Hello everyone , I'm cabbage . Because of the needs of the project , Studying recently Python The reptiles of . This one is about Python The basic knowledge of , It is also an introductory knowledge point for learning reptiles ! If you get something after reading the article , You can support bloggers three times in a row ~, Hee hee .
int()# Convert to an integer
print(int("123")) # 123
print(int(123.78)) # 123
print(int(False)) # 0
print(int(True)) # 1
It should be noted that : The conversion will fail in the following two cases

float()print(float("123.78")) # 123.78
print(float(123)) # 123.0
print(float(True)) # 1.0
print(float(False)) # 0.0
str()print(str(1))
print(type(str(1)))
print(str(1.0))
print(type(str(1.0)))
print(str(False))
print(type(str(False)))
print(str(True))
print(type(str(True)))
Running results :

bool()# The following operation results are all False
print(bool(0.0)) # Floating point value is 0
print(bool(''))
print(bool("")) # An empty string
print(bool(0)) # Integer value is 0
print(bool({
})) # The dictionary is empty
print(bool([])) # The list is empty.
print(bool(())) # Tuple is empty
Summary : Dictionary type 、 A tuple type 、 When the list type and string are empty ( That is, there is no data ), Convert to boolean type is False; Integer and floating point numbers Values for 0 when , Converting to boolean type is also False; Everything else is True
Let's first look at the operators we need to learn :
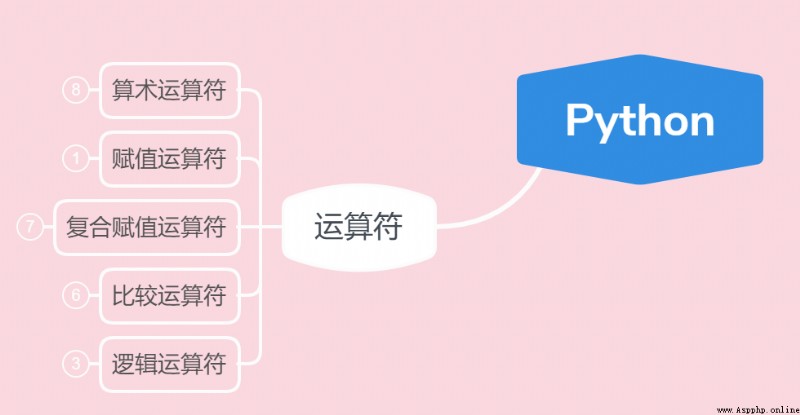
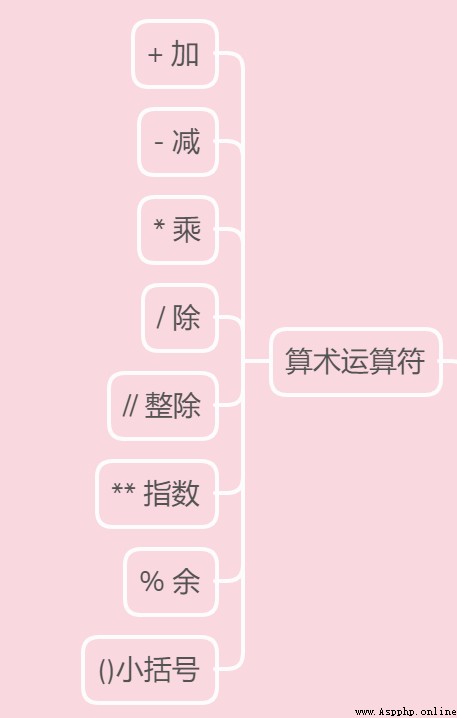
Look at their functions through the code :
a = 10
b = 3
print(a + b) # 13
print(a - b) # 7
print(a * b) # 30
print(a / b) # 3.3333333333333335
print(a // b) # 3
print(a % b) # 1
print(a ** b) # 1000
print((a + b) * 5) # 65
print(10 + 1.1) # 11.1
print((5 + 1.5) * 2) # 13.0
# Add strings
message1 = "hello,"
message2 = "world"
print(message1 + message2)
# Add numbers and strings , Direct error :TypeError: can only concatenate str (not "int") to str
# print(message1 + a)
# String multiplied by number , How many times will this string be repeated
print(message1 * b)
It should be noted that :
/ differ Java、C Programming language , Its operation is a division operation rather than an integral division operation !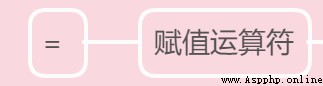
There are two main methods of assignment :
# Single assignment
a = 10
print(a) # 10
# Multiple assignments
b = c = 5
print(b) # 5
print(c) # 5
d, e, f = 1, 2, 3
print(d) # 1
print(e) # 2
print(f) # 3
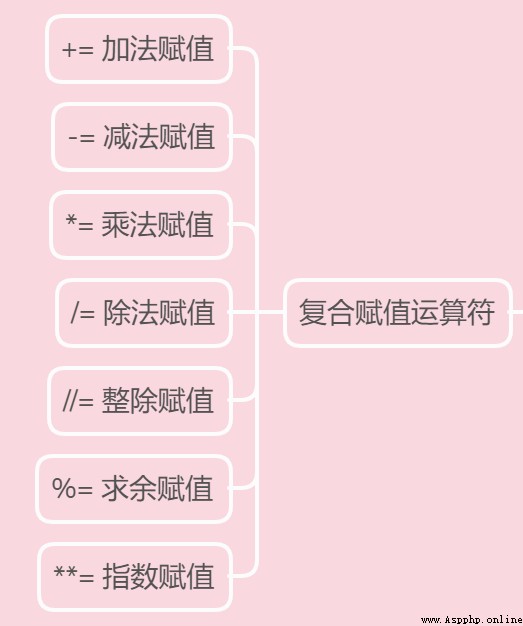
The use of compound assignment operators is also very simple , Similar to arithmetic operators :
a = 5
a += 1
print(a) # 6 Equivalent to a = a + 1
b = 5
b -= 1
print(b) # 4
c = 5
c *= 2
print(c) # 10
d = 5
d /= 2
print(d) # 2.5
e = 5
e //= 2
print(e) # 2
f = 5
f %= 2
print(f) # 1
g = 5
g **= 2
print(g) # 25
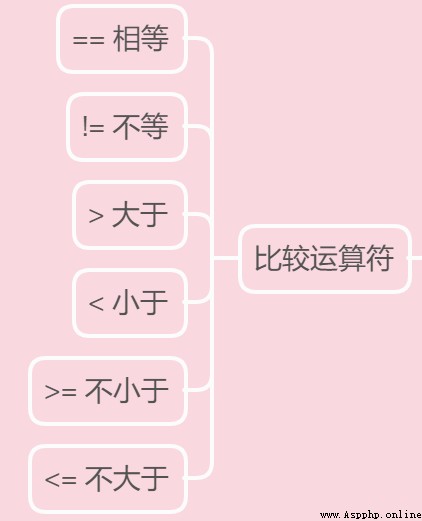
Python The use of comparison operators in is the same as in other programming languages :
print(2 == 3) # False
print(2 != 3) # True
print(2 > 3) # False
print(2 >= 3) # False
print(2 < 3) # True
print(2 <= 3) # True
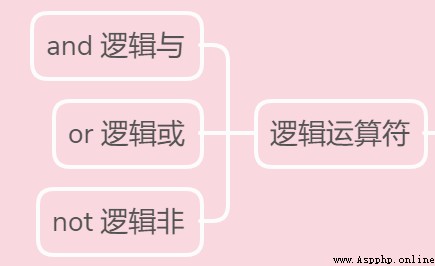
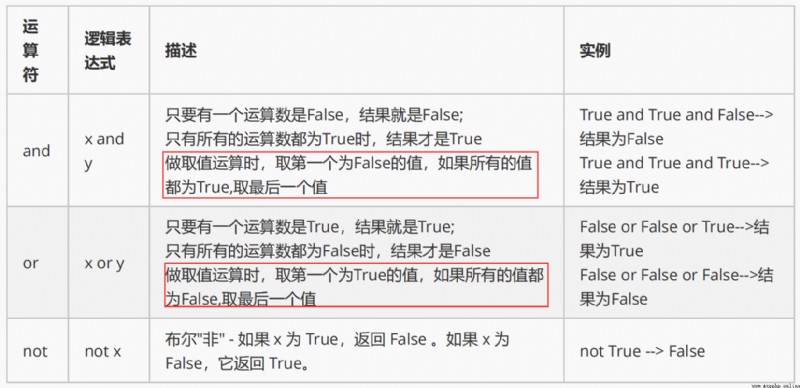
The code for :
print(True and False)
print(False or True)
print(not False)
a = 34
a > 10 and print('hello world')
a < 10 and print('hello world')
a > 10 or print(' Hello world ')
a < 10 or print(' Hello world ')
Are you right about the running results ?

Thank you for reading , Progress together , Hee hee ~