Blog links https://blog.csdn.net/cPen_web
Video link https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vK4y1o7jH
if requests.method == 'GET':
Handle GET Business logic at request
elif requests.method == 'POST':
Handle POST The business logic of the request
else:
Other request business logic
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
def test_get_post(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
pass
elif request.method == 'POST':
# Process user submitted data
pass
else:
pass
return HttpResponse('--test get post is ok--')
GET Request action , It is generally used to send messages to the server get data
Capable of producing GET The scene of the request :
– Enter... In the browser address bar URL, After returning
– <a href=“ Address ? Parameters = value & Parameters = value ”>
– form Forms Medium method by get
GET In the way of request , If there is data to be passed to the server , Usually I use Query string (Query String) Pass on 【 Be careful : Don't pass sensitive data 】
URL Format :xxx? Parameter name 1= value 1& Parameter name 2= value 2…
– Such as :http://127.0.0.1:8000/page1?a=100&b=200
The server side receives parameters
– Get client request GET Requested data
Method example :
request.GET[' Parameter name '] # QueryDict
request.GET.get(' Parameter name ', ' The default value is ')
request.GET.getlist(' Parameter name ')
# mypage?a=100&b=200&c=300&b=400
# request.GET=QueryDict({'a': ['100'], 'b': ['200', '400'], 'c': ['300']})
# a = request.GET['a']
# b = request.GET['b'] # Error
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_get_post?a=400
--test get post is ok--
# terminal
<QueryDict: {
'a': ['400', '200', '100']}>
100
['400', '200', '100']
no c
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_get_post', views.test_get_post)
]
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
def test_get_post(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
print(request.GET)
print(request.GET['a'])
# The questionnaire survey = form get Hobby - Check box
print(request.GET.getlist('a'))
print(request.GET.get('c', 'no c'))
elif request.method == 'POST':
# Process user submitted data
pass
else:
pass
return HttpResponse('--test get post is ok--')
Submit a large number of... To the server / Privacy data 
Receiving parameters if request.method == 'POST':
Handle POST Request data and respond
else:
Dealing with non POST Response to the request
request.POST[' Parameter name '] # request.POST binding QueryDict
request.POST.get(' Parameter name ', '')
request.POST.getlist(' Parameter name ')
Cancel csrf verification , otherwise Django Will reject the message from the client POST request , newspaper 403 Respond to # Cancel csrf verification
- Forbid to drop settings.py in MIDDLEWARE Medium CsrfviewsMiddleWare Middleware
MIDDLEWARE = [
...
# 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
...
]
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_get_post
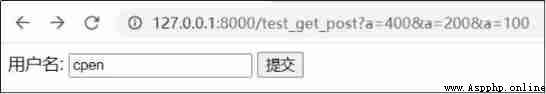
post is ok
# terminal
uname is cpen
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_get_post', views.test_get_post)
]
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
POST_FORM = ''' <form method='post' action='/test_get_post'> user name : <input type='text' name='uname'> <input type='submit' value=' Submit '> </form> '''
def test_get_post(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return HttpResponse(POST_FORM)
...
MVC representative Model-View-Controller( Model - View - controller ) Pattern .
√ M The model layer (Model), It is mainly used to encapsulate the database layer
√ V View layer (View), Used to present results to users (WHAT + HOW)
√ C control (Controller), Used to process requests 、 get data 、 Return results ( important )
effect : Reduce the coupling between modules ( decoupling )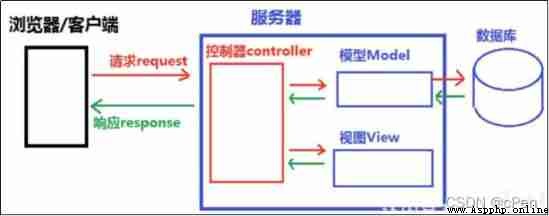
MTV representative Model-Template-View( Model - Templates - View ) Pattern .
√ M The model layer (Model) Responsible for interacting with the database
√ T Formwork layer (Template) Responsible for rendering content to the browser (HOW)
√ V View layer (View) Is the core , Responsible for receiving requests 、 get data 、 Return results (WHAT)
effect : Reduce the coupling between modules ( decoupling )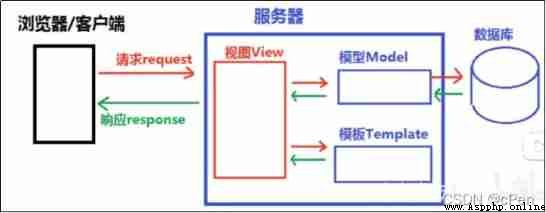
attach :MTV- Birth notes 
Dictionaries The data is dynamic html Webpage The corresponding dictionary is generated dynamically according to the dictionary data passed in the view HTML Webpage 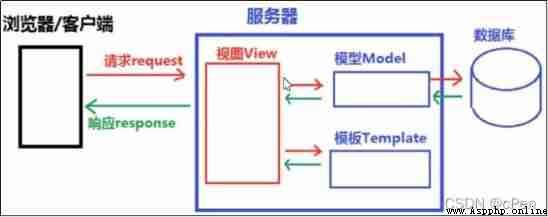
< Project name >/templatessettings.py in TEMPLATES Configuration item DIRS: Search directory for templates ( It can be one or more ) In the configuration item Parts to be modified
Set up DIRS - 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
demonstration
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/settings.py
TEMPLATES = [
{
...
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
...
from django.template import loader
# 1. adopt loader Load template
t = loader.get_template(" Template file name ")
# 2. take t convert to HTML character string
html = t.reader( Dictionary data )
# 3. Use the response object to return the converted String content to the browser
return HttpResponse(html)
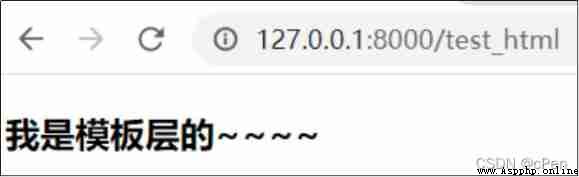
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_html
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_html', views.test_html)
]
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
def test_html(request):
from django.template import loader
t = loader.get_template('test_html.html')
html = t.render()
return HttpResponse(html)
# < Project folder >/templates/test_html.html
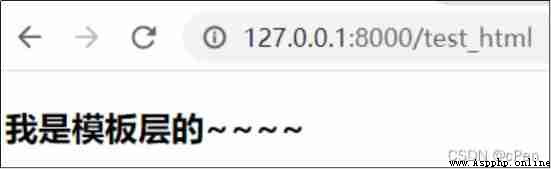
<h3> I'm from the template layer ~~~~</h3>
from django.shortcuts import render
return render(request, ' Template file name ', Dictionary data )
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_html
< Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
def test_html(request):
# programme 2
from django.shortcuts import render
return render(request, 'test_html.html')
Dictionaries Pass to template def xxx_view(request):
dic = {
" Variable 1": " value 1",
" Variable 2": " value 2",
}
return render(request, 'xxx.html', dic)
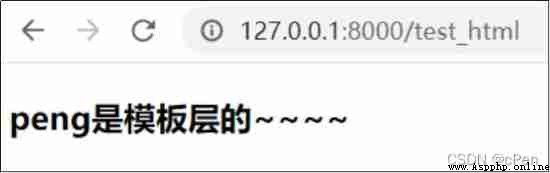
{ { Variable name }} The grammar of Call the variable passed in from the view http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_html
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_html', views.test_html)
]
# < Under the folder with the same name of the project >/views.py
def test_html(request):
from django.shortcuts import render
dic = {
'username': 'peng', 'age': 23}
return render(request, 'test_html.html', dic)
# < Project folder >/templates/test_html.html
<h3>{
{
username }} It's the template layer ~~~~</h3>