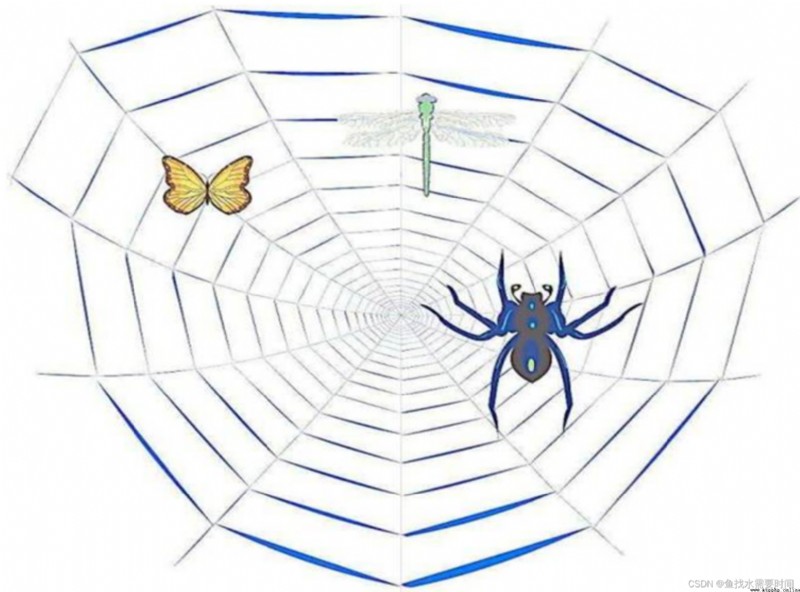
If we compare the Internet to a big spider web , The data on that computer is a prey on the spider web , And the crawler program is a small
spider , Grab the data you want along the cobweb
explain 1: Through a program , according to Url(http://www.taobao.com) Crawl web pages , Get useful information
explain 2: Use the program to simulate the browser , To send a request to the server , Get response information
Crawl to the web : Crawl the entire web page Contains all the content in the web page
Parsing data : Put the data you get in the web page To analyze
difficulty : The game between reptiles and anti reptiles
Data analysis / Manual data sets
Social software cold start
Public opinion monitoring
Competitor monitoring
Universal crawler :
example
Baidu 、360、google、sougou Wait for the search engine ‐‐‐ Bole Online
function
Access page ‐> Fetching the data ‐> data storage ‐> Data processing ‐> Provide retrieval services
robots agreement
A conventional agreement , add to robots.txt file , Explain what content on this website can't be captured , Not limiting His writing Reptiles do not need to comply
Website ranking (SEO)
1. according to pagerank Algorithm values are ranked ( Refer to website traffic 、 Click through rate and other indicators )
2. Baidu bidding ranking
shortcoming
1. Most of the captured data is useless
2. Unable to accurately obtain data according to the needs of users
Focus on reptiles
function
According to the demand , Implement crawler , Grab the data you need
Design thinking
1. Make sure you want to climb url
How to get Url
2. Simulate browser through http Agreement to access url, Get the information returned by the server html Code
How to access the
3. analysis html character string ( Extract the required data according to certain rules )
How to parse
User‐Agent:
agent IP:
Verification code access
Code platform
Cloud coding platform
Super
Loading web pages dynamically The website returns js data Not the real data of the web page
Data encryption
urllib.request.urlopen() Simulate the browser to send a request to the server
response Data returned by the server
response The data type of is HttpResponse
byte ‐‐> character string decode decode
character string ‐‐> byte code encode
read() Read binary in byte form Expand :rede(5) Returns the first few bytes
readline() Read a line
readlines() Read line by line Until the end
getcode() Get status code
geturl() obtain url
getheaders() obtain headers
urllib.request.urlretrieve()
Basic use :
Crawl Baidu homepage source code :
# Use urllib Get the source code of Baidu home page
import urllib.request
# Define a url
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
# Simulate the browser to send a request to the server
response = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
# Get the source code of the page in the response
# read Method , What is returned is binary data in byte form
# Convert binary data to string
# Binary system =》 character string decode decode(' Coding format '), The encoding format is on the page head label meta Of charset attribute
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
One type and six methods :
import urllib.request
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
response = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
# response yes HTTPResponse type
# print(type(response))
# Read byte by byte
# content = response.read()
# Read a line
# content = response.readline()
# content = response.readlines()
# Return status code , If it is 200, It proves that there is nothing wrong
# print(response.getcode())
# Return visited url Address
# print(response.geturl())
# Get some status information
print(response.getheaders())
download :
import urllib.request
# Download a web page
# url_page = 'http://www.baidu.com'
# urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_page, 'baidu.html')
# Download the pictures
# url_img = 'https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png'
# urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=url_img, filename='csdn.jpg')
# Download Video
url_video = 'https://vd2.bdstatic.com/mda-jmsy151cd1ijyz3r/hd/mda-jmsy151cd1ijyz3r.mp4?v_from_s=hkapp-haokan-hnb&auth_key=1656516999-0-0-1fcd521c8a93ff8141ca1645aa7c315c&bcevod_channel=searchbox_feed&pd=1&cd=0&pt=3&logid=0398986023&vid=3985750168738470460&abtest=102784_2-102836_3-102982_3-3000232_2&klogid=0398986023'
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_video, 'test.mp4')
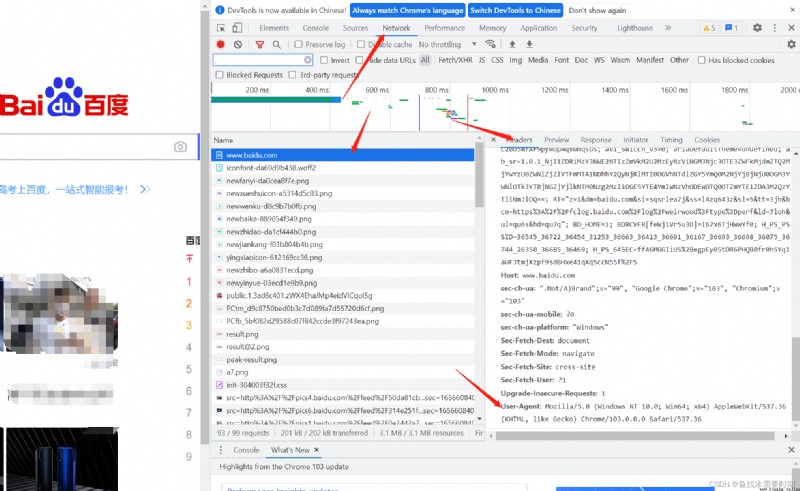
UA Introduce :User Agent The Chinese name is user agent , abbreviation UA, It's a special string header , Enables the server to identify the operating system and version used by the client 、CPU type 、 Browsers and versions . Browser kernel 、 Browser rendering engine 、 Browser language 、 Browser plug-ins, etc
grammar :request = urllib.request.Request()
Example :
import urllib.request
url = 'https://www.baidu.com'
# headers See the picture below for details
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
# Because of the problem of parameter order , You need keywords to pass parameters
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
The origin of coding :
Because computers are invented by Americans , therefore , At the very beginning 127 Characters are encoded into the computer , That is to say, the English letters in upper and lower case 、 Numbers and symbols , This code table is called ASCII code , Like capital letters A The code of is 65, Lowercase letters z The code of is 122. But to deal with Chinese, obviously one byte is not enough , At least two bytes required , And not with ASCII Encoding conflict , therefore , China made GB2312 code , It's used to compile Chinese . What you can think of is , There are hundreds of languages all over the world , Japan compiles Japanese into Shift_JIS in , South Korea compiles Korean into Euc‐kr in , Every country has its own standards , There will inevitably be conflicts , The result is , In a mixed language text , There's going to be a mess . therefore ,Unicode emerge as the times require .Unicode Unify all languages into one set of codes , So there won't be any more confusion . Unicode Standards are evolving , But the most common is to use two bytes to represent a character ( If you want to use very remote characters , Need 4 Bytes ). Modern operating systems and most programming languages directly support Unicode.
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
url = 'https://www.baidu.com/s?wd='
# Change the parameter to ASCII code
url += url + urllib.parse.quote(' Jay Chou ')
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
url = 'https://www.baidu.com/s?'
# Use dictionary type code to pass parameters
data = {
'wd': ' Jolin Tsai ',
'sex': ' Woman '
}
url += urllib.parse.urlencode(data)
print(url)
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
import json
url = 'https://fanyi.baidu.com/sug'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
data = {
'kw': 'hello'
}
# post The requested parameters must be encoded
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8')
# post The requested parameters should be placed in the customized parameters of the request object
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, data=data, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
# String to json object
obj = json.loads(content)
print(obj)
post and get difference :
get The parameters of the request mode must be encoded , The parameter is spliced to url Back , After coding, there is no need to call encode Method
post The parameters of the request mode must be encoded , Parameters are placed in the method customized by the request object , After coding, you need to call encode Method
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
import json
url = 'https://fanyi.baidu.com/v2transapi?from=en&to=zh'
# Browser console view header
headers = {
'Cookie': 'BIDUPSID=3223FE11042DAD864DA852D876FDDFA9; PSTM=1654091563; BAIDUID=3223FE11042DAD86DD7C657D63E1E52C:FG=1; APPGUIDE_10_0_2=1; SOUND_PREFER_SWITCH=1; REALTIME_TRANS_SWITCH=1; HISTORY_SWITCH=1; FANYI_WORD_SWITCH=1; SOUND_SPD_SWITCH=1; BDUSS=HExR09IbHgtdi1ibEtmblo2MVdRdHdyelc5UGk3Q1MyYk1mWUZJQW9pWEtCYjlpRVFBQUFBJCQAAAAAAAAAAAEAAAABrg80x-O-~dK7ysDI4cfp2LwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAMp4l2LKeJdiM; BDUSS_BFESS=HExR09IbHgtdi1ibEtmblo2MVdRdHdyelc5UGk3Q1MyYk1mWUZJQW9pWEtCYjlpRVFBQUFBJCQAAAAAAAAAAAEAAAABrg80x-O-~dK7ysDI4cfp2LwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAMp4l2LKeJdiM; BDORZ=B490B5EBF6F3CD402E515D22BCDA1598; delPer=0; PSINO=1; H_PS_PSSID=36545_36722_36454_31253_36663_36413_36691_36167_36693_36698_36075_36744_26350_36685_36469; BA_HECTOR=2081850k2l24ag24011hbrb0l14; ZFY=eQSkt9DtBzoEZ2DdNJW5f:BgPs:BesKMBKOGsMVfN7H5c:C; Hm_lvt_64ecd82404c51e03dc91cb9e8c025574=1654092726,1656597526; Hm_lpvt_64ecd82404c51e03dc91cb9e8c025574=1656597526; ab_sr=1.0.1_ZjlmNzdiNWNjYTIwYTY4NTcxNGY3NDk3NjE1NGY3YmZlNTdjMjdiMzhkYjJiZWE3ZjcyOGI0NGMwNjZkYWU1YzgyMmQzMjU0ZjQ2NjBhMzI0ZTVlMDk2MjZiMjAzMDE5ZjQ2NTA0ODNlYWQ2NjEzMTk5ZWRhMmZkZTE2NWJmZDc1MDkyNDQxNTUwMzk1YjczOTdiNDUxYTJkMjlkZDA1ZmM1MzVkNWIzYjJkYWQ2Y2Q5ZmNiODk5MWZkNzBkYjUz'
}
data = {
'from': 'en',
'to': 'zh',
'query': 'hello',
'transtype': 'realtime',
'simple_means_flag': '3',
'sign': '54706.276099',
'token': '406f9ef9798def66b41a2d8f61f5c96a',
'domain': 'common'
}
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8')
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, data=data, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
obj = json.loads(content)
print(obj)
# python Object to json character string ensure_ascii=False Ignore character set encoding
s = json.dumps(obj,ensure_ascii=False)
print(s)
A simple example :
import urllib.request
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/j/chart/top_list?type=24&interval_id=100%3A90&action=&start=0&limit=20'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url,headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(content)
# Save the contents in a file
# open By default gbk code , If you want to save Chinese characters , Specify the encoding format as utf-8
# fp = open('douban.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
# fp.write(content)
# fp.close()
# Another way of writing
with open('douban1.json','w', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.write(content)
Get the data from the first page of Douban to the specified number of pages
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
# Create custom request
def create_request(page):
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/j/chart/top_list?type=24&interval_id=100%3A90&action=&'
# Calculate the number of start and end entries of the current page data
start = (page - 1) * 20
limit = 20
data = {
'start': start,
'limit': limit
}
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
url += urllib.parse.urlencode(data)
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
return request
# Get request content
def get_content(request):
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
return content
# Write each content to a file
def down_load(content, page):
with open('douban_' + str(page) + '.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.write(content)
fp.close()
# Program entry , You can write it or not
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_page = 1
end_page = int(input(" Please enter the number of pages :"))
for i in range(start_page, end_page + 1):
request = create_request(i)
content = get_content(request)
down_load(content, i)
Crawling KFC Store information ( Page by page )
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
# Custom request
def create_request(page):
url = 'http://www.kfc.com.cn/kfccda/ashx/GetStoreList.ashx?op=cname'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
data = {
'cname': ' Beijing ',
'pid': '',
'pageIndex': page,
'pageSize': 10,
}
data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8')
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers, data=data)
return request
# Get request content
def get_content(request):
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
return response.read().decode('utf-8')
# Write content to local file
def down_load(page, content):
with open('KFC_' + str(page) + '.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(content)
f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_page = 1
end_page = int(input(' Please enter the number of pages :'))
for i in range(start_page, end_page + 1):
request = create_request(i)
content = get_content(request)
down_load(i, content)
brief introduction :
HTTPError Class is URLError Subclasses of classes
The imported package urllib.error.HTTPError urllib.error.URLError
http error :http An error is an error message added when the browser cannot connect to the server . Guide and tell the viewer what went wrong with the page .
adopt urllib When the request is sent , It may fail to send , If you want to make your code more robust at this time , Can pass try‐
except To catch exceptions , There are two types of exceptions ,URLError\HTTPError
import urllib.request
import urllib.error
url = 'https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43847283/article/details/1255564151'
# url = "http://adad121a.com"
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
try:
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
print(response)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
except urllib.error.HTTPError:
print(" Wrong address ")
except urllib.error.URLError:
print(" Wrong address ")
Some websites will put cookie Put in header To request ,cookie It stores the information after login . You must bring it with you when you ask cookie Can request
urllib.request.urlopen(url)
urllib.request.Request(url,headers,data)
Handler
import urllib.request
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
# obtain headler object
handler = urllib.request.HTTPHandler()
# obtain opener object
opener = urllib.request.build_opener(handler)
# call open Method
response = opener.open(request)
print(response.read().decode('utf‐8'))
Common functions of agents ?
Break through yourself IP Access restrictions , Visit foreign sites .
Visit internal resources of some units or groups
Improve access speed
Hide the truth IP
2. Code configuration agent
establish Reuqest object
establish ProxyHandler object
use handler objects creating opener object
Use opener.open Function to send a request
import urllib.request
import random
url = 'http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=ip'
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers)
# Define a proxy pool
proxies = [{
"http": "127.0.0.1:1"}, {
"http": "127.0.0.1:2"}]
# Randomly take out a proxy ip
proxie = random.choice(proxies)
handler = urllib.request.ProxyHandler(proxies=proxies)
opener = urllib.request.build_opener(handler)
response = opener.open(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf‐8')
print(content)
with open('dl.html', 'w', encoding='utf‐8')as fp:
fp.write(content)
 Computer Graduation Design Python+djang Handan Landmark Food Tour Guide Platform (source code + system + mysql database + Lw document)
Computer Graduation Design Python+djang Handan Landmark Food Tour Guide Platform (source code + system + mysql database + Lw document)
項目介紹我的家鄉是邯鄲市.邯鄲市我國為數不多的3000年沒有
 Computer graduation design Python+django furniture sales mall website (source code + system + mysql database + Lw document)
Computer graduation design Python+django furniture sales mall website (source code + system + mysql database + Lw document)
Project IntroductionWith the d