Click on the above “Python Crawler and data mining ”, Focus on
reply “ Books ” You can get a gift Python From the beginning to the advanced stage 10 This ebook
today
Japan
chicken
soup
There is no long-term plan for self-care , Empty knowledge returns to the old forest .
Life is too short , Learn quickly Python
Python It is one of the widely used programming languages today , In Data Science 、 Scientific Computing 、Web Development 、 Game development and building desktop graphical interface have applications in various fields .Python Because of its practicability in various fields 、 And Java、C and C++ And other programming languages, and commands similar to English .
If you too Python Learning enthusiasts , So today's story 13 Tips , It smells good !
List related 6 Operations , Introduce the following ;
Suppose we were Python There are two lists in , We want to merge them into a dictionary , One of the items in the list is used as the key of the dictionary , The other is the value . It's in use Python A very common problem when writing code .
But to solve this problem , We need to consider several limitations , For example, the size of two lists , The types of items in both lists , And whether there are duplicate items , Especially the project we will use As a key . We can use things like zip Such built-in functions to overcome this problem .
keys_list = ['A', 'B', 'C']
values_list = ['blue', 'red', 'bold']
# Yes 3 There are two ways to convert these two lists into dictionaries
# 1. Use Python zip、dict function
dict_method_1 = dict(zip(keys_list, values_list))
# 2. Use... With dictionary derivation zip function
dict_method_2 = {key:value for key, value in zip(keys_list, values_list)}
# 3. Recycling zip function
items_tuples = zip(keys_list, values_list)
dict_method_3 = {}
for key, value in items_tuples:
if key in dict_method_3:
pass
else:
dict_method_3[key] = value
print(dict_method_1)
print(dict_method_2)
print(dict_method_3)give the result as follows :

When we have two or more lists , We want to collect them all in a big list , All the first items of the smaller list form the first list in the larger list .
for example , If I have 4 A list [1,2,3]、['a','b','c']、['h','e','y'], and [4,5,6], We want to create a new list for these four lists ; It will be [[1,'a','h',4], [2,'b','e',5], [3,'c','y',6]] .
def merge(*args, missing_val = None):
max_length = max([len(lst) for lst in args])
outList = []
for i in range(max_length):
outList.append([args[k][i] if i < len(args[k]) else missing_val for k in range(len(args))])
return outList
merge([1,2,3],['a','b','c'],['h','e','y'],[4,5,6])give the result as follows :
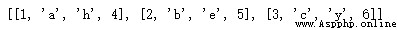
The next set of daily list tasks is sorting tasks . According to the data type of the items contained in the list , We'll sort them in a slightly different way . Let's start by sorting the dictionary list .
dicts_lists = [
{
"Name": "James",
"Age": 20,
},
{
"Name": "May",
"Age": 14,
},
{
"Name": "Katy",
"Age": 23,
}
]
# Method 1
dicts_lists.sort(key=lambda item: item.get("Age"))
# Method 2
from operator import itemgetter
f = itemgetter('Name')
dicts_lists.sort(key=f)give the result as follows :
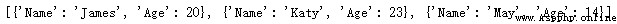
We often face lists containing strings , We need to be alphabetical 、 Sort these lists by length or any other factor we want or need for our application .
Now? , I should mention that these are direct ways to sort the list of strings , But sometimes you may need to implement a sorting algorithm to solve this problem .
my_list = ["blue", "red", "green"]
# Method 1
my_list.sort()
my_list = sorted(my_list, key=len)
# Method 2
import locale
from functools import cmp_to_key
my_list = sorted(my_list, key=cmp_to_key(locale.strcoll))give the result as follows :
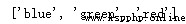
Sometimes , We may want to / You need to use one list to sort another list . therefore , We will have a list of numbers ( Indexes ) And a list that I want to sort using these indexes .
a = ['blue', 'green', 'orange', 'purple', 'yellow']
b = [3, 2, 5, 4, 1]
sortedList = [val for (_, val) in sorted(zip(b, a), key=lambda x: x[0])]
print(sortedList)give the result as follows :
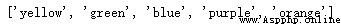
If you give a list and map it to a dictionary . in other words , I want to convert my list into a dictionary with numeric keys , What should be done ?
mylist = ['blue', 'orange', 'green']
#Map the list into a dict using the map, zip and dict functions
mapped_dict = dict(zip(itr, map(fn, itr)))Dictionary related 2 Operations , Introduce the following ;
Suppose we have two or more dictionaries , And we want to merge them all into a dictionary with unique keys .
from collections import defaultdict
def merge_dicts(*dicts):
mdict = defaultdict(list)
for dict in dicts:
for key in dict:
res[key].append(d[key])
return dict(mdict)A very common dictionary task is if we have a dictionary and want to reverse its keys and values . therefore , The key will become the value , And the value will become the key .
When we do this , We need to make sure I don't have duplicate keys , Values can be repeated , But the key cannot , And make sure that all new keys are hashable .
my_dict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
# Method 1
my_inverted_dict_1 = dict(map(reversed, my_dict.items()))
# Method 2
from collections import defaultdict
my_inverted_dict_2 = defaultdict(list)
{my_inverted_dict_2[v].append(k) for k, v in my_dict.items()}
print(my_inverted_dict_1)
print(my_inverted_dict_2)give the result as follows :
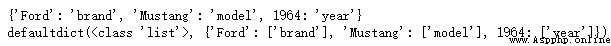
String related 3 Operations , Introduce the following ;
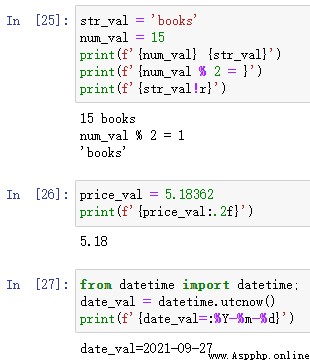
Formatting strings can be the first task you need to do almost every day . stay Python There are several ways to format strings in ; My favorite is to use f character string .
str_val = 'books'
num_val = 15
print(f'{num_val} {str_val}')
print(f'{num_val % 2 = }')
print(f'{str_val!r}')
price_val = 5.18362
print(f'{price_val:.2f}')
from datetime import datetime;
date_val = datetime.utcnow()
print(f'{date_val=:%Y-%m-%d}')give the result as follows :
A very common task I have to perform many times before is , Check whether the string is in the string list .
addresses = ["123 Elm Street", "531 Oak Street", "678 Maple Street"]
street = "Elm Street"
# Method 1
for address in addresses:
if address.find(street) >= 0:
print(address)
# Method 2
for address in addresses:
if street in address:
print(address)give the result as follows :

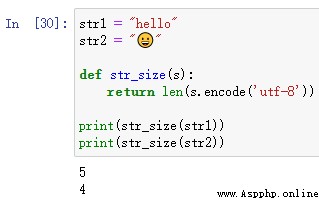
Sometimes , Especially when building memory critical applications , We need to know how much memory our string uses . Fortunately, , This can be done quickly with one line of code .
str1 = "hello"
str2 = ""
def str_size(s):
return len(s.encode('utf-8'))
print(str_size(str1))
print(str_size(str2))give the result as follows :
With the input / Output operation related 2 Operations , Introduce the following ;
In data science and many other applications , We often need to read data from or write data to files . But to do that , We need to check if the file exists . therefore , Our code will not terminate due to errors .
# Method 1
import os
exists = os.path.isfile('/path/to/file')
# Method 2
from pathlib import Path
config = Path('/path/to/file')
if config.is_file():
passAnother very common file interaction is parsing data from spreadsheets . Fortunately, , We have CSV Module to help us perform the task effectively .
import csv
csv_mapping_list = []
with open("/path/to/data.csv") as my_data:
csv_reader = csv.reader(my_data, delimiter=",")
line_count = 0
for line in csv_reader:
if line_count == 0:
header = line
else:
row_dict = {key: value for key, value in zip(header, line)}
csv_mapping_list.append(row_dict)
line_count += 1friends , Practice it quickly ! If in the process of learning , Have encountered any Python problem , Welcome to add my friend , I'll pull you in Python The learning exchange group discusses learning together .

------------------- End -------------------
Excellent articles in the past are recommended :
How to set a group of lists ( More than three , Different types of values ) Save as txt file
Python In the process of web crawler , When building a network request , Parameters `stream=True` Use
Inventory Python A hole in the list when deleting
Hands teach you how to use Python Extract express information

Welcome to give the thumbs-up , Leaving a message. , forward , Reprint , Thank you for your company and support
Want to join Python Learning group, please reply in the background 【 Enter into Group 】
All rivers and mountains are always in love , Order one 【 Looking at 】 OK?