Python edition
class Iou:
def compute_iou(self, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4):
# The sum of the two matrix areas
area = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1) + (x4 - x3) * (y4 - y3)
# The coordinates of the upper left corner and the lower right corner of the intersecting part of the two matrices are determined
middle_x1 = max(x1, x3)
middle_x2 = min(x2, x4)
middle_y1 = max(y1, y3)
middle_y2 = min(y2, y4)
middle_w = max(0.0, middle_x2 - middle_x1)
middle_h = max(0.0, middle_y2 - middle_y1)
# Intersection of two matrices
middle_area = middle_w * middle_h
# return hand over / and
return middle_area / (area - middle_area)
if __name__=="__main__":
rec1 = [27, 661, 47, 679]
rec2 = [27, 662, 47, 682]
a = Iou().compute_iou(*rec1, *rec2)
print(f"a: {
a}")
C++ edition
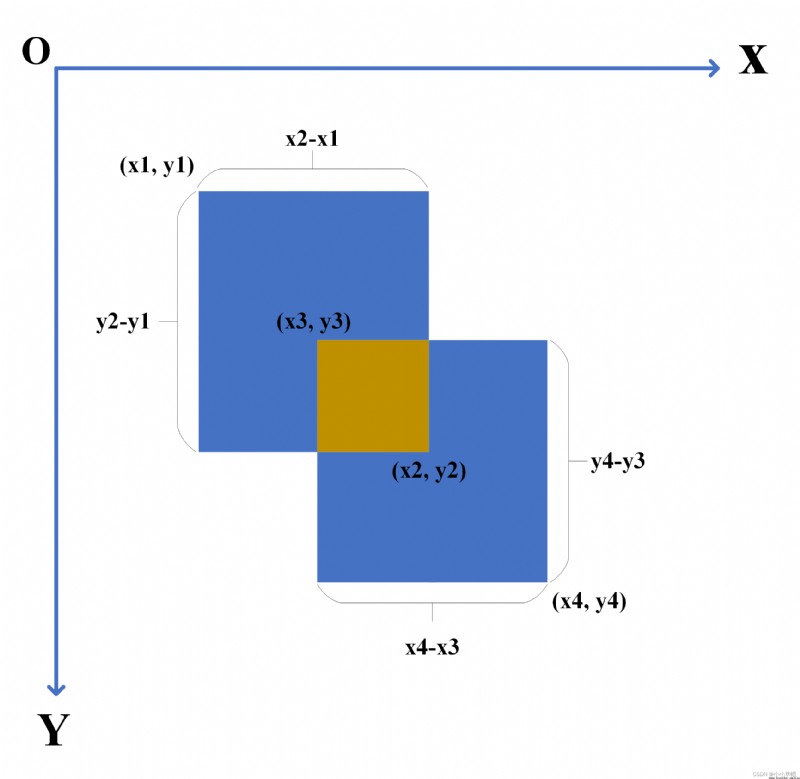
IOU The formula is as follows :
I O U = two Moment front hand over / two Moment front and IOU = The intersection of two matrices / The union of two matrices IOU= two Moment front hand over / two Moment front and
Take the upper left corner as the far point . For two matrices The coordinates of the upper left corner and the lower right corner , Calculation IOU. In particular ,
The first rectangle rec1, Top left :(x1, y1) , The lower right :(x2, y2) ;
The second rectangle rec2, Top left :(x3, y3) , The lower right :(x4, y4) ;
It is easy to calculate the sum of two matrices , The formula is as follows :
a r e a = r e c 1 + r e c 2 = ( x 2 − x 1 ) ∗ ( y 2 − y 1 ) + ( x 4 − x 3 ) ∗ ( y 4 − y 3 ) area = rec1 + rec2 = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1) + (x4 - x3)*(y4 - y3) area=rec1+rec2=(x2−x1)∗(y2−y1)+(x4−x3)∗(y4−y3)
To calculate the intersection of two matrices , Determine the upper left and lower right coordinates of the intersecting area , Then there are :
m i d d l e _ l e f t = m a x ( x 1 , x 3 ) middle\_left = max(x1, x3) middle_left=max(x1,x3)
m i d d l e _ r i g h t = m i n ( x 2 , x 4 ) middle\_right = min(x2, x4) middle_right=min(x2,x4)
m i d d l e _ t o p = m a x ( y 1 , y 3 ) middle\_top = max(y1, y3) middle_top=max(y1,y3)
m i d d l e _ b u t t o m = m i n ( y 2 , y 4 ) middle\_buttom = min(y2, y4) middle_buttom=min(y2,y4)
So the intersection of the matrix is :
m i d d l e _ a r e a = ( m i d d l e _ r i g h t − m i d d l e _ l e f t ) ∗ ( m i d d l e _ b u t t o m − m i d d l e _ t o p ) middle\_area = (middle\_right - middle\_left) * (middle\_buttom - middle\_top) middle_area=(middle_right−middle_left)∗(middle_buttom−middle_top)
The union of the matrix is :
Moment front Of and = Moment front Of and − Moment front Of hand over Union of matrices = Sum of matrices - Intersection of matrices Moment front Of and = Moment front Of and − Moment front Of hand over
So the final formula is
I O U = m i d d l e _ a r e a a r e a − m i d d l e _ a r e a IOU = \frac{middle\_area}{area - middle\_area} IOU=area−middle_areamiddle_area
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Solution:
def nms(self, boxes, threshold):
# Calculate the area of all candidate frames , utilize numpy Calculate all candidate boxes at once
x1, y1, x2, y2, score = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3], boxes[:, 4]
# Calculate the area of each box
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# Rank the confidence of each box from small to large ,order Stored is the corresponding score Index value from small to large in
order = np.argsort(score)
# keep Is the return value , after NMS Select the box after
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
# Add the box with the highest pre reliability to the return value , And use it to suppress iou> Box for a given threshold , If the box is smaller than the threshold, continue NMS, Until all boxes are selected
index = order[-1]
keep.append(index)
# Calculate the confidence of the box with the largest confidence and that of the other boxes iou, The quantity calculated here is current order.size - 1.
middle_x1 = np.maximum(x1[index], x1[order[:-1]])
middle_x2 = np.minimum(x2[index], x2[order[:-1]])
middle_y1 = np.maximum(y1[index], y1[order[:-1]])
middle_y2 = np.minimum(y2[index], y2[order[:-1]])
# Special case handling , Judge the coordinates of the upper left corner and the lower right corner : Lower right coordinates - Top left coordinates > 0 Return the corresponding value , Otherwise return to 0
middle_w = np.maximum(0.0, middle_x2 - middle_x1 + 1)
middle_h = np.maximum(0.0, middle_y2 - middle_y1 + 1)
middle_area = middle_h * middle_w
# Calculate the relation between the box with the largest pre reliability and the other boxes iou, take iou Boxes larger than the threshold are deleted
iou_ratio = middle_area / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - middle_area)
# Pick one that is less than a given threshold iou Keep going NMS
left = np.where(iou_ratio < threshold)
# Will all < threshold Take out the index of
order = order[left]
return keep
def plot_bbox(self, dets, c='k'):
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
plt.plot([x1, x2], [y1, y1], c)
plt.plot([x1, x1], [y1, y2], c)
plt.plot([x1, x2], [y2, y2], c)
plt.plot([x2, x2], [y1, y2], c)
plt.title(" nms")
if __name__=="__main__":
boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 250, 250, 0.8],
[250, 250, 420, 420, 0.95],
[220, 220, 320, 330, 0.92],
[100, 100, 210, 210, 0.7],
[230, 240, 325, 330, 0.81],
[220, 230, 315, 340, 0.9]])
threshold = 0.7
s1 = Solution()
a = s1.nms(boxes, threshold)
for i in boxes[a]:
print(f"boxes_nms: {
i}")
# visualization NMS effect
plt.figure(1)
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.sca(ax1)
s1.plot_bbox(boxes, 'k') # before nms
keep = a
plt.sca(ax2)
s1.plot_bbox(boxes[keep], 'r') # after nm
plt.show()
python Calculation iou as well as nms
python Realization IOU Calculation