Hello, everyone ! I'm a panda
A lot of learning Python Our friends will encounter many problems in the realization of functions in the actual project , Some problems are not very difficult , Or there is a good way to solve it . Of course , Which makes perfect , When we are proficient in code , Naturally, we can sum up some useful skills , But for those who are just familiar with Python Our classmates may not be so relaxed .
This time I recommend a good resource to learn these skills “30-seconds-of-python”, All techniques and methods as long as 30 In seconds get To , You can use your business time to accumulate . Let's take a quick look at .
https://github.com/30-seconds/30-seconds-of-python

Here is 30 Secology Python The entire catalog of , It is divided into several parts :List、Math、Object、String、Utility, Here is the brain map of the mind .
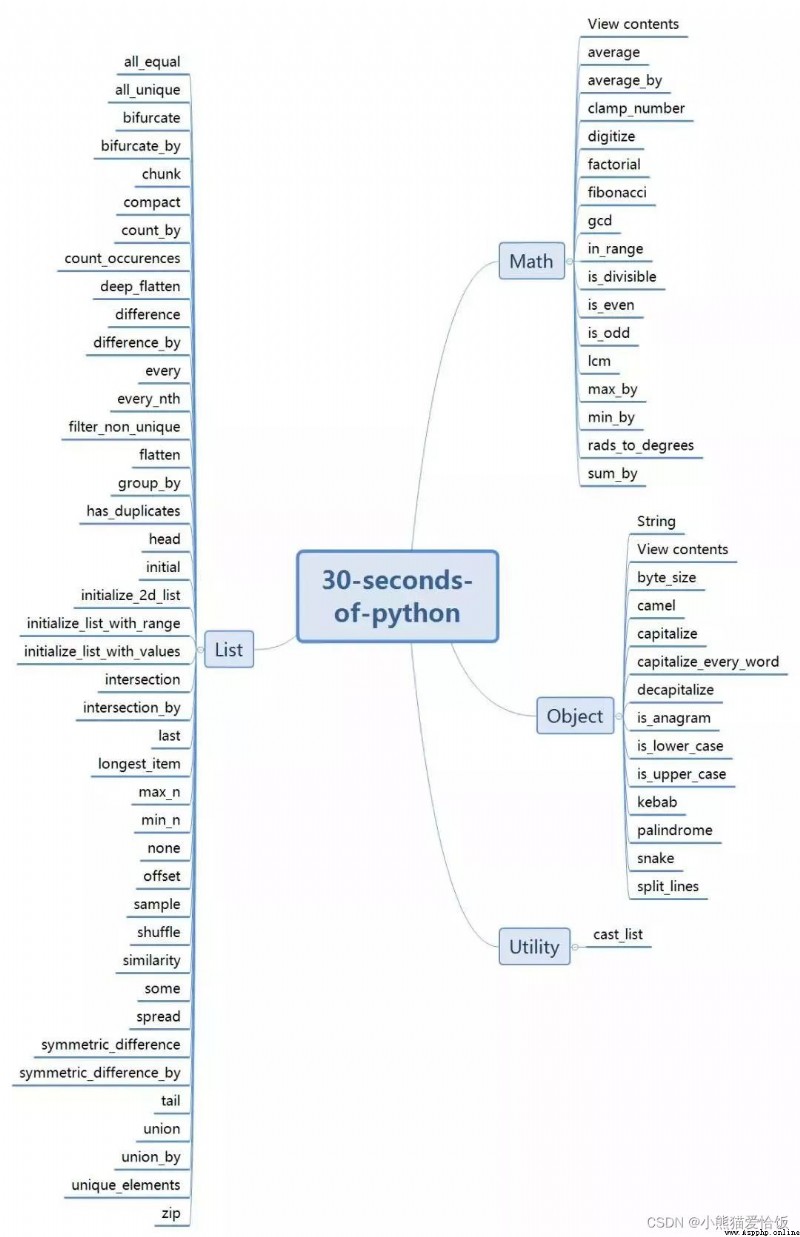
what are you having? python I won't answer the related error report 、 Or source code information / Module installation / Women's clothing bosses are proficient in skills You can come here :(https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=2Q3YTfym) Or the private number at the end of the text
I chose 10 A practical and interesting way to share , The rest of you can learn by yourself .
1. List:all_equal
Function realization : Verify that all elements in a list are the same .
Reading : Use [1:] and [:-1] To compare all elements of a given list .
def all_equal(lst):
return lst[1:] == lst[:-1]
give an example :
all_equal([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) # False
all_equal([1, 1, 1, 1]) # True
2. List:all_unique
Function realization : If all values in the list are unique , return True, otherwise False
Reading : Use set... On a given list set() duplicate removal , Compare it with the length of the original list .
def all_unique(lst):python Learn to exchange skirts :660193417###
return len(lst) == len(set(lst))
give an example :
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
y = [1,2,2,3,4,5]
all_unique(x) # True
all_unique(y) # False

3. List:bifurcate
Function realization : Group list values . If in filter The element is True, So the corresponding element belongs to the first group ; Otherwise it belongs to the second group .
Reading : Use list derivation and enumerate() be based on filter Elements to groups .
def bifurcate(lst, filter):
return [
[x for i,x in enumerate(lst) if filter[i] == True],
[x for i,x in enumerate(lst) if filter[i] == False]
]
give an example :
bifurcate(['beep', 'boop', 'foo', 'bar'], [True, True, False, True])
# [ ['beep', 'boop', 'bar'], ['foo'] ]
4. List:difference
Function realization : Return to two iterables Differences between .
Reading : establish b Set , Use a The list derivation of is not in _b The elements in .
def difference(a, b):
_b = set(b)
return [item for item in a if item not in _b]
give an example :
difference([1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 4]) # [3]
5. List:flatten
Function realization : One off consolidated list .
Reading : Use nested lists to extract each value of a sublist .
def flatten(lst):
return [x for y in lst for x in y]
give an example :
flatten([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]]) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]

6. Math:digitize
Function realization : Decompose a number into digits .
Reading : take n Use... After charring map() Function combination int Complete the transformation
def digitize(n):
return list(map(int, str(n)))
give an example :
digitize(123) # [1, 2, 3]
7. List:shuffle
Function realization : Randomly shuffle the list elements .
Reading : Use Fisher-Yates Algorithm reorders list elements .
from copy import deepcopy
from random import randint
def shuffle(lst):
temp_lst = deepcopy(lst)
m = len(temp_lst)
while (m):
m -= 1
i = randint(0, m)
temp_lst[m], temp_lst[i] = temp_lst[i], temp_lst[m]
return temp_lst
give an example :
foo = [1,2,3]
shuffle(foo) # [2,3,1] , foo = [1,2,3]
8. Math:clamp_number
Function realization : The digital num The clamp is made by a and b In the range specified by the boundary value .
Reading : If num To the full extent , return num; otherwise , Returns the closest number in the range .
def clamp_number(num,a,b):
return max(min(num, max(a,b)),min(a,b))
give an example :
clamp_number(2, 3, 5) # 3
clamp_number(1, -1, -5) # -1

9. String:byte_size
Function realization : Returns the number of bytes in the string .
Reading : Use string.encode(‘utf-8’) Decode the given string , Return length .
def byte_size(string):
return len(string.encode('utf-8'))
give an example :
byte_size('') # 4
byte_size('Hello World') # 11
10. Math:gcd
Function realization : Calculate the greatest common factor of several numbers .
Reading : Use reduce() and math.gcd Implement... On a given list .
from functools import reduce
import math
def gcd(numbers):
return reduce(math.gcd, numbers)
give an example :
gcd([8,36,28]) # 4
That's all 30 Secology python All kinds of tricks . What about? , Is there any new inspiration for some common operations , besides , There are many other skills that you can learn slowly , I hope it will help you .
https://github.com/30-seconds/30-seconds-of-python
