Want to try crawling pictures yes , As a result, Chinese garbled code appeared when the picture name was printed .
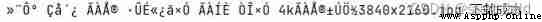
The code looks like this
# -- coding:UTF-8 --
from lxml import etree
import requests
import os
if __name__ == "__main__":
if not os.path.exists(' Beauty pictures '):
os.mkdir(' Beauty pictures ')
headers = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla / 5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64) AppleWebKit / 537.36(KHTML, likeGecko) Chrome / 97.0.4692.71Safari / 537.36Edg / 97.0.1072.55"
}
url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/4kmeinv/'
page_text = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers).text
tree = etree.HTML(page_text)
li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="slist"]/ul/li')
for li in li_list:
img_src = 'http://pic.netbian.com'+li.xpath('./a/img/@src')[0]
print(img_src)
img_name = li.xpath('./a/img/@alt')[0]+'.jpg'
img_data = requests.get(url=img_src,headers=headers).content
img_path = ' Beauty pictures /'+img_name
with open(img_path,'wb') as fp:
fp.write(img_data)
print(img_name,' Download successful ')
Later, I found several methods on the Internet , There are two possible .
1、 Directly in the obtained web source code 'iso-8859-1' code .
page_text = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers).text.encode('iso-8859-1')2、 Do it first where the code is garbled 'iso-8859-1' code , Proceed again 'gbk' decode .
For example, here is a picture with a garbled name , Encode and decode the picture name .
img_name = li.xpath('./a/img/@alt')[0]+'.jpg'
img_name = img_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('gbk')You can go to Baidu for specific coding and decoding principles , Many bloggers write well , Not much here .
Next is how to crawl pictures ?
If the web page is not dynamically loaded , It's easy to resolve to the address of the picture . If so Ajax Dynamic loading , Then you need to use selenium, Dynamic loading will be discussed later .
Take this time as an example , Through the developer tool, we know that the address of the image is stored in <li> In the label .
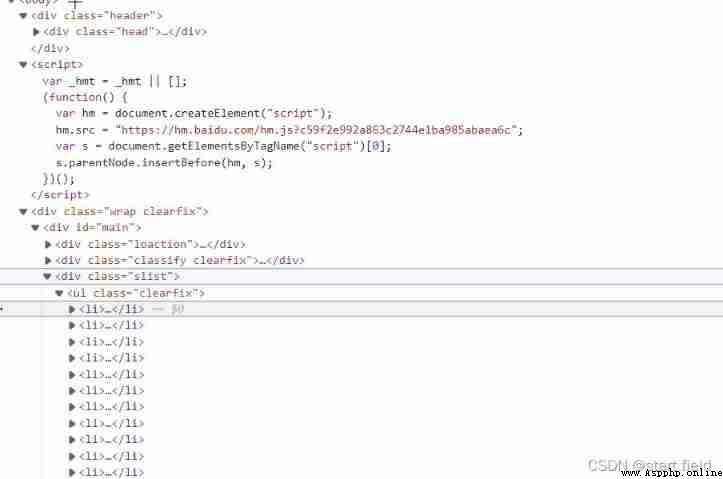
We can go straight through xpath Get all <li> label , Put it in a list .
li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="slist"]/ul/li')
Then analyze the address of the picture one by one , open <li> You can find another one under the label <a> label ,<a> In the label href Attribute is the address of the picture .
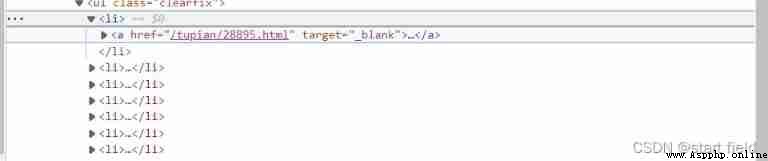
But this address is incomplete , We need to complete it manually .
for li in li_list:
img_src = 'http://pic.netbian.com'+li.xpath('./a/img/@src')[0]Now you have the full address of the picture , Just relax the request for this address , Get binary data , Just save it again
img_data = requests.get(url=img_src,headers=headers).content
Here is the complete code
# -- coding:UTF-8 --
from lxml import etree
import requests
import os
if __name__ == "__main__":
if not os.path.exists(' Beauty pictures '):
os.mkdir(' Beauty pictures ')
headers = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla / 5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64) AppleWebKit / 537.36(KHTML, likeGecko) Chrome / 97.0.4692.71Safari / 537.36Edg / 97.0.1072.55"
}
url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/4kmeinv/'
page_text = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers).text.encode('iso-8859-1')
tree = etree.HTML(page_text)
li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="slist"]/ul/li')
for li in li_list:
img_src = 'http://pic.netbian.com'+li.xpath('./a/img/@src')[0]
img_name = li.xpath('./a/img/@alt')[0]+'.jpg'
# General solution to deal with Chinese garbled code
# img_name = img_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('gbk')
img_data = requests.get(url=img_src,headers=headers).content
img_path = ' Beauty pictures /'+img_name
with open(img_path,'wb') as fp:
fp.write(img_data)
print(img_name,' Download successful ')