Process library :gevent
Thread library : threading
Process library : multiprocessing
import gevent,time
def demo1(num):
for i in range(num):
print(' coroutines 1:{:-<30}'.format(111))
# Simulation time operation ,geven Created t After encountering time-consuming operations, the collaboration process will switch to other collaboration processes
gevent.sleep(0.5)
def demo2(num):
for i in range(num):
print(' coroutines 2:{:->30}'.format(222))
gevent.sleep(0.5)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create a collaboration object , Internal parameters ( The name of the function pointed to by the coroutine , Parameters to pass )
g1=gevent.spawn(demo1,4)
g2=gevent.spawn(demo2,4)
# Wait for the cooperation process to complete
g1.join()
g2.join()Print the results :
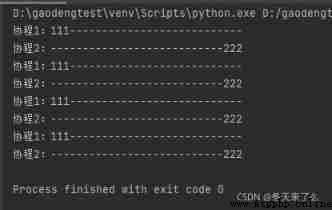
import threading
from time import sleep
def song(num):
for i in range(num):
print('{:*^30}'.format(' Sing a song '))
sleep(1)
def dance(num):
for i in range(num):
print('{:-^30}'.format(' dance '))
sleep(1)
def main():
# Instantiate two threads , And start the
#target Pointing function ,args Followed by parameters in tuple format , Pass it into the function as an actual parameter
threading.Thread(target=song,args=(5,)).start()
threading.Thread(target=dance,args=(5,)).start()
# Number of printing threads
print(threading.enumerate())
if __name__ =='__main__':
main()Print the results :
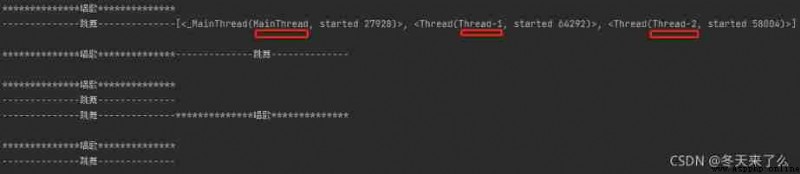
You can see a main thread and two sub threads
import multiprocessing,os
from time import sleep
def song(num):
for i in range(num):
print('{:*^30}'.format(' Sing a song '))
# View the status of the process id
print(os.getpid())
sleep(1)
def dance(num):
for i in range(num):
print('{:-^30}'.format(' dance '))
# View the status of the process id
print(os.getpid())
sleep(1)
def main():
# Instantiate two processes , And start the
#target Pointing function ,args Followed by parameters in tuple format , Pass it into the function as an actual parameter
multiprocessing.Process(target=song,args=(5,)).start()
multiprocessing.Process(target=dance, args=(5,)).start()
# View the main process id
print(os.getpid())
if __name__ =='__main__':
main()Print the results :
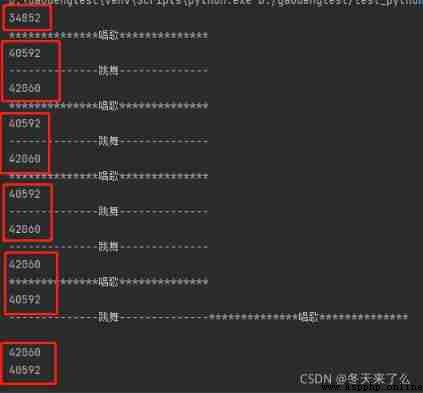
You can see a main process number and two sub process numbers