is %.3f kg '%socreNum)
print(' My student number is %03d' %stu)
# My name is xxx This year, xx My weight is xx The kilogram student number is xx
print(' My name is %s This year, %d My weight is %0.3f The kilogram student number is %03d Next year, %d year ' %(name,age,socreNum,stu,age+1))
print(f' My name is {name} This year, {age} My weight is {socreNum} The kilogram student number is {stu} Next year, {age+1} year ')Running state ,, Splice data types
Escape character : It's line feed and a table Distance of
End character : The end character is replaced at the end of the run print Line feed after running
# Escape character
print('hello \n word') # Line break
print('hello \t word') # Space One table Distance of
# Terminator
print('1',end='\n')
print('2',end='\t')
print('3',end='....')
print('4') 
Let the user input , Then use a function to receive .
No matter what type the user enters here, it is str Type is string . Here you can type convert .
# Input function
userName = input(' Enter your account number :')
passWord = input(' Enter your password :')
print(f' Your account number is :{userName} \n The password is :{passWord}')Let the user input the value and output it after receiving

and java It's like
1. Arithmetic operator
2. Assignment operator
3. Composite operators
4. Comparison operator
5. Logical operators
# Operator
# 1 Arithmetic operator
print(1+1)
print(3*2)
print(2+1)
print(100/2)
print(100/2)
print(100//4.5) # to be divisible by
print(2 ** 4) # Namely 2*2*4
print((1+4)*3)
# 2 Assignment operator =
num = 1 # Single variable assignment
num1,num2,num3,str1 = 1,2,3,'hwllo word' # Multiple assignment operators
a = b =100 # Multivariable assignment
# 3 Compound assignment operator
c = 1
a = 1
c+=a;
print(c);
# 4 Comparison operator
1==1
1!=2
# 5 Logical operators
qq = 0
bb = 1
print(qq < bb and bb>bb) # It's all true
print(qq < bb or bb>bb) # When it's true, it's true A holiday is a holiday
print(not False) # Not : Take the opposite Running results

You can convert some directly into
I want to convert to int You can write int( Variable name ) Write what type of conversion
# Data type conversion
userInput = 1;
print(type(float(userInput)))
print(float(userInput))The grammar is as follows :
Here is an example of an Internet cafe
userAge = input(" Enter your age :")
if int(userAge) <= 18:
print(f" Your age is {userAge} Can not be ")
elif int(userAge) <= 28:
print(f" Your age is {userAge} Sure ")
else:
print(f" Your age is {userAge} Sure ")
Here is a . Ask for money to get on the bus , Get on the bus and judge whether there is a seat
# Get on the bus and find a seat
money =1; # There is a dollar
seat = 1; # There is a seat
if money==1:
print(" Get on the train successfully ")
if seat==1:
print(' Congratulations on your seat ')
else:
print(' Stand here, you ')
else:
print(' Can't go up ')It feels and java Also write one on the top import random.
and java The guide bag is the same .
# Man machine stone scissors paper
userChu = int(input(' Enter what you want 0- stone ;1- scissors ;2- cloth '))
# The computer computer
computer = random.randint(0,2)
print(computer)
if (userChu==0) and (computer==1) or (userChu==1) and (computer==2) or (userChu==2) and (computer==0):
print(' Players win ')
elif (computer==1) and (userChu==1):
print(" flat ")
else:
print(' Computer victory ')Here is a simple judgment structure . and java There are a little more ternary operators of
# Ternary operator There are two variables to compare the size if the variable 1 Greater than the variable 2 Execution variables 1- Variable 2 Otherwise execution 2- Variable 1
aa=50
bb=20
cc = aa - bb if aa > bb else bb -aa
print(cc)Loop structure here is a record of the even sum
i = 1
result =0
while i<=100:
if i%2==0:
result+=i
i +=1
print(result)Running results
break, Cycle here once , Come in break So I recorded a 2 The output from . End the program directly
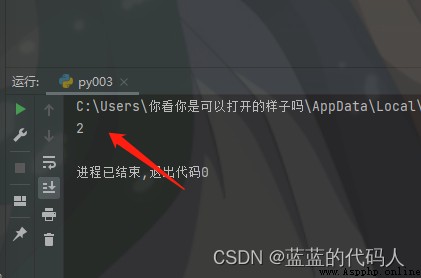

continue Continue to execute the code , This is not to stop the code . Here is the direct dead cycle
Here is an example , I want you three times a day for three days
i=0
while i<3:
print(f' The first {i} God ')
j = 0
while j<3:
print(" care about you ")
j+=1
i += 1 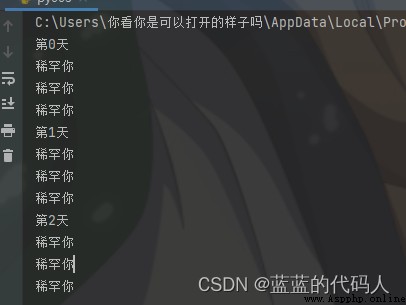
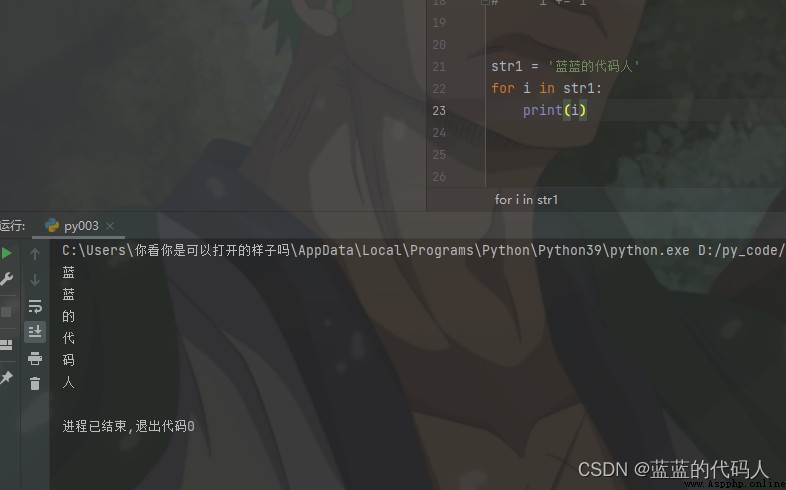
java To for Loops are common , But here and java Of feach Same function variable string characters
str1 = ' Blue code man '
for i in str1:
print(i)
-------------------------------------------- The end -------------------------------------------------