I just arrived at the company in the morning , During breakfast , Attracted by such a problem in the Group , As shown in the figure below :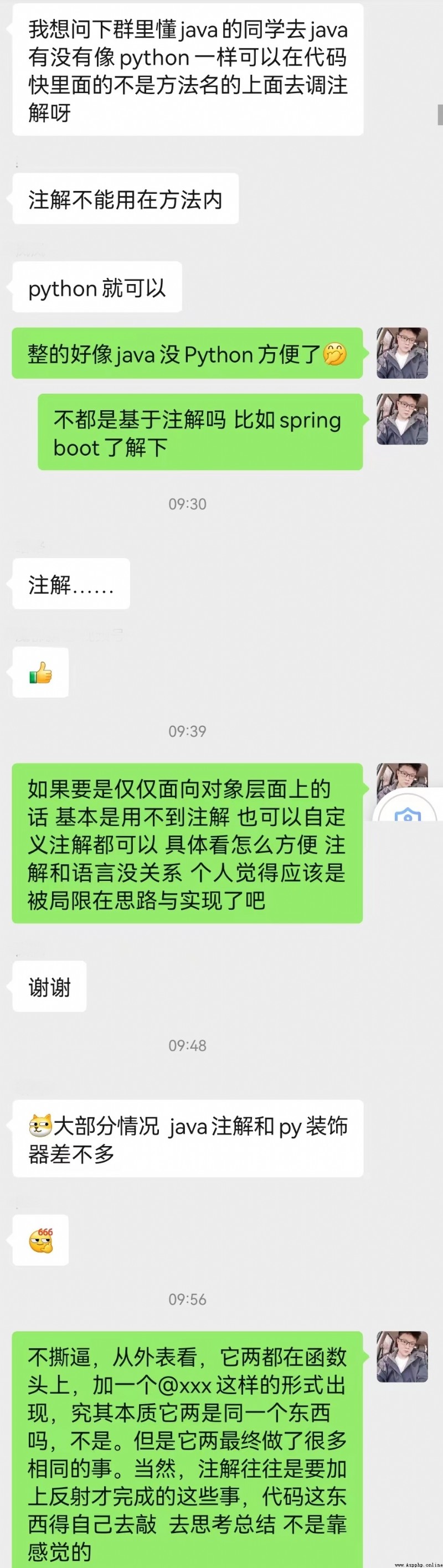
Then I thought again , I feel that what I said is not all right , So I want to make a corroboration from the perspective of procedure .
Of course , Before writing this article , I also consulted many articles , Some views on this issue , The summary is as follows :
Seriously, these conceptual things , I really see it in the clouds , I suggest reading Wikipedia or textbooks .
My personal point of view , It must be that annotations and decorators are not the same .
Don't talk much , Or go straight to the code , Let's use actual cases !
@zhujie(' Parameters ')
All are @ start , annotation 、 Decorators can be customized 、 Can take parameters 、 Can be executed before the code block is marked .
The sample code is as follows :
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PlaylistInfo{" +
"curtime='" + curtime + '\'' +
", issmarter='" + issmarter + '\'' +
", xmusicnum='" + xmusicnum + '\'' +
", picurl=" + picurl +
", playlist=" + playlist +
", systemtime=" + systemtime +
'}';
}
@Override: The meaning of rewriting , If you are not satisfied with the parent class, you can implement it yourself , Generally, methods are checked during compilation .
Obviously , The annotation is placed above the method , Only responsible for compiling 、 Check , The content of the method and the function of the method have not been changed .
The example code is as follows :
class TestClass():
@property
def myValue(self):
return self.value
if __name__=="__main__":
TestClass.myValue = ' Decorator !'
print (TestClass.myValue)
@property: As an attribute
It is obvious that , Decorators directly change the function .
From the above we can see that , The difference between annotations and decorators :
Come here , Do you think , They are not the same thing at all , Because it's not the same at all .
Actually , stay java Annotation and reflection in can be implemented python The effect of the interior decorator .
Have you been cheated again ? Don't worry. , Let's look back !
The benefits of annotation : Without changing the source code , Implement new functions for source code . If there is a large area of code that needs to change the same function , You can use annotations on methods or classes to implement
Use them separately python And Java The way , Realize the verification of program calculation , Write the abnormal results to error.log In file
The example code is as follows :
# In this case, it is used as the result of write error
def check(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
return res
except Exception as err:
with open("error.log", mode="at", encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("start".center(50, '*'))
f.write('\n')
f.write(str(func))
f.write('\n')
f.write(str(err.__class__))
f.write('\n')
f.write("end".center(50, '*'))
f.write('\n')
return wrapper
@check
def add(a, b):
print(a + b)
@check
def divide(a, b):
print(a / b)
add(50, 50)
divide(100, 0)
The sample code is as follows :
public class Calculator {
@Check
public void add() {
System.out.println(50 + 50);
}
@Check
public void divide() {
System.out.println(100 / 0);
}
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Check {
}
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CheckDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Calculator test = new Calculator();
Class<? extends Calculator> c = test.getClass();
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("input.txt"));
for (Method m :
methods) {
if (m.isAnnotationPresent(Check.class)) {
try {
m.invoke(test);
} catch (Exception e) {
bw.newLine();
bw.write(e.getCause().getMessage()+"----");
bw.newLine();
bw.write(String.valueOf(e.getCause().getClass()));
}
}
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
Run their compilers separately , The results are shown in the following figure :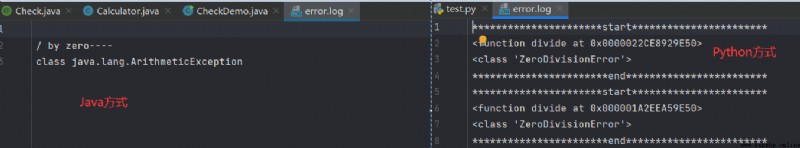
It can be seen from the above that ,Java Annotation and reflection in can be implemented python The effect of the interior decorator .
Enter the user password , Return to the user information interface
The sample code is as follows :
from flask import Flask
import json
from flask import request
app = Flask(__name__) # start-up
@app.route('/rongrong/getUserInfo',methods=['GET']) # Request path 、 Request mode
def login():
username = request.args.get("username") # obtain url In the parameter “username” Value
password = request.args.get("password") # obtain url In the parameter “password” Value
if username and password: # If the value passed in is true, print the following information
data = json.dumps({
"username":username,
"password":password,
"code":"200",
"message":" success "
},ensure_ascii=False) # Solve the problem of Chinese garbled code
else: # If the transmission parameter is empty, print the following information
data = json.dumps({
"message":" Please pass the parameter "
},ensure_ascii=False)
return data
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run() # function
The sample code is as follows :
@RequestMapping(value = "/rongrong/getUserInfo", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Result<List<Student>> findStudentByName(HttpServletRequest request) {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
JsonRootBean jsonRootBean = new JsonRootBean();
jsonRootBean.setUsername(username);
jsonRootBean.setPassword(password);
jsonRootBean.setCode("200");
jsonRootBean.setMessage(" success ");
Result result = ResultUtils.success(jsonRootBean);
return result;
}
python result :
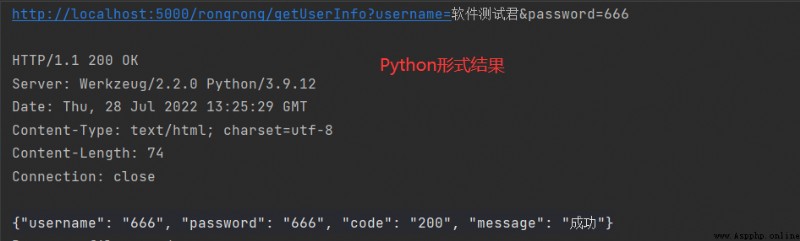
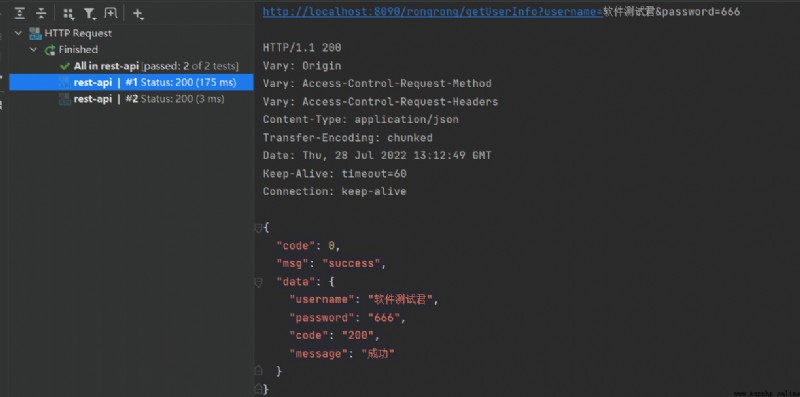
Java result :
Python The decorator is very simple , It is to modify the behavior of a function through a layer of shell , and @decorator_func It's just a grammar sugar , The writing method used to beautify ornaments .
Java The comments in are different , It is from the language level for the classes in the code , function , Add some metadata that can be read by runtime to the field , The annotation provider should read these metadata at run time , And deal with it accordingly .
The author's lack of talent and learning , Writing this article is entirely out of technical itch , Naturally, I have consulted a lot of articles , Only then has this article .
The following is a personal opinion only :
Through various means, they can become one thing , So in terms of results , you 're right , It can be regarded as one thing .
let me put it another way , Sometimes I feel that the decorator is more like Java A design pattern of .
Do you think? ? Welcome to comment area for discussion !