The program consists of modules , One module corresponds to python The source file , The general suffix is :.py
Modules consist of statements
The sentence is python The construction unit of a program , For creating objects 、 Variable assignment 、 Call function 、 Control statements, etc .
Each object consists of : identification (ID)、 type (type)、 value (value) form
identification : Used to uniquely identify objects , Equivalent to the address in computer memory . Use built-in functions id(123) You can go back to 123 The logo of
type : Equivalent to the storage of objects " data " The type of . Type can limit the value range and executable operations of an object , Use type(123) Get the type .
value : Information representing the data stored by the object . Use print(123) Directly type here, insert the code chip and print the value .
stay Python The variable in is called : References to objects . Because variables store the address of the object . The variable references the object by address .
For variables 、 function 、 class 、 Name of module, etc .
Case sensitive
The first character must be a letter 、 Underline . Followed by : Letter 、 Numbers 、 Underline
Cannot use keyword
Beginning or ending with a double underscore usually has a special meaning , Try to avoid this kind of writing .
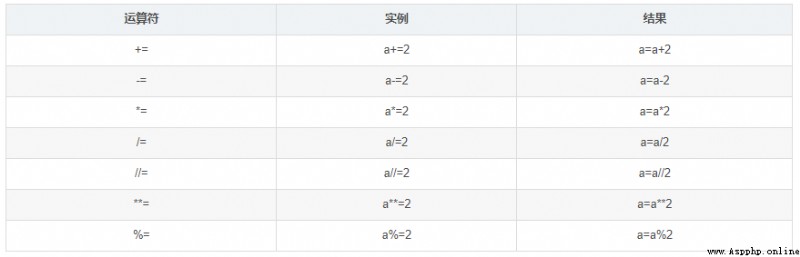
Used to bind a variable to an object , The format is : Variable name = expression
for example a=3, In operation , The interpreter first runs the expression on the right , Generate an object representing the operation result of the expression ; Then assign the address of the object to the variable on the left .
Variables should be initialized before use ( assignment ), Otherwise, an error will be reported .
adopt del Statement to delete variables that are no longer used
When the variable is deleted , Object will have no variable references , The object will be recycled to the garbage collector , Clear memory space .
>>> a=123
>>> a
123
>>> del a
>>> a
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'a' is not defined
>>>
Used to assign the same object to multiple variables
Python Basic programming concepts _1315963786 The blog of -CSDN Blog
A series of data is assigned to variables corresponding to the same number
a,b,c=4,5,6 amount to a=4,b=5,c=6
Python Constants are not supported , You can only agree on the naming rules of constants , And the logic of the program does not modify the value of the constant .
>>> print(max_speed)
120
>>> max_speed = 140 # In fact, it can be changed , Logically cannot be changed
>>> print(max_speed)
140
integer ( Integers )
floating-point ( decimal )
Boolean type ( Contains only True、False)
String type ( A sequence of characters )
Floating point numbers are rounded off directly . Such as int(9.9) The result is :9
Boolean value True Convert to 1,False To 0. Such as int(True) The result is 1
The string conforms to integer format ( Floating point number format does not work ) Then it is directly converted to the corresponding integer , Otherwise, the report will be wrong .
>>> int("456")
456
>>> int("456abc")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '456abc'
>>> int("456.789")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '456.789'
>>> int(456.789)
456
>>>
Mixed operation of integer and floating point number , The result of the expression is automatically converted to floating point . such as 2+8.0=10.0
Python2 in int yes 32 position , Can store up to plus or minus 21 Million integers ;Python3 in ,int Can store integers of any size .
Be similar to int(), You can also use float() Convert other types to floating point numbers
After integer and floating-point operation, the expression result will be floating-point number automatically
After integer and floating-point operation, the expression result will be floating-point number automatically
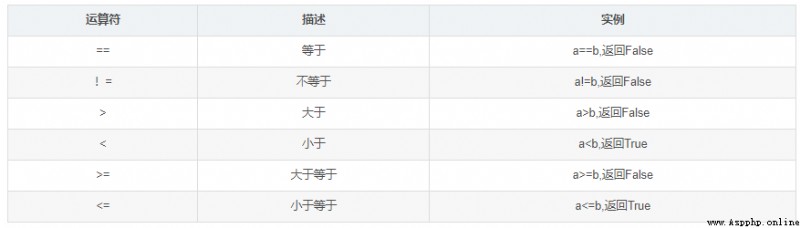
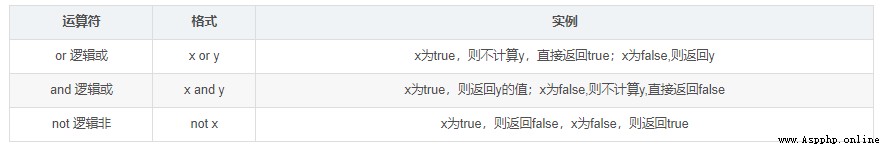
Storage unit used to compare two objects , Actually compare the addresses of two objects .
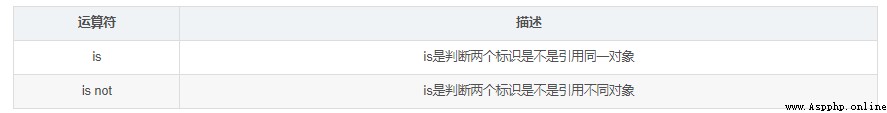
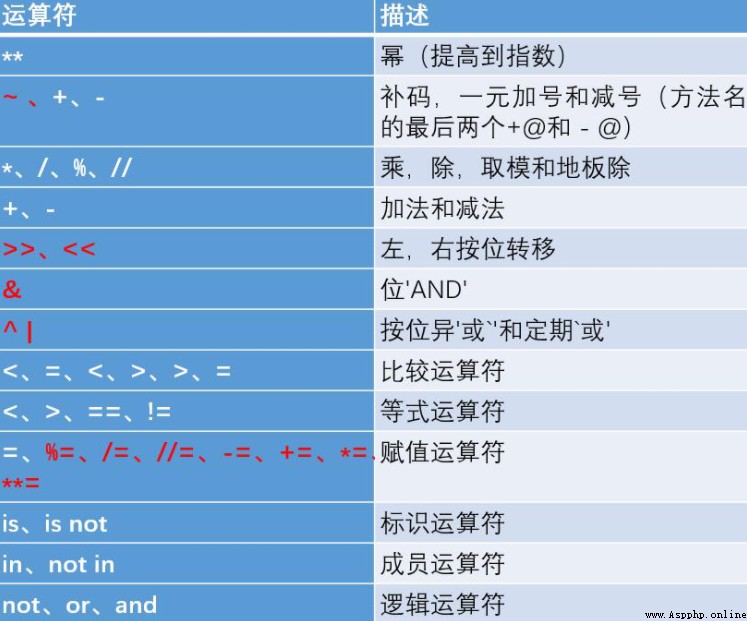
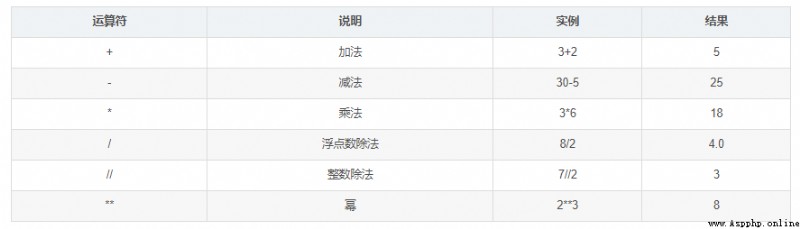
Multiplication and division take precedence over addition and subtraction
Bit operation and arithmetic operation > Comparison operations > The assignment operation > Logical operations