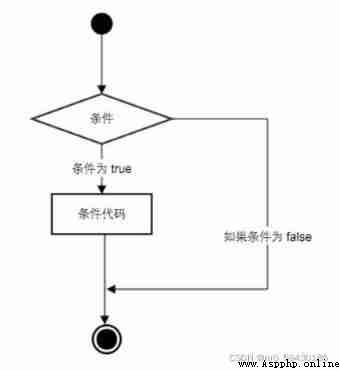
Python A conditional statement is the result of execution through one or more statements (True perhaps False) To determine the code block to execute .
The following figure summarizes the execution process of conditional statements :
Format :
if + Conditions :
What to do
......
ps: If indents are different , Represents different levels
if Judgment statement :
Code execution
elif Judgment statement :
Code execution
elif Judgment statement :
Code execution
else:
Code execution
color="red"
if (color=="green"):
print(" It's passable ")
if (color=="red"):
print(" No passage ")
if (color=="yellow"):
print(" Need to slow down ")
print(" try ,python Levels are related to indentation ")
#----------------------------#
if color==" ":
pass # If there is no judgment content , Need to write a pass placeholder . If there is content in the structure, there is also pass,pass You can ignore .
print(" Space ")
#----------------------------#
color="green"
if (color=="red"):
print("stop")
else:
print("go")
#----------------------------#
color="green"
if color=="green":
print("go")
elif color=="red":
print("stop")
elif color=="yellow":
print("slow")
else:
pass
print(" The judgment is over ")
#----------------------------#
carType=input(" Please enter the type of car :")
lightColor=input(" Please enter the lamp color :")
if carType in ("jiuhu","jingche","jiuhuo"):
print(" Special vehicles pass directly ")
else:
if lightColor=="green":
print("go")
elif lightColor=="red":
print("stop")
elif lightColor=="yellow":
print("slow")
else:
print("randomaction")
print(" The judgment is over ")
#----------------------------#
score=int(input(" Please enter the score :"))
if score<60:
print(" fail, ")
elif score>=60 and score<75:
print(" pass ")
elif score>=75 and score<90:
print(" good ")
else:
print(" good ")
Programming languages provide a variety of control structures , Allow more complex execution paths . A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements many times , The following is the general form of a loop statement in most programming languages :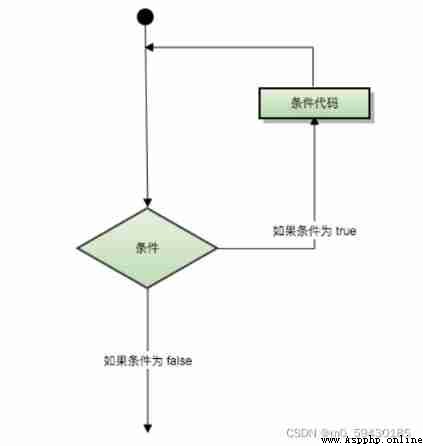
Python Provides for Circulation and while loop ( stay Python There is no do…while loop )
Loop control statement can change the order of statement execution .Python The following loop control statements are supported :
Python Programming while Statements are used to loop programs , Under certain conditions , Loop through a program , To deal with the same tasks that need to be repeated . Its basic form is :
while Conditional expression :
Conditions met , Execute loop statement
The value of the variable changes
# If the judgment condition is True, For infinite circulation
Example :
a=1
while a<=50:
print(" Print page "+str(a)+" Two papers ")
a+=1
#----------#
a=1
while True:
print(" Print page "+str(a)+" Two papers ")
a+=1
if a==51:break
#----------#
# Judge according to the input , If you pass, you will end the exam , If you fail, try again
a=int(input(" Please enter a number :"))
while a>=0:
if a>=60:
print(" End the exam ")
break
else:
print(" Retest ")
break
#----------#
# Judge according to the input , If you pass, you will end the exam , If you fail, try again
while True:
a=int(input(" Please enter the score :"))
if a>=60:
print(" Quit the exam , The score is :"+str(a))
break
else:
print(" Failing to pass the exam ,"+" The current score is :"+str(a))
continue
#----------#
while True:
a=int(input(" Please enter the temperature :"))
if a>35 or (a>=-20 and a<5):
print(" Please turn on the air conditioner ,"+" The current temperature is :"+str(a))
break
elif a>=5 and a<=35:
print(" The temperature is right , No need to turn on the air conditioner ,"+" The current temperature is :"+str(a))
break
elif a<-20:
break
#----------#
while True:
temp=int(input(" Please enter the outside temperature :"))
if temp<-20:
print(" It's too cold , The air conditioner is frozen ")
break
elif temp>=5 and temp<=35:
print(" The temperature is right , There is no need to turn on the air conditioner ")
else:
print(" The temperature is not suitable , Need to turn on the air conditioner ")
print(" Program end !")
Python for Loop can traverse any sequence of items , Like a list or a string .
for The syntax of the loop is as follows :
for Variable in Sequence
Loop statement
for i in range(51):
print(" The first "+str(i)+" Test paper printing ")
#----------#
for i in [1,2,3,4,5]:
print(i)
#----------#
a=(1,2,3,4,5)
for i in a:
print(i)
#----------#
# Chicken and rabbit in the same cage ,40 A chicken and a rabbit ,120 One foot , Find the number of chickens and rabbits
# Suppose there is x chicken ,40-x Rabbit
for x in range(41):
b=40-x
c=2*x+4*b
if c==120:
print(" The number of chickens is :"+str(x))
print(" The number of rabbits is :"+str(40-x))
for i in range(5):
print("-----")
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
if i==3:
break
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
if i==3:
continue
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
#if i==3:
#break
continue
print(i)
Python pass It's an empty statement , To maintain the integrity of the program structure .pass Not doing anything , Generally used as occupation statement .
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# Output Python Every letter of
for letter in 'Python':
if letter == 'h':
pass
print ' This is a pass block '
print ' The current letter :', letter
print "Good bye!"
# result
The current letter : P
The current letter : y
The current letter : t
This is a pass block
The current letter : h
The current letter : o
The current letter : n
Good bye!
# Single loop print rectangle
for i in range(5):
print("* * * * *")
# Double loop print rectangle ( print() Line break ,end='' Don't wrap )
for i in range(5): # Outer loop control line
for j in range(5): # Inner loop control column
print("* ",end='')
print()
# Print right triangle
## The right angle is on the lower left
for x in range(5):
for y in range(x+1):
print("* ",end='')
print()
## The right angle is on the left
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5-x):
print("* ",end='')
print()
## The right angle is on the right
def num(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
if j<i:
print(' ',end=' ')
else:
print('*',end=' ')
print()
num(5)
## The right angle is at the bottom right
def num(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
if i+j<=n:
print(' ',end=' ')
else:
print('*',end=' ')
print()
num(5)
# Print diamond
for x in range(5):
for y in range(4-x):
print(" ",end='')
for y in range(2*x+1):
print("*",end='')
print()
for x in range(5):
for y in range(x+1):
print(" ",end='')
for y in range(7-x*2):
print("*",end='')
print()
# Print prime numbers
lower = int(input(" Enter the minimum value of the range : "))
upper = int(input(" Enter the maximum value of the range : "))
for num in range(lower, upper + 1):
# The prime number is greater than 1
if num > 1:
for i in range(2, num):
if (num % i) == 0:
break
else:
print(num)
#----------------------------------
for x in range(2,101):
for y in range(2,x+1):
if x%y==0 and x!=y: # If x There are factors other than yourself , be x Not primes
break
if x==y:
print(" prime number :"+str(x))
break
# Count the daffodils
for i in range(100,1000):
a=int(i%10)
b=int((i%100)/10)
c=int(i/100)
if a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==i:
print(i)
# Decomposing prime factor :https://www.pianshen.com/article/962070061/
num=int(input(" Please enter a positive integer :"))
son=2
print(str(num)+"=",end='')
while num!=son:
if num%son==0:
num/=son
print(str(son)+"*",end='')
else:son+=1
print(son)
# Calculation and number , For example, the input 3, The value is 3+33+333
a=int(input(" Please enter a number :"))
n=a
sum=0
for x in range(a):
sum+=n
n=n*10+a
print(sum)