The authors introduce :【 Lonely and cold 】—CSDN High quality creators in the whole stack field 、HDZ Core group members 、 Huawei cloud sharing expert Python Full stack domain bloggers 、CSDN The author of the force program
- This article has been included in Python Full stack series column :《Python Full stack basic tutorial 》
- Popular column recommendation :《Django Framework from the entry to the actual combat 》、《 A series of tutorials from introduction to mastery of crawler 》、《 Reptile advanced 》、《 Front end tutorial series 》、《tornado A dragon + A full version of the project 》.
- This column is for the majority of program users , So that everyone can do Python From entry to mastery , At the same time, there are many exercises , Consolidate learning .
- After subscribing to the column But there are more than 1000 people talking privately Python Full stack communication group ( Teaching by hand , Problem solving ); Join the group to receive Python Full stack tutorial video + Countless computer books : Basics 、Web、 Reptiles 、 Data analysis 、 visualization 、 machine learning 、 Deep learning 、 Artificial intelligence 、 Algorithm 、 Interview questions, etc .
- Join me to learn and make progress , One can walk very fast , A group of people can go further !
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" __author__ = Xiaoming - Code entities """
import sys
print('\n'.join(sys.path))
(base) D:\PycharmProjects\demo1>python pythonlearn/test.py
D:\PycharmProjects\demo1\pythonlearn
D:\Anaconda3\python37.zip
D:\Anaconda3\DLLs
D:\Anaconda3\lib
D:\Anaconda3
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\win32
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\win32\lib
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\Pythonwin
(base) D:\PycharmProjects\demo1>set PYTHONPATH=.
(base) D:\PycharmProjects\demo1>python pythonlearn/test.py
D:\PycharmProjects\demo1\pythonlearn
D:\PycharmProjects\demo1
D:\Anaconda3\python37.zip
D:\Anaconda3\DLLs
D:\Anaconda3\lib
D:\Anaconda3
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\win32
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\win32\lib
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\Pythonwin
The grammar is as follows :
import module1[, module2[,... moduleN] A module can only be imported once , No matter how many times you execute import. This prevents the import module from being executed over and over again .
When we use import At the time of statement ,Python The interpreter will look in the search path , The search path is made up of a series of directory names ,Python The interpreter looks for the introduced modules from these directories in turn .
Practical explanation :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" __author__ = Lonely and cold """
# The import module
from pprint import pprint
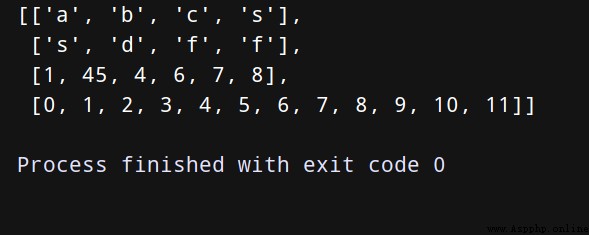
nested = [list("abcs"), list("sdff"), [1, 45, 4, 6, 7, 8], list(range(12))]
# Now you can call the functions contained in the module
pprint(nested)
Python Of from Statement allows you to import a specified part from a module into the current namespace .
from…import amount to java Static import of , Import only the specified part of a module
The grammar is as follows :
from modname import name1[, name2[, ... nameN]]for example , To import a module datetime Of datetime function , Use the following statement :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" __author__ = Lonely and cold """
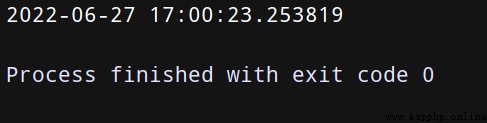
from datetime import datetime
d = datetime.now()
print(d)
and import The difference between :
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" __author__ = Lonely and cold """
import datetime
d = datetime.datetime.now()
print(d)
As can be seen from the above example ,from…import The imported method can directly call ,import The imported method must be added with the class name .
It is also possible to import all the contents of a module into the current namespace , Just use the following statement :from modname import *
For example, we want to introduce math Everything in the module , The statement is as follows :
from math import *
By default ,Python The interpreter will search the current directory 、 All installed built-in modules and third-party modules , Search paths are stored in sys Modular path variable :
>>> import sys
>>> sys.path
['', '/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages/pycrypto-2.6.1-py2.7-macosx-10.9-intel.egg', '/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages/PIL-1.1.7-py2.7-macosx-10.9-intel.egg', ...]
If we want to add our own search directory , There are two ways :
One is direct modification sys.path, Add directory to search :
>>> import sys
>>> sys.path.append('E:/demo')
This way is Modify... At run time , Failure after operation .
The second way is to set the environment variables PYTHONPATH, The contents of this environment variable will be automatically added to the module search path . Setting mode and setting Path Environment variables are similar to . Note that just add your own search path ,Python Your own search path is not affected .
for example :
set PYTHONPATH=.
dir() You can find all the names defined within the module . Return as a list of strings :
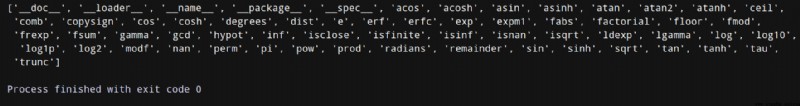
# coding=utf-8
import math
print(dir(math))
 ad locum , Special string variables __name__ Point to the name of the module ,__file__ The name of the import file pointing to the module .
ad locum , Special string variables __name__ Point to the name of the module ,__file__ The name of the import file pointing to the module .
If there is no given parameter , that dir() The function lists all the names currently defined :
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'math']
__all__& Import... From a package *from sound.effects import *
Will execute effects Under the bag __init__.py And import the content defined inside , If there is __all__ List variables , Then you can import the modules specified in the list .
stay :file:sounds/effects/__init__.py Contains the following code :
__all__ = ["echo", "surround", "reverse"]
This means that when you use from sound.effects import * In this way , The three sub modules in the package will be imported .
__main__Python The interpreter will run the __name__ Set as __main__
if __name__=='__main__':
test()
When we run on the command line hello Module file ,Python The interpreter takes a special variable __name__ Set as __main__, And if you import it elsewhere hello When the module ,if Judgment will fail , therefore , such if Testing allows a module to execute some extra code through the command line runtime , The most common is running tests .
from car import Car # Import this class from a module that contains only one class
from car import ElectricCar # Import a class from a module that contains multiple classes
from car import Car, ElectricCar # Import multiple classes from a module with multiple classes
import car # Import the entire module We use grammar module_name.class_name Access the required classes
from module_name import * # Import all the classes in the module ( Not recommended , If you want to use , It is recommended to import the entire module )
The first one is :
import datetime # Import the whole datetime modular
a = datetime.datetime.now() # Get the current time
# first datetime It's a module , the second datetime It is the class in the module ,,now() Is a method in a class
The second kind :
(1)
from datetime import datetime # Import a class in the module
a = datetime.now() # Just one datetime Is the class in the module
(2)
from datetime import * # Import all classes in this module
a = datetime.now() # Just one datetime Is the class in the module
The third kind of :
from datetime import datetime as y # Take the alias
a = y.now()
sys.path A list for storing import paths , Similar to... In environment variables PATH
sys.argv View the current file path
__pycache__: Cache file
Example :
import sys
print(sys.path) # Under this path , You can go through import Direct import . A list of , The path in front has high priority .
# Only the paths in this list can be imported .
The first question is :
If you write a file and python A module with the same name , And the file you wrote is in this directory , If you import this module directly , This directory has the highest priority , You cannot import the module that comes with it , What to do ?
resolvent : sys.path.insert(0, Pathname ), Change the path of the module you want to import to the front of the list .
The second question is :
If the module to be imported is on another disk , That is, it is not in the path list , How to import ?
sys.path.append(r' Pathname ')