python Basic data type
First, you need to install your computer Python Environmental Science , And it's installed Python development tool .
python Data types in have only int and float Two kinds of ( Nothing like short,long,double Points )
Here you can see the data types used in various situations python Medium type function
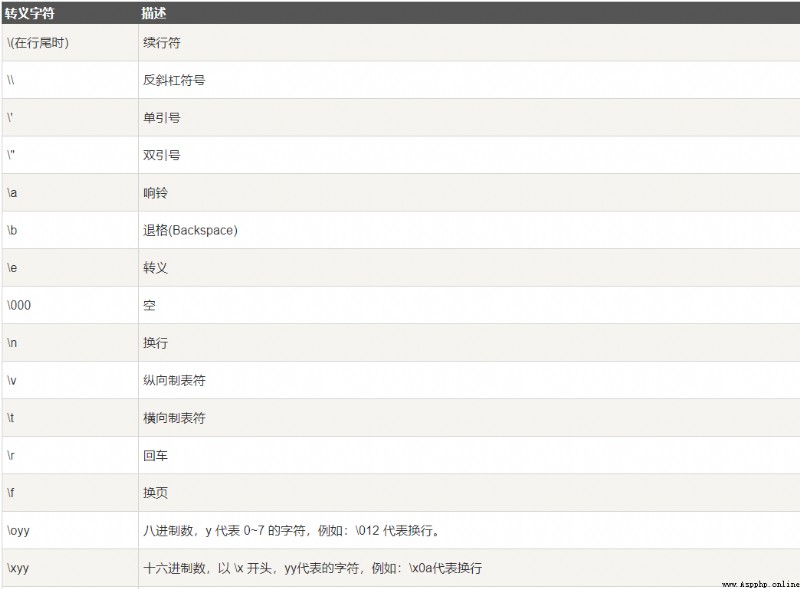
print(type(1))
print(type(-1))
print(type(1.1111))
print(type(1+1))
print(type(1+1.0)) # because 1.0 by float type ,python take 1+1.0 Automatically convert to float type
print(type(1*1))
print(type(1*1.0))
# python The division in '/' The result is float type , Use "//" by int type
print(type(2/2))
print(type(2//2))
print(type(1//2)) # Similar to other languages python Division by middle ignores the number after the decimal point
Running results :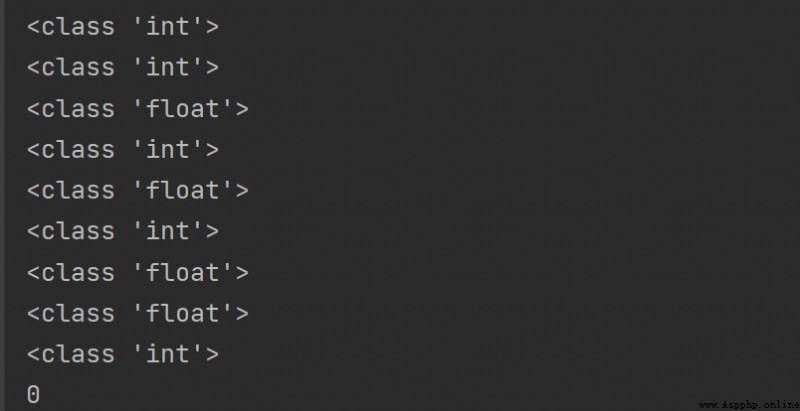
Summary :
# bool Types include True and False Two kinds of
print(type(True))
print(type(False))
# take bool Type conversion to int type
print(int(True))
print(int(False))
# python in 0 For false , Not 0 It's true ( Regardless of base )
print(bool(1))
print(bool(0))
print(bool(2.2))
print(bool(0b10))
# Take a Boolean value on a string
print(bool('abc'))
print(bool(''))
# Take Boolean values for the list
print(bool([1,2,3]))
print(bool([]))
Running results :
Summary
True and False The beginning should be capitalized
In the numbers :0 by False, Others are True; In other types : Empty as False, Not empty True
# The binary identifier is 0b, Print out the decimal number it represents
print(0b10)
print(0b11)
# The octal identifier is 0o, Print out the decimal number it represents
print(0o10)
print(0o11)
# The hexadecimal identifier is 0x, Print out the decimal number it represents
print(0x10)
print(0x1F)
# The input number defaults to decimal
print(10)
result :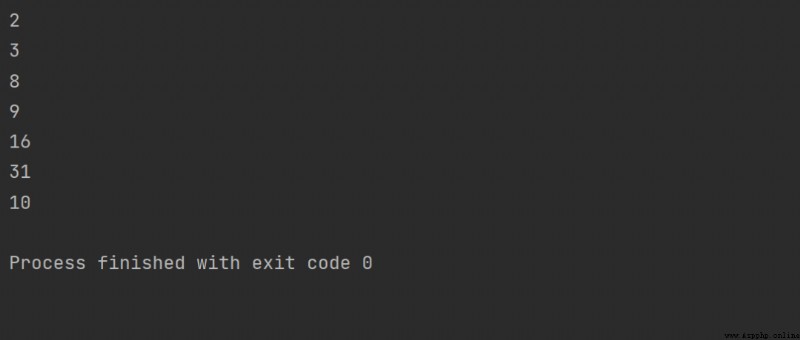
Summary : Keep in mind the various decimal representations
# Convert to binary
print(bin(10))
print(bin(0o7))
print(bin(0xE))
# Convert to octal
print(oct(0b111))
print(oct(0x777))
# Convert to decimal
print(int(0b111))
print(int(0o777))
# Convert to hex
print(hex(888))
print(hex(0b111))
print(hex(0o7777))
Running results :
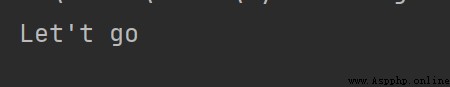
print("Let't go")
print('Let't go') # This statement will report an error
Running results :
Two strings can be added and spliced into one string
Multiply the string by a number n, obtain n This string
# Operation of string
print("he"+"llo")
print("hello"*3)
result
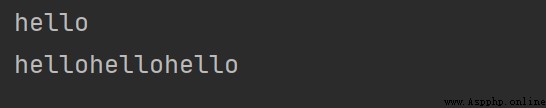
# Output the character at the specified position
print("hello world"[0])
print("hello world"[1])
print("hello world"[2])
print("hello world"[-1])
print("hello world"[-2])
result 
among i It can be negative , Represents getting the penultimate i Digit number
print("hello world"[0:5])
print("hello world"[-5:11])
print("hello world"[-5:])
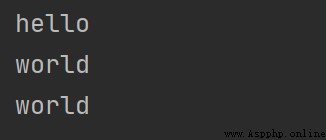
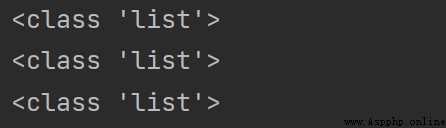
# List types that can be stored
print(type([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]))
print(type(["hello", 1, False]))
print(type([[1, 2], [3, 4], [True, False]])) # Nested list
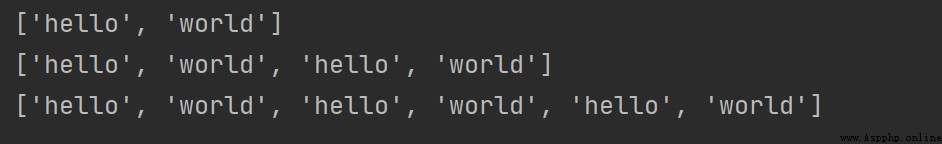
# Read the elements in the list
print(["hello", "world"][0:]) # and str Type is read in the same way

# The operation of the list ( and str The operations of are similar )
print(["hello", "world"] + ["hello", "world"])
print(["hello", "world"] * 3)
# Tuple storage is a data type
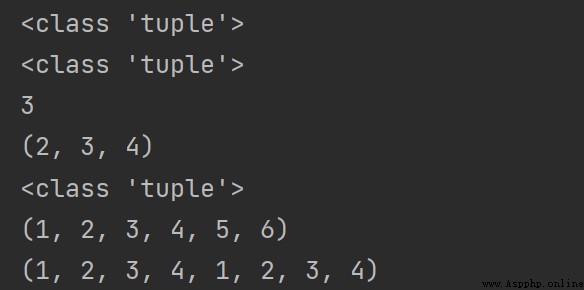
print(type((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)))
print(type((1, 2, "hello", [1, 2, 3], True)))
# Get the specified location element
print((1, 2, 3, 4)[2])
# Get the specified area element
print((1, 2, 3, 4)[1:])
print(type((1, 2, 3, 4)[1:])) # The return type is tuple
# The operation of tuples
print((1, 2, 3, 4)+(5, 6))
print((1, 2, 3, 4)*2)
The data in the set is A disorderly , so You can't use subscripts Visit
The elements in the collection No repetition
# Find the difference set of two sets
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} - {
2, 3}) # '-' For the symbol of the difference set
# Find the intersection of two sets
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} & {
2, 3}) # '&' To find the symbol of intersection
# Find the union of two sets
print({
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} | {
5, 6, 7}) # '-' For the symbol of the difference set

>>> set()
# Input format of dictionary type
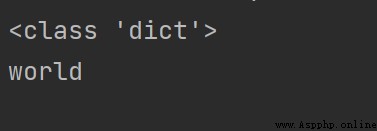
print(type({
1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}))
# The use of dictionaries
print({
1:"Hello", 2:"world"}[2])
Escape character