Python There are four very common data types in , They are strings , list , Tuples and dictionaries . Here are four basic data types .
Python The handling of strings is very strong , So master some Python Basic operations on strings are very necessary .
String representation
assignment
str='hello'
Fill in the string
str="%d little pigs come out or I'll %s and %s and %s"% (3,'huff','puff','blow down')
transformation
pi =3.14
print'pi = '+str(pi)
toggle case
str.lower()str.upper()
Remove the leading and trailing spaces
str.strip()
Determine whether all characters in a character are letters / Numbers / Space
str.isalpha()
str.isdigit()
str.isspace()
Determine whether a string starts with a substring / ending
str.startswith(' ')
str.endswith()
Find the position of the substring in the string , No return found -1
str.find('th')
String replacement
str.replace('old','new')
Segmentation of strings , return list
str.split('delim')'delim'.join(list)
Coding problem
stay Python2 The default is to use unicode Coded , and windows The default file is gbk code , and linux The default file is utf8 code , So the conversion between codes is essential .
Definition unicode character string
ustr =u'A unicode \u018e string \xf1'
transformation utf-8 code
utfstr = ustr.encode('utf-8')
Conversion meeting unicode code
unistr = unicode(utfstr,'utf-8')
The list is Python It's a very important data structure , It's also a very common data structure .
The representation of the list
initialization
colors = ['red','blue','green']
Expand
# Choose the list fruits Contains characters 'a', And all converted to uppercase
fruits = ['apple', 'cherry', 'bannana', 'lemon']
# ['APPLE', 'BANNANA']
afruits = [ s.upper() for s in fruits if 'a' in s ]
Additive elements
list.append(elem)
stay i Add elements to location elem
list.insert(i,elem)
take list2 Add elements from to list in
list.extend(list2)
Get elements elem The index number of
list.index(elem)
Delete the first element that appears elem
list.remove(elem)
Delete the first i Elements
list.pop(i)
to list Sort
list.sort()
Reverse list
list.reverse()
sorted The basic method
a = [5, 1, 4, 3]
print sorted(a) ## [1, 3, 4, 5]
print sorted(a, reverse=True) ##[5, 4, 3, 1]
print a ## [5, 1, 4, 3]
sorted Sort by keyword
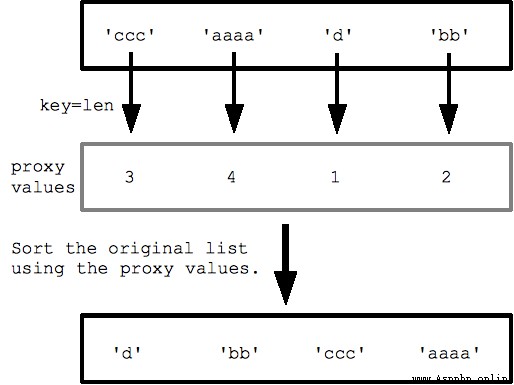
Sort by the length of the string
strs = ['ccc', 'aaaa', 'd', 'bb']
print sorted(strs, key=len) ## ['d', 'bb', 'ccc', 'aaaa'] #len representative len() This function
The details of its function processing are shown in the figure below :
Sort by custom keyword function
# Sort by the last character of the string
strs = ['xc', 'zb', 'yd' ,'wa']
# Define a function , The input is a string , Returns the last character
def MyFn(s):
return s[-1]
# Pass on key=MyFn As a parameter
print sorted(strs, key=MyFn) ## ['wa', 'zb', 'xc', 'yd']
Tuples
A tuple is an array . The size of its elements cannot be changed .
Tuples represent
assignment ( Include the element in parentheses )
tuple = (1, 2, 'hi')
print len(tuple) ## 3
print tuple[2] ## hi
Change the element
# Report errors , Tuple element cannot be changed
tuple[2] = 'bye'
# this works
tuple = (1, 2, 'bye')
The dictionary says
assignment
# We can use {} Start building empty dictionaries , Then add key value pairs to the dictionary in the form of assignment
dict = {}
dict['a'] = 'alpha'
dict['g'] = 'gamma'
dict['o'] = 'omega'
print dict ## {'a': 'alpha', 'o': 'omega', 'g': 'gamma'}
View and change elements
print dict['a'] # see 'a' Corresponding value 'alpha'
dict['a'] = 6 # to 'a' Reassign
if 'z' in dict: print dict['z'] # Avoid reporting mistakes
print dict.get('z') # None (instead of KeyError)
Dictionary method
Get dictionary keywords
dict.keys()
Get the dictionary value
dict.values()
Get dictionary key value pairs ( Returns a tuple list )
dict.items()
Get the key and value in the loop
for k,v in dict.items():
print k, '>', v
Remove elements ( Yes list Also applicable )
dict = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
del dict['b'] # Delete 'b' Elements
print dict ## {'a':1, 'c':3}
Dictionary sort
sorted Method
dict1={'A': 9, 'C': 5, 'B': 1, 'E': 14, 'D': 3, 'G': 3, 'F': 3, 'I': 9, 'H': 7, 'J': 1, 'L': 2, 'O': 8, 'N': 3, 'P': 4, 'S': 10, 'R': 5, 'U': 1, 'T': 17, 'W': 1, 'V': 1}
# Sort dictionaries by value , Returns... As a tuple
print sorted(dict1.iteritems(),key=lambda dict1:dict1[1],reverse=True)
# Sort the dictionary keys , Returns... As a tuple
print sorted(dict1.iteritems(),key=lambda dict1:dict1[0],reverse=False)