python基本數據類型
首先需要你的電腦安裝好了Python環境,並且安裝好了Python開發工具。
python中的數據類型僅有int和float兩種(沒有如short,long,double之分)
這裡查看各種情況的數據類型運用到了python中的type函數
print(type(1))
print(type(-1))
print(type(1.1111))
print(type(1+1))
print(type(1+1.0)) # 由於1.0為float類型,python將1+1.0自動轉化為float類型
print(type(1*1))
print(type(1*1.0))
# python中的除法使用'/'結果為float類型,使用"//"為int類型
print(type(2/2))
print(type(2//2))
print(type(1//2)) # 與其他語言類似python中整除會忽略小數點後數字
運行結果: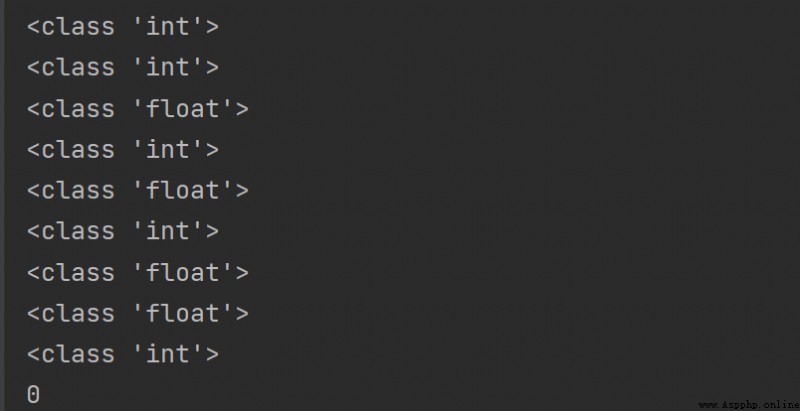
小結:
# bool類型包括 True和 False兩種
print(type(True))
print(type(False))
# 將bool類型轉換為int類型
print(int(True))
print(int(False))
# python中0為假,非0為真(無論進制)
print(bool(1))
print(bool(0))
print(bool(2.2))
print(bool(0b10))
# 對字符串取布爾值
print(bool('abc'))
print(bool(''))
# 對列表取布爾值
print(bool([1,2,3]))
print(bool([]))
運行結果:
小結
True和False開頭需大寫
數字中:0為False,其他均為True;在其他類型中:空為False,非空為True
# 二進制標識符為 0b,打印輸出其代表的十進制數
print(0b10)
print(0b11)
# 八進制標識符為 0o,打印輸出其代表的十進制數
print(0o10)
print(0o11)
# 十六進制標識符為 0x,打印輸出其代表的十進制數
print(0x10)
print(0x1F)
# 輸入數字默認為十進制
print(10)
結果: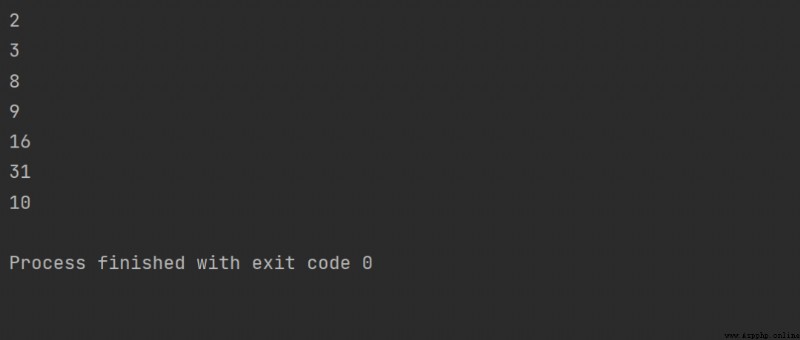
小結:需牢記各種進制的表示形式
# 轉換為二進制
print(bin(10))
print(bin(0o7))
print(bin(0xE))
# 轉換為八進制
print(oct(0b111))
print(oct(0x777))
# 轉換為十進制
print(int(0b111))
print(int(0o777))
# 轉換為十六進制
print(hex(888))
print(hex(0b111))
print(hex(0o7777))
運行結果: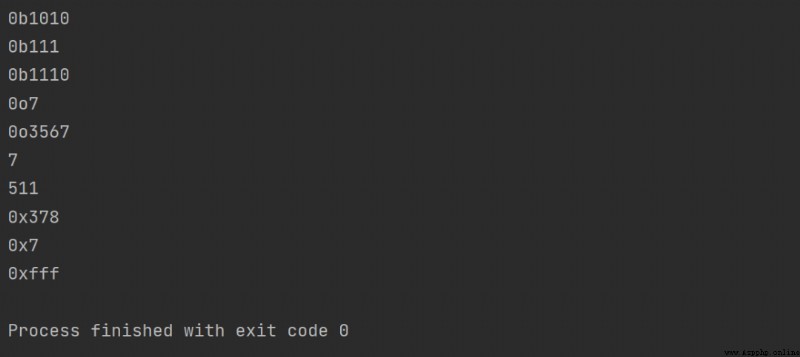
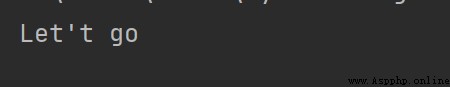
print("Let't go")
print('Let't go') # 其中此語句會報錯
運行結果:
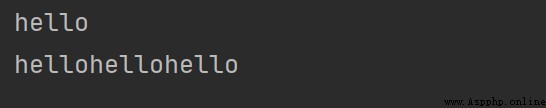
兩字符串間可相加拼接成一個字符串
字符串乘上一個數n,得到n個該字符串
# 字符串的運算
print("he"+"llo")
print("hello"*3)
結果
# 輸出指定位置的字符
print("hello world"[0])
print("hello world"[1])
print("hello world"[2])
print("hello world"[-1])
print("hello world"[-2])
結果
其中i可為負數,代表獲取倒數第i位的數字
print("hello world"[0:5])
print("hello world"[-5:11])
print("hello world"[-5:])
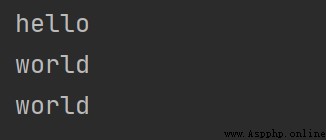
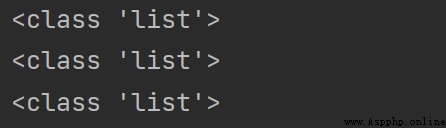
# 列表可存儲的類型
print(type([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]))
print(type(["hello", 1, False]))
print(type([[1, 2], [3, 4], [True, False]])) # 嵌套列表
# 讀取列表中的元素
print(["hello", "world"][0:]) # 和str類型的讀取方式相同

# 列表的運算(和str的運算相似)
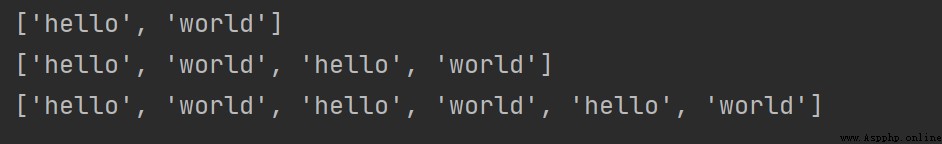
print(["hello", "world"] + ["hello", "world"])
print(["hello", "world"] * 3)
# 元組存儲是數據類型
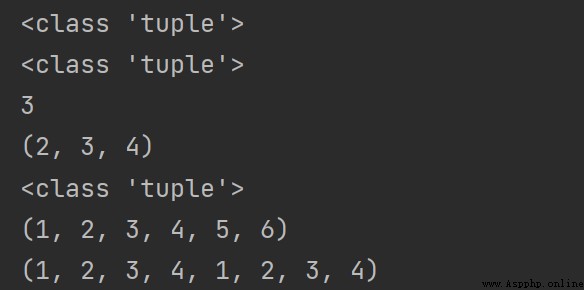
print(type((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)))
print(type((1, 2, "hello", [1, 2, 3], True)))
# 獲取指定位置元素
print((1, 2, 3, 4)[2])
# 獲取指定區域元素
print((1, 2, 3, 4)[1:])
print(type((1, 2, 3, 4)[1:])) # 返回類型為tuple
# 元組的運算
print((1, 2, 3, 4)+(5, 6))
print((1, 2, 3, 4)*2)
集合中的數據是無序的,故不能用下標進行訪問
集合中的元素不重復
# 求兩個集合的差集
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} - {
2, 3}) # '-'為求差集的符號
# 求兩個集合的交集
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} & {
2, 3}) # '&'為求交集的符號
# 求兩個集合的並集
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} | {
5, 6, 7}) # '-'為求差集的符號

>>> set()
# 字典類型的輸入格式
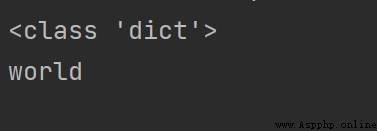
print(type({
1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}))
# 字典的使用
print({
1:"Hello", 2:"world"}[2])
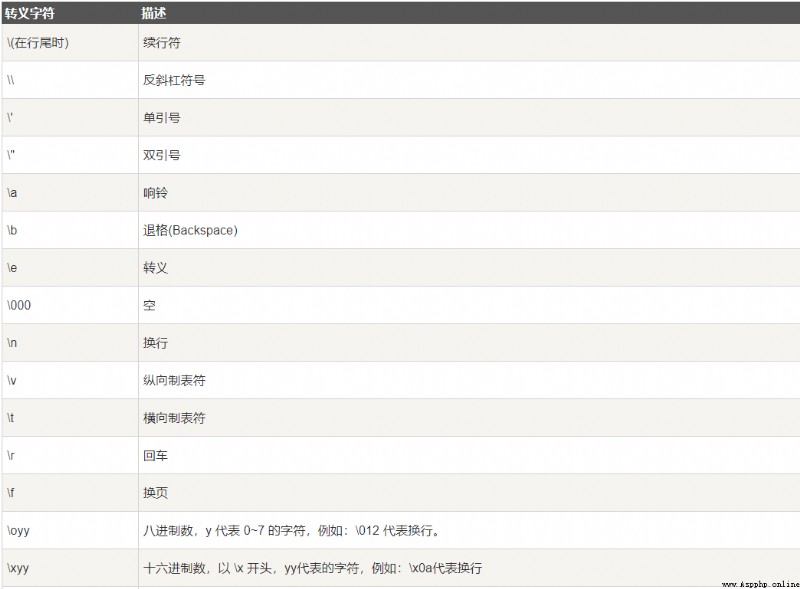
轉義字符