Any programming language has its own Syntax , The compiler or interpreter is responsible for converting the syntactic program code into CPU The machine code that can be executed, and then execute ,Python No exception , It also has its own syntax rules and parser .
Python Programs are case sensitive , If the case is wrong , The program will report an error .
python The most distinctive feature is the use of indentation to represent code blocks , You don't need braces {}
The number of indented spaces is variable , But the statements of the same code block must contain the same number of indented spaces , The number of indented spaces is inconsistent , Can cause a run error .
One copy Python Code example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print("hello Python");
if True:
print ("True")
else:
print ("False")
The number of indented spaces is inconsistent , The following code will report an error :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print("hello Python");
if True:
print ("True")
else:
print ("False") # The code block here is not aligned with the code block above
/*
Operation error prompt :
PS C:\Users\11266> & C:/Users/11266/AppData/Local/Programs/Python/Python38-32/python.exe d:/linux-share-dir/Python/python_code.py
File "d:/linux-share-dir/Python/python_code.py", line 7
print ("False")
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
*/
Make sure that the module , function , Methods and inline comments use the right style
Python There are single line and multi line comments in .
Python Middle single line comment with # start , for example :
# This is a comment
print("hello world!")
Multiline comments use three single quotes ''' Or three double quotes """ Enclose the notes , for example :
1、 Single quotation marks (''')
#!/usr/bin/python3
'''
This is a multiline comment , Use three single quotes
This is a multiline comment , Use three single quotes
This is a multiline comment , Use three single quotes
'''
print("Hello, World!")
2、 Double quotes (""")
#!/usr/bin/python3
"""
This is a multiline comment , Use three double quotes
This is a multiline comment , Use three double quotes
This is a multiline comment , Use three double quotes
"""
print("Hello, World!")
print(' '),print(" "): Enclose the specified string in quotation marks , To output the specified text .
The only difference is that certain characters within single quotation marks need to use escape characters "\", Double quotation marks are not required .
Of course , An escape character is required for double quotation marks , You don't need... In single quotation marks .
for example : print('hello world!'), After running, the output is hello world!
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print("hello world!")
print('hello world!')
print('hello \'world!\'')
print("hello 'world!'")
print("hello \"world!\"")
Output results :
hello world!
hello world!
hello 'world!'
hello 'world!'
hello "world!"
print Function can also accept multiple strings , Comma “,” separate , Can be connected into a string of output .
Where a comma is used, the output will become a space .
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print(" welcome "," Study ","Python Programming ")
print(' welcome ',' Study ','Python Programming ')
Output results :
welcome Study Python Programming
welcome Study Python Programming
print You can also print integers , The result of the calculation is .
print(2019),print(100+200)
Output results :
2019
300
print You can also output multiple lines .( Triple single quotation marks or triple double quotation marks ''',""")
#!/usr/bin/python3
print(''' welcome
Study
Python
Programming ''')
print(""" welcome
Study
Python
Programming """)
Output results :
welcome
Study
Python
Programming
welcome
Study
Python
Programming
print() You can also print integers or calculation results :
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print(200+300)
print("200+300=",200+300)
print("100*2=",100*2)
print("(10+2)*4-10=",(10+2)*4-10)
Output results :
500
200+300= 500
100*2= 200
(10+2)*4-10= 38
print The default output is line feed , If you want to implement no line wrapping, you need to add... At the end of the variable end=""
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
print("hello ")
print("world")
print("hello ",end="")
print("world")
Output results :
hello
world
hello world
Python Provides input() The built-in function reads a line of text from standard input , The default standard input is the keyboard .
input Can receive a Python Expression as input , And return the result to .
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
str = input(" Please enter :")
print (" What you input is : ", str)
Output results :
Please enter : Welcome to learn python Programming
What you input is : Welcome to learn python Programming
When you run the code and press enter ,Python The interactive command line is waiting for your input . At this time , You can type any character , Then press enter to complete the input .
When you're done typing , The content just entered is stored in str In variables .
input() The function also supports displaying a string to prompt the user , such , The user can input the specified content according to the prompt :
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
name = input(" Please enter your name :")
print (" Your name is :", name)
Output results :
Please enter your name :Python
Your name is : Python
stay python3.0 In later versions ,input It's a string ;input() The input data is processed in string mode , If you want to get other types of data , The type needs to be converted :
Example :
#!/usr/bin/python3
my_float = float(input(' Please enter a floating point number :'))
my_int = int(input(' Please enter an integer :'))
my_str = input(' Please enter a string :')
identifier ( The name of the variable ) Is a set of valid strings allowed as names in computer languages . among , Part of it is keywords , The identifier that makes up the language ; Such an identifier cannot be used for other purposes , Otherwise it will cause syntax errors .
Rules for defining identifiers :
(1) The first character must be a letter or underscore in the alphabet _
Be careful : Underscores have special meaning for the interpreter , For normal variables, you should avoid the naming style starting with an underscore .
(2) The rest of the identifier consists of the letters 、 Numbers and underscores
(3) Identifiers are case sensitive .
(4) stay Python 3 in , You can use Chinese as the variable name , Not ASCII Identifiers are also allowed .
(5) Python The keyword of cannot be used as an identifier
Keywords in any language should be relatively stable , But because Python It's a growing and evolving language ,Python The standard library of provides a keyword modular , You can output all keywords of the current version :
#!/usr/bin/python3
import keyword
print(keyword.kwlist)
The output is as follows :
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
Sample code :
#!/usr/bin/python3
str="hello world"
data=6666
Variable =" China " # Use Chinese treat as Variable name
print("str=",str)
print("data=",data)
print(" Variable =", Variable )
Output result :
str= hello world
data= 6666
Variable = China
And other programming languages ( Such as Java、C Language ) Use braces “{}” Separate code blocks are different ,Python Using code indents and colons ( : ) To distinguish the layers between blocks of code .
stay Python in , For class definitions 、 Function definition 、 Flow control statement 、 Exception handling statements, etc , The colon at the end of the line and the indent of the next line , Indicates the beginning of the next block of code , The end of the indentation indicates the end of the code block .
Python Indent the code in , You can use spaces or Tab Key implementation . But whether it's manual typing spaces , Or use Tab key , Usually, we use 4 Space length as an indent ( By default , One Tab The key means 4 A space ).
Sample code :
#!/usr/bin/python3
if 123>456: # Denoted by a colon if Code block of statement
print("123>456") #print The code needs to be indented , Cannot be associated with if Align the top case like a statement , Otherwise, an error will be reported
else: # Denoted by a colon else Code block of statement
print("123<456") #print The code needs to be indented

chart 3-6-1
Because the current computer CPU Only numbers can be processed , To process text , You need to convert text into numbers to process .
The first computers were designed with 8 A bit (bit) As a byte (byte), The largest integer a byte can represent is 255( Binary system 11111111= Decimal system 255), If you want to represent a larger integer , You have to use more bytes .
such as : The largest integer that two bytes can represent is 65535,4 The largest integer that a byte can represent is 4294967295.
Because computers are invented by Americans , At the very beginning 127 Characters are encoded into the computer , Contains upper and lower case English letters 、 Numbers and symbols , This code table is called ASCII code , Like capital letters A The code of is 65, Lowercase letters z The code of is 122.
But to deal with Chinese, obviously one byte is not enough , At least two bytes required , And not with ASCII Encoding conflict , therefore , China made GB2312 code , It's used to compile Chinese .
What you can imagine is , There are hundreds of languages all over the world , Japan compiles Japanese into Shift_JIS in , South Korea compiles Korean into Euc-kr in , Every country has its own standards , There will inevitably be conflicts , The result is , In a mixed language text , There's going to be a mess .
therefore , It was born Unicode code .Unicode Unify all languages into one set of codes , So there won't be any more confusion .
Unicode Standards are evolving , But the most common is to use two bytes to represent a character ( If you want to use very remote characters , Need 4 Bytes ). Modern operating systems and most programming languages directly support Unicode.
ASCII Coding and Unicode Coding differences :ASCII Encoding is 1 Bytes , and Unicode Coding is usually 2 Bytes .
Letter A use ASCII The code is decimal 65, The binary 01000001;
character 0 use ASCII The code is decimal 48, The binary 00110000, Pay attention to the characters '0' And integer 0 Is different ;
There are more than ASCII The range of coding , use Unicode The code is decimal 20013, The binary 01001110 00101101.
If you put ASCII Coded A use Unicode code , Just fill in the front 0 Can , therefore ,A Of Unicode Encoding is 00000000 01000001.
If we unify all text codes into Unicode code , The garbled code problem disappears ; however , If the text you write is basically all in English , use Unicode Coding ratio ASCII Coding requires twice as much storage space , It's very uneconomical in storage and transmission .
therefore , There's another one Unicode Code to “ Variable length encoding ” Of UTF-8 code .
UTF-8 Code a Unicode Characters are encoded into... According to different number sizes 1-6 Bytes , Common English letters are encoded as 1 Bytes , Chinese characters are usually 3 Bytes , Only rare characters are encoded as 4-6 Bytes . If the text to be transmitted contains a large number of English characters , use UTF-8 Coding saves space .
character
ASCII
Unicode
UTF-8
A
01000001
00000000 01000001
01000001
in
x
01001110 00101101
11100100 10111000 10101101
From the table above, we can find , ASCII Coding can actually be thought of as UTF-8 Part of coding , therefore , A large number only support ASCII The history of coding legacy software can be found in UTF-8 Keep working under the code .
Currently in the computer memory , Unified use Unicode code , When you need to save to a hard disk or need to transfer , Just switch to UTF-8 code .
When editing with Notepad , Read from file UTF-8 The characters are converted to Unicode Characters in memory , After editing , Save it with Unicode Convert to UTF-8 Save to file .
When browsing the web , The server will dynamically generate Unicode Content to UTF-8 Then transfer to browser .
By default ,Python 3 Source files are all in UTF-8 code , All strings are unicode character string .
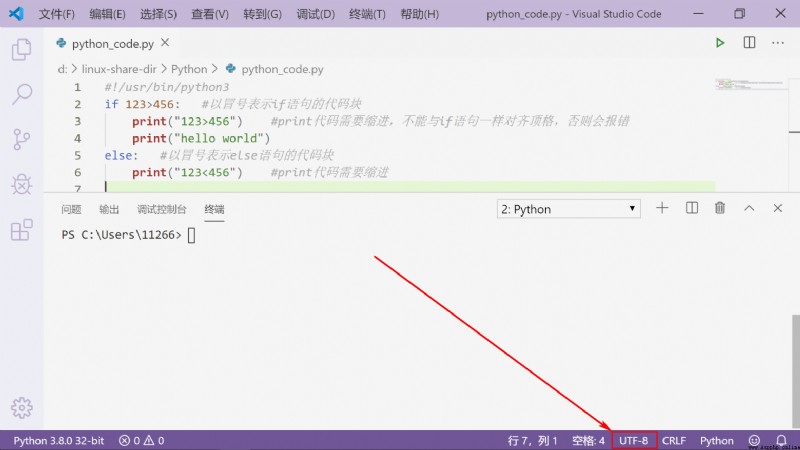
chart 3-7-1
Code can also specify different codes for source files .
such as : Defines that... Is allowed in the source file Windows-1252 Character encoding in character set , The appropriate language is Bulgarian 、 White rose 、 Macedonian 、 Russian 、 Serbian .
# -*- coding: cp-1252 -*-
Define source code usage UTF-8 code :
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
if 123>456: # Denoted by a colon if Code block of statement
print("123 Greater than 456") #print The code needs to be indented , Cannot be associated with if Align the top case like a statement , Otherwise, an error will be reported
print("hello world")
else: # Denoted by a colon else Code block of statement
print("123 Less than 456") #print The code needs to be indented
The first line of comment is to tell Linux/OS X System , This is a Python Executable program ,Windows The system ignores this comment .
The second comment is to tell Python Interpreter , according to UTF-8 Code read source code , otherwise , The Chinese output you write in the source code may be garbled .
The statement UTF-8 Coding doesn't mean your .py The document is UTF-8 Coded , You must and make sure that the text editor is in use UTF-8 code .