What is memory management mechanism
One 、 Reference counting mechanism
Two 、 Data pool and cache
What is memory management mechanismpython When creating objects in , First, I will apply for the memory address , Then initialize the object , All objects are maintained in one
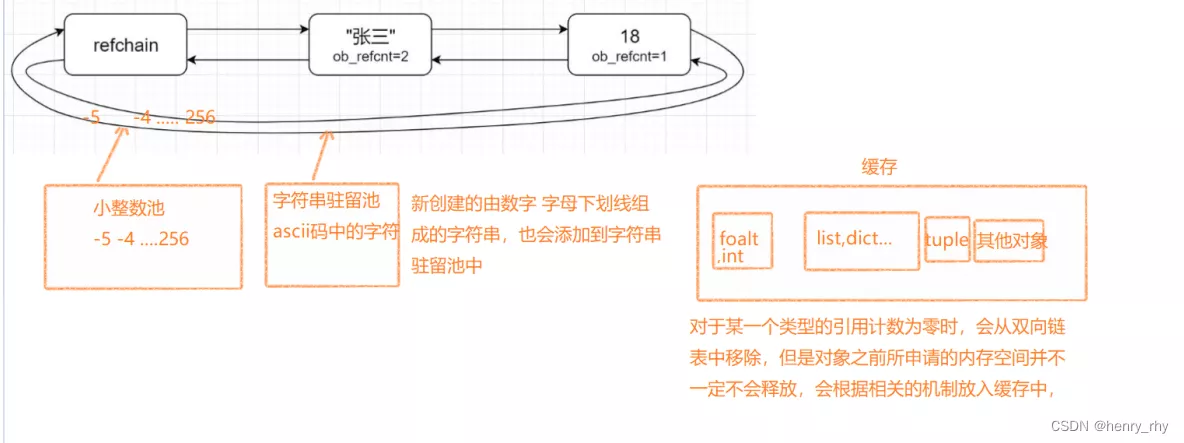
One is called refchain In a two-way circular list , Each data stores the following information :
One 、 Reference counting mechanism1. Pointer to the data before and after the data in the linked list
2. Type of data
3. Data values
4. Reference count of data
5. Length of data (list,dict..)
Increase in reference count :
1.1 Object created
1.2 Object is referenced by another variable ( Another name )
1.3 Objects are treated as elements , Put in container ( For example, it is put in the list as an element )
1.4 Object is passed as a parameter to a function
import sysa = [11,22] # Object created b = a # Object is referenced by another variable c = [111,222,333,a] # Objects are treated as elements , Put in container # Gets the reference count of the object print(sys.getrefcount(a)) # Object is passed as a parameter to a function The final result of the execution is ,a This variable is referenced 4 Time
Reference count reduction :
The alias of the object is explicitly destroyed
An alias of an object is assigned to another object ( example : Like the original a=10, Changed to a=100, here 10 The reference count is reduced )
Object is removed from the container , Or the container is destroyed ( example : Object is removed from the list , Or the list is destroyed )
A reference leaves its scope ( The parameters passed in when calling the function , After the function runs , The reference to this parameter is destroyed )
import sysdel b # The alias of the object is explicitly destroyed b = 999 # An alias of an object is assigned to another object del c # List destroyed ( The container was destroyed )c.pop() # Delete the last data in the list ( Object is removed from the container ) Two 、 Data pool and cache There are two types of data pools : A small pool of integers and Large integer pool
A small pool of integers (-5 To 256 Data between )
Operating mechanism :Python Automatically put -5~256 The integers of are cached into a small integer pool , When you assign these integers to variables , It's not going to happen again
Create objects , Instead, use the cache objects that have been created , When deleting references to these data , There's no recycling
beyond -5 To 256 The integer will not be in the cache , The object will be recreated
for example :
For exceeding -5 To 256 The integer will not be in the cache ,Python The object will be recreated , return id
# scene 1: Data as list , be not in -5~256 The scope of the >>> a = [11]>>> b = [11]>>> id(a),id(b)(1693226918600, 1693231858248) ========》 id Dissimilarity # Scene two : The data is an integer , stay -5~256 The scope of the >>> aa = 11>>> bb = 11>>> id(aa),id(bb)(140720470385616, 140720470385616) id equally # Scene three : Data not present -5~256 The scope of the >>> bb = -7>>> aa = -7>>> id(aa),id(bb)(1843518717904, 1843518717776) id Dissimilarity # Scene 4 : Data not present -5~256 The scope of the >>> a = 257>>> b = 257>>> id(a),id(b)(2092420910928, 2092420911056) id Dissimilarity Large integer pool ( String resident pool / intern Mechanism )
advantage : When creating a new string object , We will first find out whether there are existing objects with the same value in the cache pool ( identifier , That is, it contains only numbers 、 Letter 、 String of underscores ), If there is , Take it directly ( quote ), Avoid frequent creation and destruction of memory , Improve efficiency
for example :
Data that is not in the identifier will not be cached ,Python The object will be recreated , return id
# scene 1:>>> a = '123adsf_'>>> b = '123adsf_'>>> id(a),id(b)(61173296, 61173296) ========》 id equally # Scene two : >>> b1 = '123adsf_?'>>> b2 = '123adsf_?'>>> id(b1),id(b2)(61173376, 61173416) id Dissimilarity Caching mechanisms
about python Cache of commonly used built-in data types in :
float: cache 100 Objects
list: 80 Objects
dict: 80 Objects
set: 80 Objects
Tuples : According to the length of tuple data , The cache tuple length is 0-20 The object of
This is about Python This is the end of the super detailed article on memory management mechanism , More about Python Please search the previous articles of SDN or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope you can support SDN more in the future !
 Understand the working principle of genetic algorithm (with Python Implementation)
Understand the working principle of genetic algorithm (with Python Implementation)
Datawhale dried food &nb
 Python Programming for children 6-computer data structures and algorithms
Python Programming for children 6-computer data structures and algorithms
data structure It is an opera