import cv2
img = cv2.imread("./edge1.png") # Read the picture
a = []
b = []
def on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN(event, x, y, flags, param):
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
a.append(x)
b.append(y)
cv2.circle(img, (x, y), 3, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
print("[{},{}]".format(a[-1], b[-1])) # Output the coordinates of the last click
cv2.namedWindow("image")
cv2.setMouseCallback("image", on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
design sketch 1 as follows :

There is still room for revision , I modified it in passing
Make it directly mark the coordinates in the picture
The code is as follows :
import cv2
img = cv2.imread("./edge1.png") # Path to picture
a = []
b = []
def on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN(event, x, y, flags, param):
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
xy = "[%d,%d]" % (x, y)
a.append(x)
b.append(y)
cv2.circle(img, (x, y), 3, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.putText(img, xy, (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
1.0, (107, 73, 251), thickness=1) # If you do not want to display the coordinates on the picture, you can annotate the line
cv2.imshow("image", img)
print("[{},{}]".format(a[-1], b[-1])) # Output coordinates in the terminal
cv2.namedWindow("image")
cv2.setMouseCallback("image", on_EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
design sketch 2 as follows :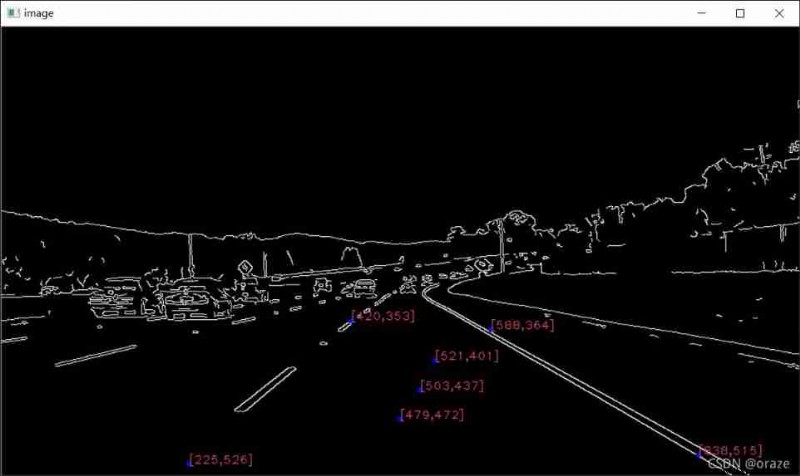
Reference resources here.
 One of the appium tutorials for app automated testing - environment building (appium+python+mumu simulator)
One of the appium tutorials for app automated testing - environment building (appium+python+mumu simulator)
app One of the automated test
 Python tutorial 95 -- Summary of Python knowledge points of Excel operation
Python tutorial 95 -- Summary of Python knowledge points of Excel operation
One 、 demand :1、Excel Preproce