This paper mainly introduces NumPy Module and its multidimensional array properties , more Pyton Advanced Series , Please refer to Python Advanced learning Play data series
Summary :
NumPy yes Numerical Python Abbreviation , For more details, please refer to NumPy Official website .
Import NumPy Module and check Its version : Usually np As NumPy Another name for .
import numpy as np
version = np.__version__
print(version)
Output :
1.19.1
.ndim: Dimension of array
.size: The total number of array elements or the number of elements of a specific dimension of the array
.shape: It's a tuple , The elements in the code are the number of each dimension element .
axis: Array a dimension
The illustration :
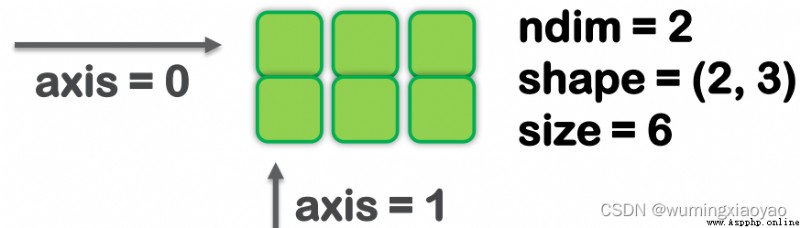
The black frame indicates the 1 dimension
The red box indicates the 2 dimension
The blue box indicates the 3 dimension 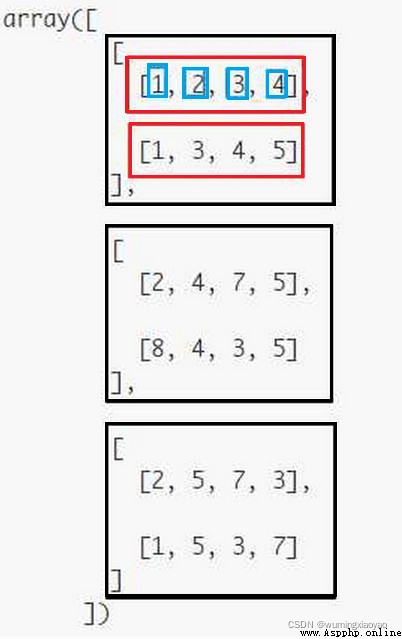
Code :
import numpy as np
arr_1_d = np.array ([1,2,3,4])
arr_2_d = np.array ([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]])
arr_3_d = np.array([[[1,2,3,4],[1,3,4,5]],[[2,4,7,5],[8,4,3,5]],[[2,5,7,3],[1,5,3,7]]])
print("1 dimension array============================")
print("arr_1_d:{}".format(arr_1_d))
print("arr_1_d ndim:{}".format(arr_1_d.ndim))
print("arr_1_d shape:{}".format(arr_1_d.shape))
print("arr_1_d size:{}".format(arr_1_d.size))
print("arr_1_d #No.1 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_1_d, axis=0)))
print("2 dimension array============================")
print("arr_2_d:{}".format(arr_2_d))
print("arr_2_d ndim:{}".format(arr_2_d.ndim))
print("arr_2_d shape:{}".format(arr_2_d.shape))
print("arr_2_d size:{}".format(arr_2_d.size))
print("arr_2_d #No.1 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_2_d, axis=0)))
print("arr_2_d #No.2 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_2_d, axis=1)))
print("3 dimension array============================")
print("arr_3_d:{}".format(arr_3_d))
print("arr_3_d ndim:{}".format(arr_3_d.ndim))
print("arr_3_d shape:{}".format(arr_3_d.shape))
print("arr_3_d size:{}".format(arr_3_d.size))
print("arr_3_d #No.1 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_3_d, axis=0)))
print("arr_3_d #No.2 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_3_d, axis=1)))
print("arr_3_d #No.3 dimension size:{}".format(np.size(arr_3_d, axis=2)))
Output :
1 dimension array============================
arr_1_d:[1 2 3 4]
arr_1_d ndim:1
arr_1_d shape:(4,)
arr_1_d size:4
arr_1_d #No.1 dimension size:4
2 dimension array============================
arr_2_d:[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]]
arr_2_d ndim:2
arr_2_d shape:(3, 2)
arr_2_d size:6
arr_2_d #No.1 dimension size:3
arr_2_d #No.2 dimension size:2
3 dimension array============================
arr_3_d:[[[1 2 3 4]
[1 3 4 5]]
[[2 4 7 5]
[8 4 3 5]]
[[2 5 7 3]
[1 5 3 7]]]
arr_3_d ndim:3
arr_3_d shape:(3, 2, 4)
arr_3_d size:24
arr_3_d #No.1 dimension size:3
arr_3_d #No.2 dimension size:2
arr_3_d #No.3 dimension size:4