All the demonstration data of this article , Are based on the following four tables . The following four tables should be familiar to you , This is online transmission 50 Taoist classics MySQL Several original tables used in the interview questions . About the relationship between the following tables , I won't explain it to you , Look closely at the field name , Should be able to find .
1) brief introduction
pandas Medium DataFrame It's a two-dimensional table , The table in the database is also a two-dimensional table , So in pandas Use in sql The sentence appears to be natural ,pandasql Use SQLite As its operational database , meanwhile Python Bring their own SQLite modular , No installation required , It can be used directly .
One thing to note here is that : Use pandasql Read DataFrame Columns in date format , By default, the date will be read 、 Minutes and seconds , So we should learn to use sqlite Date handling functions in , It is convenient for us to convert the date format , Below is sqlite A complete collection of commonly used functions in , I hope it helps you .
sqlite Function Daquan :http://suo.im/5DWraE
Import related libraries :
import pandas as pd
from pandasql import sqldf
2) To declare a global variable 2 Ways of planting
① Before use , Declare the global variable
Python Learn to exchange skirts :279199867 ###
df1 = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
df2 = pd.read_excel("sc.xlsx")
df3 = pd.read_excel("course.xlsx")
df4 = pd.read_excel("teacher.xlsx")
global df1
global df2
global df3
global df4
query1 = "select * from df1 limit 5"
query2 = "select * from df2 limit 5"
query3 = "select * from df3"
query4 = "select * from df4"
sqldf(query1)
sqldf(query2)
sqldf(query3)
sqldf(query4)
Some of the results are as follows :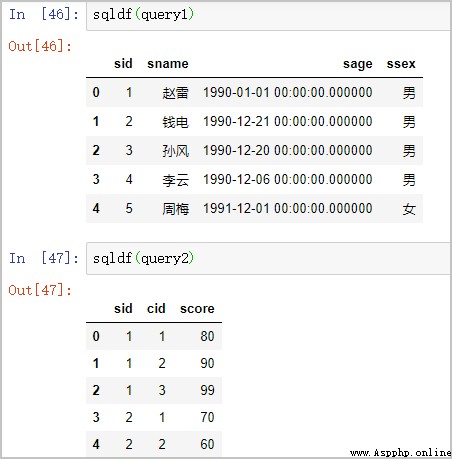
② Declare global variables at one time
df1 = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
df2 = pd.read_excel("sc.xlsx")
df3 = pd.read_excel("course.xlsx")
df4 = pd.read_excel("teacher.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query1 = "select * from df1 limit 5"
query2 = "select * from df2 limit 5"
query3 = "select * from df3"
query4 = "select * from df4"
sqldf(query1)
sqldf(query2)
sqldf(query3)
sqldf(query4)
Some of the results are as follows :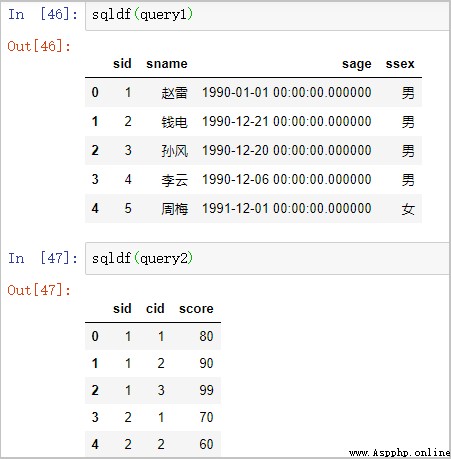
3) Write a few simple SQL sentence
① see sqlite Version of
student = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query1 = """ select sqlite_version(*) """
pysqldf(query1)
give the result as follows :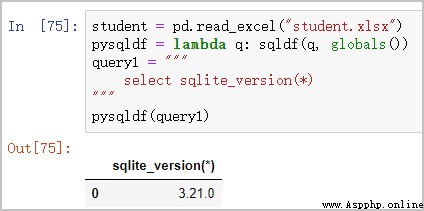
② where Screening
student = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query1 = """ select * from student where strftime('%Y-%m-%d',sage) = '1990-01-01' """
pysqldf(query1)
give the result as follows :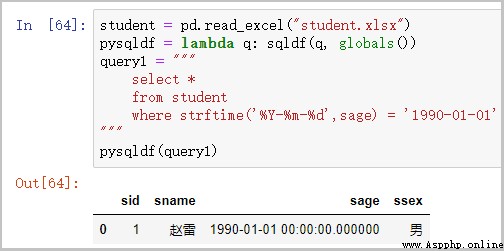
③ Multiple table joins
student = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
sc = pd.read_excel("sc.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query2 = """ select * from student s join sc on s.sid = sc.sid """
pysqldf(query2)
Some of the results are as follows :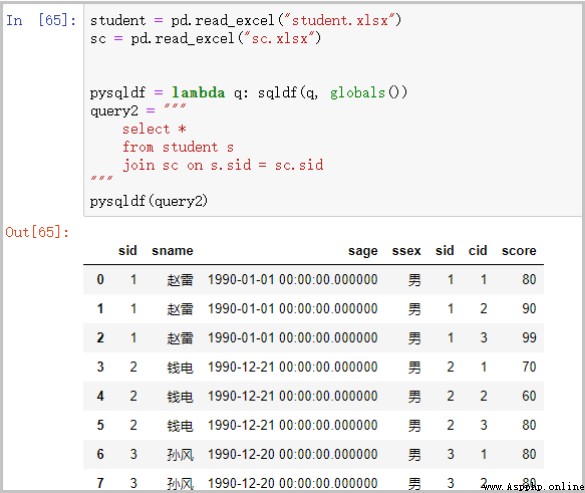
④ Group aggregation
student = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
sc = pd.read_excel("sc.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query2 = """ select s.sname as full name ,sum(sc.score) as Total score from student s join sc on s.sid = sc.sid group by s.sname """
pysqldf(query2)
give the result as follows :
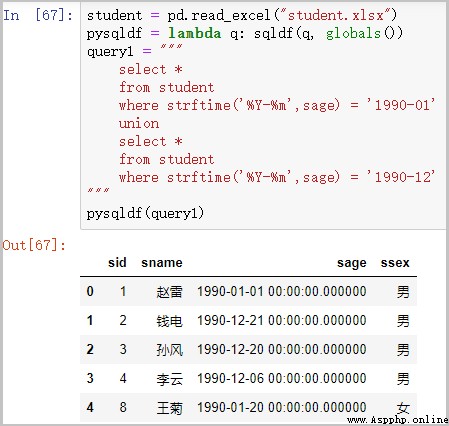
⑤ union Inquire about
student = pd.read_excel("student.xlsx")
pysqldf = lambda q: sqldf(q, globals())
query1 = """ select * from student where strftime('%Y-%m',sage) = '1990-01' union select * from student where strftime('%Y-%m',sage) = '1990-12' """
pysqldf(query1)
give the result as follows :