近期收到了電子工業出版社贈送的一本網絡安全書籍《python黑帽子》,書中一共24個實驗,今天復現第22個實驗( wmi進程監控),我的測試環境是windows10虛擬機(64位)+conda開發環境+python3.7。這個實驗可以監控windows系統中運行的進程,有助於收集每個進程的啟動信息,便於分析進程的好壞~
1、在py37hack環境中,將python腳本編譯成exe可執行程序
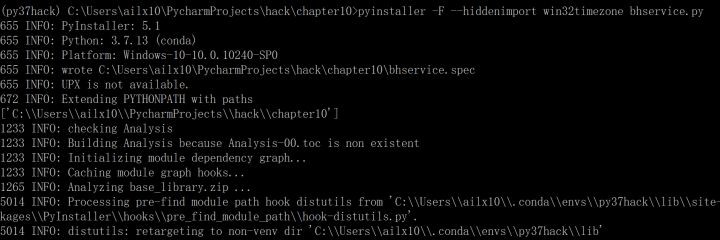
2、進入dist目錄下安裝並運行bhservice服務
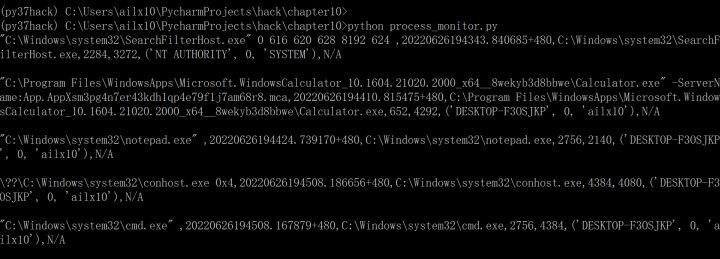
3、上面2個步驟可以忽略,這裡開始利用WMI監控進程,運行monitor腳本,就可以監控之後運行的所有進程,這裡我測試了calc計算器、notepad記事本、cmd命令行,全成功了,這裡可以看到記錄了計算機的用戶名稱、進程PID、還有進程所在文件位置等信息,非常nice ~
4、喝個咖啡,等一會兒,打開腳本所在目錄下的txt文件,查看計算機偷偷做了哪些事,這裡記錄了不少~

參考代碼:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/6/26 7:10 PM
# @Author : ailx10
# @File : process_monitor.py
import os
import sys
import win32api
import win32con
import win32security
import wmi
def log_to_file(message):
with open("process_monitor_log.csv","a") as fd:
fd.write(f"{message}\r\n")
def monitor():
head = "CommandLine,Time,Executable,Parent,PID,PID,User,Privileges"
log_to_file(head)
c = wmi.WMI()
process_watcher = c.Win32_Process.watch_for("creation")
while True:
try:
new_process = process_watcher()
cmdline = new_process.CommandLine
create_date = new_process.CreationDate
executable = new_process.ExecutablePath
parent_pid = new_process.ParentProcessId
pid = new_process.ProcessId
proc_owner = new_process.GetOwner()
privileges = "N/A"
process_log_message = (f"{cmdline},{create_date},{executable},{parent_pid},{pid},{proc_owner},{privileges}")
print(process_log_message)
print()
log_to_file(process_log_message)
except Exception:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
monitor()