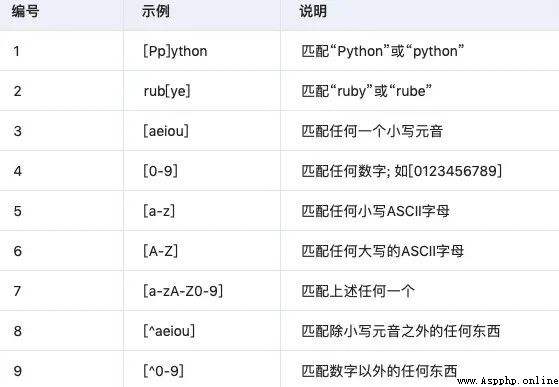
Regular expressions are for strings ( Include normal characters ( for example ,a To z Between the letters ) And special characters ( be called “ Metacharacters ”)) A logical formula for operation , It is to use some specific characters defined in advance 、 And the combination of these specific characters , Form a “ Rule string ”, This “ Rule string ” A filter logic used to express strings . Regular expressions are a text pattern , This pattern describes one or more strings to match when searching for text .
It's all official instructions , The blogger's own understanding is ( For reference only ): By specifying some special character matching rules in advance , These characters are then combined to match a variety of complex string scenarios . For example, today's crawlers and data analysis , String checking and so on need to use regular expressions to process data .
python The regular expression of re Module :
re Module enable Python The language has all the regular expression functions .
re The module also provides functions that are fully consistent with the functions of these methods , These functions use a pattern string as their first argument .
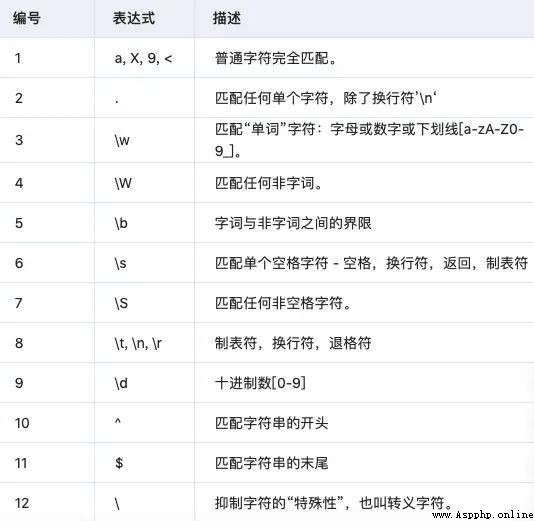
Only from the beginning of a string with pattern Match , Here is the syntax of the function :
re.match(pattern, string, flags = 0)
Here is a description of the parameters :
pattern - This is the regular expression to match .
string - This is a string , It will be searched for patterns that match the beginning of a string .
flags - You can use bitwise OR(|) Different signs specified . These are modifiers , As listed in the table below .
re.match Function returns the matching object on success , Return... On failure None. Use match(num) or groups() Function to match the object to get the matching expression .

Example
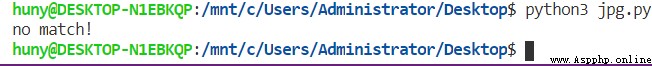
# Not matched from initial position , Returns the None
import re
line = 'i can speak good english'
matchObj = re.match(r'\s(\w*)\s(\w*).*',line)
if matchObj:
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group())
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(1))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(2))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(3))
else:
print('no match!')
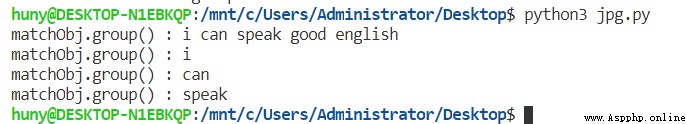
# Match from initial position
import re
line = 'i can speak good english'
matchObj = re.match(r'(i)\s(\w*)\s(\w*).*',line)
if matchObj:
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group())
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(1))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(2))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(3))
else:
print('no match!')
And match() It works the same way , however search() It doesn't match from the beginning , It's about finding the first match from anywhere . Here is the syntax of this function :
re.match(pattern, string, flags = 0)
Here is a description of the parameters :
pattern - This is the regular expression to match .
string - This is a string , It will be searched for patterns that match the beginning of a string .
flags - You can use bitwise OR(|) Different signs specified . These are modifiers , As listed in the table below .
re.search Function returns the matching object on success , Otherwise return to None. Use match Object's group(num) or groups() Function to get the matching expression .
Example
import re
line = 'i can speak good english'
matchObj = re.search('(.*) (.*?) (.*)',line)
if matchObj:
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group())
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(1))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(2))
print('matchObj.group() :',matchObj.group(3))
else:
print('no match!')
Using regular expressions re One of the most important modules is sub.
re.sub(pattern, repl, string, max=0)
This method uses repl Replace all that appears in RE The string of patterns , Replace all that appears , Unless max. This method returns the modified string .
Example
import re
line = 'i can speak good english'
speak = re.sub(r'can','not',line)
print(speak)
speak1 = re.sub(r'\s','',line) # Replace all spaces
print(speak1)
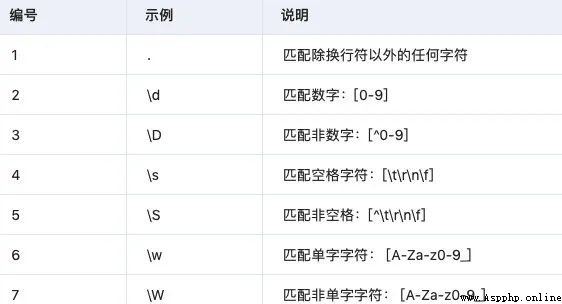
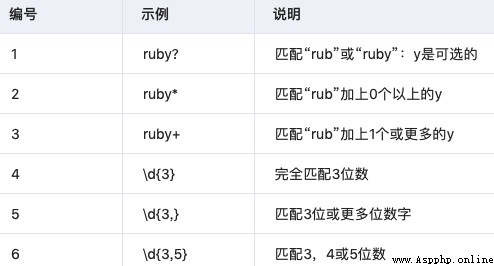
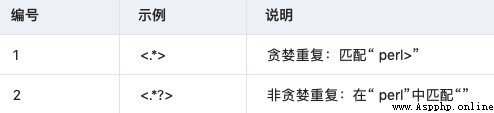
This matches the minimum number of repetitions :
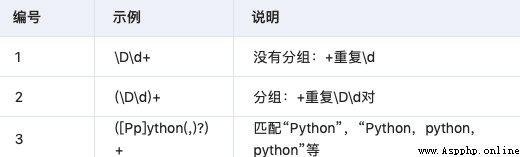
3.5 Parentheses are grouped
3.6 backreferences
Match the previously matched group again
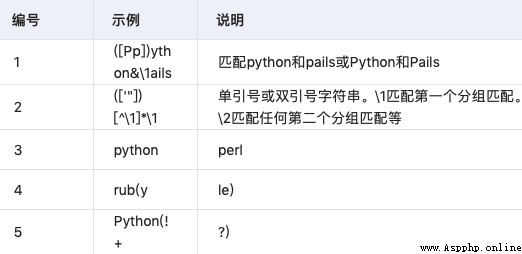
3.7 Anchor point
You need to specify a matching location .
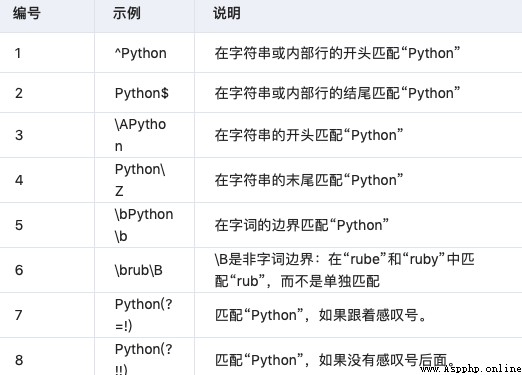
3.8 Special syntax with parentheses

Python That's all for regular expressions , Go to study !!!