String formatting Used to convert integers 、 Objects such as real numbers are converted to strings in a specific format
% Format characters :% The previous string is the format string , The next part is the content to be formatted .
for example :
name = "cspsy"
job = "student"
print("My name is %s." % name)
# If there is more than one content that needs to be formatted , Need to use () Wrap it in .
print("My name is %s and my job is %s." % (name, job))
format(): .format() The previous string is the format string , The contents of the inner part are the contents that need to be formatted .
In the format string {} The content and content of format() The contents inside correspond to .
format() Method to format :
name = "cspsy"
job = "student"
print("My name is {} and my job is {}.".format(name, job))

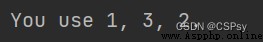
one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print("You use {0}, {2}, {1}.".format(one, two, three))
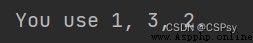
{} The user-defined parameter name is used in the , Corresponding to the content to be formatted .one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print("You use {o}, {thr}, {tw}.".format(o=one, tw=two, thr=three))
Will unpack the name ,key Value in the format string .
for example :
number = {
'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3}
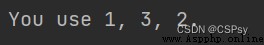
print("You use {one}, {three}, {two}.".format(**number))

Hexadecimal conversion
one, two, three = 11111, 2222, 3
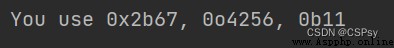
print("You use {0:#x}, {1:#o}, {2:#b}".format(one, two, three))
Keep the decimal point
Use :.xf,x For the number of decimal points you want to keep , If : With +, The symbol output is preserved .
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
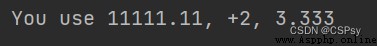
print("You use {0:.2f}, {1:+.0f}, {2:.3f}".format(one, two, three))
Scientific enumeration
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
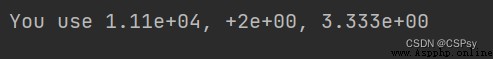
print("You use {0:.2e}, {1:+.0e}, {2:.3e}".format(one, two, three))
Percentage form
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:.0%}, {1:.2%}, {2:.3%}".format(one, two, three))

Separated by commas
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:,}, {1:,}, {2:,}".format(one, two, three))

Use :cxn To carry out ,n Is the minimum length ,c When the length is not enough , Filled characters ( If it is not written, it will be a blank space )x For alignment : among ,^: In the middle ,<: Align left ,>: Right alignment
for example :
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:#^12.2f}, {1:.<+8.0f}, {2:>7.3f}".format(one, two, three))
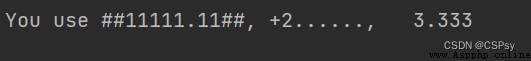
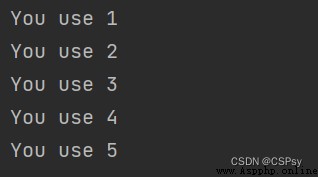
Can be built through map() Function to format string output :
formatter = "You use {0}".format
for num in map(formatter, range(1, 6)):
print(num)
This example is equivalent to the following :
formatter = "You use {0}".format
for num in range(1, 6):
print(formatter(num))
from Python 3.6.x Start to support a new format for Strings , The official name is Formatted String Literals, abbreviation f- character string , Prefix the string with a letter f, stay {} in Fill in the expression .
Use as follows :
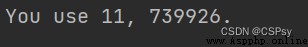
one, two, three = 11, 222, 3333
print(f'You use {
one}, {
two * three}.')
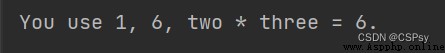
Python 3.8 after , just so so {xxx=}, take xxx= Output and output its corresponding value :
one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print(f'You use {
one}, {
two * three}, {
two * three = }.')