It takes two days , Finally sorted out this article . Mainly strings 、 Basic usage of lists and dictionaries , Including definition 、 characteristic 、 Add, delete, modify and check common functions and basic grammar .
Catalog
character string
1. String definition & characteristic
2. String common operations
Formatted string
Specify the minimum output width
Specify alignment
Specify decimal precision
3. String common functions
center() function
count() function
endwith() function
isdigit() function
join () function
replace() function
split () function
list
1. Definition of list & characteristic
2. Add, delete and check the list 、 Sort
increase :
append () function
extend() function
insert() function
Delete :
pop() function
remove() function
del() function
clear() function
check :
index() function
count() function
in
Sort the list & reverse
sort () function
sorted() function
reverse() function
Slicing and step size
section :
step
Dictionaries
Definition & characteristic
Dictionary creation
Look up the dictionary
increase :
Delete :
Nesting of dictionaries ( Link attached )
1. A string is a Orderly The set of characters in the
2. Define character sets from left to right , Subscript from 0 Start visiting
3. Can be carried out section operation

4. String cannot be modified
Conversion specifiers are placeholders , The specific content will be replaced by the value of the following expression .
Use repr() The function converts an expression to a string
%s Use str() Function to convert an expression to a stringYou can also specify the minimum output width , such as :
%2d Indicates that the integer width of the output is at least 2;
%10s Indicates that the output string is at least 10.
When the actual width of the data Less than the specified width when , Will be in The left side is filled with spaces , When the actual width of the data is greater than the specified width , Specifying the width loses its original function .
python The output data is aligned to the right by default . You can also add a sign before the minimum width to change the alignment .
Some notes :
- For integers , When specifying left alignment , Make up on the right 0 It doesn't work , Because it changes the value of an integer .
- For decimals , The above three symbols can exist at the same time .
- For strings , Only use
-sign , Because symbols have no meaning for Strings , And complement 0 Will change the value of the string .
python It is allowed to specify the number of digits after the decimal point .
The precision value needs to be placed after the minimum width , Intermediate use Order number . separate ; You can also not write the minimum width , Write precision only . The specific format is as follows :
%m.nf
%.nfm Represents the minimum width ,n Indicates output accuracy ,. Must exist .
as follows :
f = 3.141592653
# Minimum width is 8, After the decimal point 3 position
print("%8.3f" % f)
# Minimum width is 8, After the decimal point 3 position , Left complement 0
print("%08.3f" % f)
# Minimum width is 8, After the decimal point 3 position , Left complement 0, Signed
print("%+08.3f" % f)Running results :

Returns a length of width、 Use... On both sides fillchar( A single character ) Filled string .
grammar :str.center(width,"fillchar")
Be careful : Quotation marks cannot be omitted
Look up a string , The number of times a character appears
grammar :str.count(sub,start,end)
sub: Search for substrings
start: The index value of the subscript to start the search . The default is the first character , The first character index value is 0.
end: The index value of the subscript that ends the search .
Determine whether the string ends with the specified character or string
grammar :str.endswith("suffix", start, end) or str[start,end].endswith("suffix")
The return value is of boolean type (True,False)
startwith() function
Determine whether the string starts with the specified character or string
grammar :str.startwith("suffix", start, end)
find () function
To find the character , There is a return subscript , There is no return -1
grammar :str.find(str,start,end)
Determine whether a string is composed of only numbers
grammar :str.isdigit( )
String concatenation
grammar :str.join(item)
Be careful :item Represents a member , There must be only one member in brackets , such as ','.join('a','b') This kind of writing doesn't work .
Replace a value of the original string
grammar :str.replace( Old value , New value , Number of replacements )
Separate the strings according to the separator
grammar :str.split(sep,num)
sep: Separator , Don't write sep when , Default means Space ,\n,\t Delimited string
num: Number of separations , Yes sep Press sep Value separation of
The list is an ordered , Modifiable ( Add or delete check change ), Elements are separated by commas , Sequence enclosed in brackets .
[ ] Separated by commas , By index , Store all kinds of data types , Each position represents an element
Can store multiple values , Define list elements from left to right , Subscript from 0 Start visiting , The value corresponding to the specified index position can be modified
Append new elements to the end of the list
grammar :list.append(obj)
obj: Objects added to the end of the list
Appends multiple values from another sequence at once at the end of the list ( Extend the original list with the new list )
grammar :list.extend(seq)
seq : List of elements , It must be an iterative sequence
Inserts the specified object into the specified location in the list
grammar :list.insert(index, obj)
index : object obj Index location to insert .
obj : To insert an object in the list
Used to delete an element in the list , Default last element , And returns the value of that element
grammar :list.pop( obj=list[n] )
obj : To delete an object in the list
n: Index subscript
Be careful :obj Is an optional parameter
Delete a value in the list ( Specify the element name ) The first match of
grammar :list.remove(obj)
obj : Objects to be removed from the list
Delete the whole list or some data in the list ,del yes Python The built-in function , Not unique to the list
Clear the elements in the current list
grammar :list.clear()
Check if there is a substring in the string str , If specified beg( Start ) and end( end ) Range , Then check whether it is included in the specified range , The method and python find() The method is the same , Just if str be not in string An exception will be reported in .
grammar :str.index(str, beg=0, end=len(string))
str : Specifies the string to retrieve
beg : Start index , The default is 0.
end : End index , The default is the length of the string
Count , Returns the number of elements to count in the list
grammar :str.count(sub,start=0,end=len(string))
sub -- Search for substrings
start -- Where the string starts searching . The default is the first character , The first character index value is 0.
end -- Where to end the search in the string . The index of the first character in the character is 0. Default to the last position of the string .
Find out if the element is in the list , Back in true, Otherwise return to false
grammar :list.sort()
Sort order : Capitalization 、 A lowercase letter 、 chinese ( Numbers are sorted by size )
Be careful : This method will change a Oneself
a = [7,5,9,3]
# True In reverse order ,False In the positive order
a.sort(reverse = False)
print(a)
a.sort(reverse = True)
print(a)
[3, 5, 7, 9]
[9, 7, 5, 3]
Sort , With this method, the sorted list can be assigned to other lists , That is to say, the original list value will not change .
a = [7,5,9,3]
# reverse by True The reverse ,reverse by False positive sequence
b = sorted(a,reverse=True)
print(b)
b = sorted(a,reverse=True)
print(b)
# The original list value will not change
print(a)
[9, 7, 5, 3]
[9, 7, 5, 3]
[7, 5, 9, 3]
Invert the elements in the list
a = [11,23,45,7]
a.reverse()
print(a)
[7, 45, 23, 11]
Definition :
Get a data element by specifying a subscript , Or get a set of elements of a sequence by specifying a subscript range , This way of accessing a sequence is called slicing .
grammar :
[start:end:step]
start: Starting index , from 0 Start
end: End index , however end-1 Is the actual index value
step: step , Step is timing , From left to right . When the step size is negative , Reverse value
Be careful The result of the slice does not contain the end index , That is, it doesn't include the last one ,-1 Represents the last position index of the list ,
Similar to string , It's also front closed and back open
Two slicing methods :
From left to right :
list[3:-1:2]From 0 The subscript starts fetching , Take it from left to right , The interval step is 2.
From right to left :
list[3:-2:-1]-1 It means taking... From right to left , In steps of 1
Intermittently fetch the specified number , Take the head, not the tail
grammar :list[start:end:step]
list[1:]: It means to get the last number
list[1:-1]: It means getting the penultimate number , And contains the penultimate number
The dictionary is Python Provides a common data structure , It is used for Store data with mapping relationship . A dictionary holds two sets of data , One set of data is Key data , go by the name of key; Another set of data It can be done by key To visit , go by the name of value.
dic={key1:value1,key2:value2}
: To the left of the colon is key, On the right is value
characteristic
1.key:value structure
2.key Must be immutable data type ( character string 、 Numbers ), Must be unique
3.value There can be multiple 、 Modifiable 、 Not the only one
4. disorder
5. Fast query speed , And not affected by the size of the dictionary
1. Using functions dict Create dictionaries from other mappings or sequences of key value pairs
items=[('name','Tom'),('age',18)]
d=dict(items)
print(d)
# The result is {'name': 'Tom', 'age': 18}
# If not for dict Function passes in data , An empty dictionary will be created
t=dict()
print(t)
# The result is {}
2. Specify keyword parameters to create a dictionary
d=dict(name='swamm',age=18)
print(d)
# The result is {'name':'swamm','age':18}
dic['key'] = value
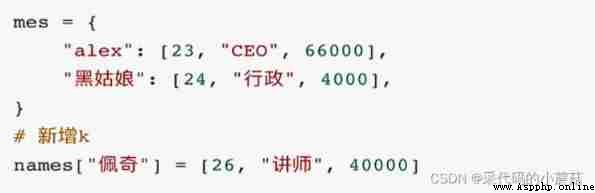
setdefault set default
pop Delete the specified key
del Delete the specified key
popitem Random delete
clear Empty dict

Change :
update: If key There is... In the dictionary , new value Will replace the original value Value , If it doesn't exist , Then add a new value .
check :
see key Is it in the dictionary :key in dict
dic.keys() Print all key value
dic.values () Print all value value
dic.items() Display the dictionary as a list
get() function
Get the key value , Print if you have , If there is no error
Add : The loop of the list
for k in dic:
print(k) # Print k
print(k,dic[k]) #k and value Print together
len(dic) Find the length
len() Methods can also be used for lists 、 character string
You can store lists in dictionaries , Store the dictionary in the list , Store dictionaries in dictionaries and so on .python Almost all data types in , Can be saved in a dictionary .
Click the link below for details :
python Dictionary nesting
Due to my limited ability , There are some omissions in the article , If there is an error , Please correct me more .