API When testing ,Request Body and Response Body The format could be JSON Format , So for JSON It is very important to deal with . About JSON Please refer to this article for the concept of 《REST Assured 22 - JSON》
Python Yes JSON The operation of is very convenient , There are mainly the following 4 A way .
write file json.load() Read the file in json The string element of form is converted to Python type Summary :
json.dumps()1. Dictionaries dict Turn it into JSON
import json
d = {
"key1" : "value1", "key2" : "value2"}
json_string = json.dumps(d)
print("dic: {}".format(d))
print("json string: {}".format(json_string))
Output :
dict in key/value All are Single quotation marks Of ,json Medium key/value yes Double quotes Of .
dic: {
'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
json string: {
"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2"}
2. Format output JSON
Control indent ,key value Connector between
import json
d = {
"key1" : "value1", "key2" : "value2"}
json_string_pretty_1 = json.dumps(d, indent=2, separators=(',', ':'))
json_string_pretty_2 = json.dumps(d, indent=4, separators=(',', '='))
print("json string pretty 1 :\n {}".format(json_string_pretty_1))
print("json string pretty 2 :\n {}".format(json_string_pretty_2))
Output : Two different formats
json string pretty 1 :
{
"key1":"value1",
"key2":"value2"
}
json string pretty 2 :
{
"key1"="value1",
"key2"="value2"
}
3. Press Key Sort output JSON character string sort_keys=True Press key Sort
import json
d_dis_order = {
"name" : "peter", "age": 18, "gender" : "men"}
json_in_order = json.dumps(d_no_order, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print("dic disorder:\n {}".format(d_dis_order))
print("json string inorder:\n {}".format(json_in_order))
Output :
dic disorder:
{
'name': 'peter', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'man'}
json string inorder:
{
"age": 18,
"gender": "man",
"name": "peter"
}
4. Convert the class object to JSON character string
Custom objects are converted to JSON character string , You need to customize one JSONEncoder Subclass to override the default Serialization is assigned to cls Parameters .
To use a custom
JSONEncodersubclass (e.g. one that overrides the.default()method to serialize additional types), specify it with theclskwarg; otherwiseJSONEncoderis used.
import json
from json import JSONEncoder
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
class PersonEncoder(JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o):
return o.__dict__
peter = Person("Peter", 18, "Men")
json_peter = json.dumps(peter, indent=4, cls=PersonEncoder)
print("peter object:\n{}".format(peter))
print("json peter:\n{}".format(json_peter))
Output :
peter object:
<__main__.Person object at 0x000001FE156C9648>
json peter:
{
"name": "Peter",
"age": 18,
"gender": "Men"
}
json.loads()1. visit JSON The value in
adopt json.loads() Methods will JSON String to python Of dict Object can access its key value
import json
json_string = '''{"name":"peter", "age":18, "gender":"Men"}'''
data = json.loads(json_string)
print("json string:\n{}".format(json_string))
print("data:\n{}".format(data))
print("age: {}".format(data["age"]))
Output :
json string:
{
"name":"peter", "age":18, "gender":"Men"}
data:
{
'name': 'peter', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'Men'}
age: 18
2. visit JSON Nested objects
obtain JSON In a string salary Value
import json
json_string = ''' { "company": { "person": { "name": "peter", "age": 18, "gender": "Men", "pay": { "salary": 3000, "bonus": 5000 } } } } '''
data = json.loads(json_string)
print("json string:\n{}".format(json_string))
print("data:\n{}".format(data))
print("salary: {}".format(data["company"]["person"]["pay"]["salary"]))
Output :
adopt data[“company”][“person”][“pay”][“salary”] Accessing nested values
json string:
{
"company": {
"person": {
"name": "peter",
"age": 18,
"gender": "Men",
"pay": {
"salary": 3000,
"bonus": 5000
}
}
}
}
data:
{
'company': {
'person': {
'name': 'peter', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'Men', 'pay': {
'salary': 3000, 'bonus': 5000}}}}
salary: 3000
3. take JSON String into class object object_hook Is used to JSON The string is decoded into a custom class object , Default object_hook= None Is decoded into dict. So you need to customize a decoding method .
object_hookis an optional function that will be called with the result of any object literal decode (adict). The return value ofobject_hookwill be used instead of thedict. This feature can be used to implement custom decoders (e.g. JSON-RPC class hinting).
import json
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def PersonDecoder(obj):
return Person(obj['name'], obj['age'], obj['gender'])
person_json_string = '''{"name" : "peter", "age": 18, "gender" : "men"}'''
person_object = json.loads(person_json_string, object_hook=PersonDecoder)
print("person json string:\n{}".format(person_json_string))
print("peson object:\n{}".format(person_object))
print("name:{}\nage:{}\ngender:{}".format(person_object.name, person_object.age, person_object.gender))
Output :
person json string:
{
"name" : "peter", "age": 18, "gender" : "men"}
peson object:
<__main__.Person object at 0x000001FFBCF4AA88>
name:peter
age:18
gender:men
4. Judge JSON Is the format correct
The following JSON String One less. ’ } '
json_string = ''' { "company": { "person": { "name": "peter", "age": 18, "gender": "Men", "pay": { "salary": 3000, "bonus": 5000 } } } '''
def is_valid_JSON(json_data):
try:
json.loads(json_data)
except ValueError as err:
return False
return True
is_valid = is_valid_JSON(json_string)
print("json string is valid: {}".format(is_valid))
Output :
json string is valid: False
5. obtain JSON One of the strings key All the values
Get the following JSON All in string name Of value
import json
json_string = ''' [ { "id":1, "name":"peter", "hobby":[ "reading", "movie" ] }, { "id":2, "name":"lina", "hobby":[ "sleep", "shopping" ] } ] '''
json_data = json.loads(json_string)
name_list = [item.get("name") for item in json_data]
print(name_list)
Output :
['peter', 'lina']
write file json.dump()1. Dictionaries dict Turn it into JSON write file
import json
d = {
"name" : "peter", "age": 18, "gender" : "men"}
with open("json.txt", 'w+') as f:
json.dump(d, f, indent=4)
json.txt Content 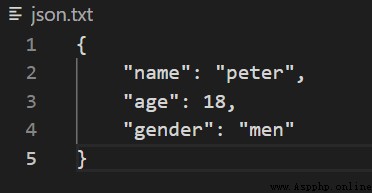
2. Custom class objects are converted to JSON Write text
You need to customize one JSONEncoder Subclass to override the default Serialization is assigned to cls Parameters .
import json
from json import JSONEncoder
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
class PersonEncoder(JSONEncoder):
def default(self, o):
return o.__dict__
person = Person("peter", 18, "men")
with open("json.txt", 'w+') as f:
json.dump(d, f, indent=4, cls=PersonEncoder)
json.txt Content 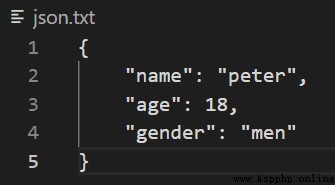
Read the file in json The string element of form is converted to Python type json.load()1. In the text json String to dict
with open("json.txt", 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print(data)
Output :
{
'name': 'peter', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'men'}
2. In text json String into a custom class object object_hook Is used to JSON The string is decoded into a custom class object , Default object_hook= None Is decoded into dict. So you need to customize a decoding method .
import json
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def PersonDecoder(obj):
return Person(obj['name'], obj['age'], obj['gender'])
with open("json.txt", 'r') as f:
person = json.load(f, object_hook=PersonDecoder)
print("name:{}\nage:{}\ngender:{}".format(person.name, person.age, person.gender))
Sometimes we put json Of request In a text file , But not every request is fixed json body, You need to dynamically modify the values , Finally, it has to be transformed into json String as request body.
for example :json.txt Content of text
Need modification collection-id Value of field , Change the json String input request As body
Be careful :json body key They are all in double quotation marks , So make sure that python The object of is transformed into json character string , To pass in request.
{
"search": {
"query": {
"collection-id": ["collection"]
}
},
"targets": [
{
"type": "subscription-id",
"value": [
1234
]
}
]
}
import json
with open("json.txt", 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print("data:\n{}".format(data))
data["search"]["query"]["collection-id"] = ["collection_1", "collection_2", "collection_3"]
print("new data:\n{}".format(data))
json_data = json.dumps(data, indent=4)
print("json data:\n{}".format(json_data))
Output :
data:
{
'search': {
'query': {
'collection-id': ['collection']}}, 'targets': [{
'type': 'subscription-id', 'value': [1234]}]}
new data:
{
'search': {
'query': {
'collection-id': ['collection_1', 'collection_2', 'collection_3']}}, 'targets': [{
'type': 'subscription-id', 'value': [1234]}]}
json data:
{
"search": {
"query": {
"collection-id": [
"collection_1",
"collection_2",
"collection_3"
]
}
},
"targets": [
{
"type": "subscription-id",
"value": [
1234
]
}
]
}