In this paper, Queue stay Deepstream/Gstreamer The role of .
Description of the environment :
stay Deepstream Python Of Official case in ,deepstream-test3 Many cases are used queue modular , Whole pipeline The code for is as follows :
def main(args):
# Check input arguments
if len(args) < 2:
sys.stderr.write("usage: %s <uri1> [uri2] ... [uriN]\n" % args[0])
sys.exit(1)
for i in range(0,len(args)-1):
fps_streams["stream{0}".format(i)]=GETFPS(i)
number_sources=len(args)-1
# Standard GStreamer initialization
GObject.threads_init()
Gst.init(None)
# Create gstreamer elements */
# Create Pipeline element that will form a connection of other elements
print("Creating Pipeline \n ")
pipeline = Gst.Pipeline()
is_live = False
if not pipeline:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create Pipeline \n")
print("Creating streamux \n ")
# Create nvstreammux instance to form batches from one or more sources.
streammux = Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvstreammux", "Stream-muxer")
if not streammux:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create NvStreamMux \n")
pipeline.add(streammux)
for i in range(number_sources):
print("Creating source_bin ",i," \n ")
uri_name=args[i+1]
if uri_name.find("rtsp://") == 0 :
is_live = True
source_bin=create_source_bin(i, uri_name)
if not source_bin:
sys.stderr.write("Unable to create source bin \n")
pipeline.add(source_bin)
padname="sink_%u" %i
sinkpad= streammux.get_request_pad(padname)
if not sinkpad:
sys.stderr.write("Unable to create sink pad bin \n")
srcpad=source_bin.get_static_pad("src")
if not srcpad:
sys.stderr.write("Unable to create src pad bin \n")
srcpad.link(sinkpad)
queue1=Gst.ElementFactory.make("queue","queue1")
queue2=Gst.ElementFactory.make("queue","queue2")
queue3=Gst.ElementFactory.make("queue","queue3")
queue4=Gst.ElementFactory.make("queue","queue4")
queue5=Gst.ElementFactory.make("queue","queue5")
pipeline.add(queue1)
pipeline.add(queue2)
pipeline.add(queue3)
pipeline.add(queue4)
pipeline.add(queue5)
print("Creating Pgie \n ")
pgie = Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvinfer", "primary-inference")
if not pgie:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create pgie \n")
print("Creating tiler \n ")
tiler=Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvmultistreamtiler", "nvtiler")
if not tiler:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create tiler \n")
print("Creating nvvidconv \n ")
nvvidconv = Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvvideoconvert", "convertor")
if not nvvidconv:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create nvvidconv \n")
print("Creating nvosd \n ")
nvosd = Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvdsosd", "onscreendisplay")
if not nvosd:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create nvosd \n")
nvosd.set_property('process-mode',OSD_PROCESS_MODE)
nvosd.set_property('display-text',OSD_DISPLAY_TEXT)
if(is_aarch64()):
print("Creating transform \n ")
transform=Gst.ElementFactory.make("nvegltransform", "nvegl-transform")
if not transform:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create transform \n")
print("Creating EGLSink \n")
sink = Gst.ElementFactory.make("nveglglessink", "nvvideo-renderer")
if not sink:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to create egl sink \n")
if is_live:
print("Atleast one of the sources is live")
streammux.set_property('live-source', 1)
streammux.set_property('width', 1920)
streammux.set_property('height', 1080)
streammux.set_property('batch-size', number_sources)
streammux.set_property('batched-push-timeout', 4000000)
pgie.set_property('config-file-path', "dstest3_pgie_config.txt")
pgie_batch_size=pgie.get_property("batch-size")
if(pgie_batch_size != number_sources):
print("WARNING: Overriding infer-config batch-size",pgie_batch_size," with number of sources ", number_sources," \n")
pgie.set_property("batch-size",number_sources)
tiler_rows=int(math.sqrt(number_sources))
tiler_columns=int(math.ceil((1.0*number_sources)/tiler_rows))
tiler.set_property("rows",tiler_rows)
tiler.set_property("columns",tiler_columns)
tiler.set_property("width", TILED_OUTPUT_WIDTH)
tiler.set_property("height", TILED_OUTPUT_HEIGHT)
sink.set_property("qos",0)
sink.set_property("sync", 0)
print("Adding elements to Pipeline \n")
pipeline.add(pgie)
pipeline.add(tiler)
pipeline.add(nvvidconv)
pipeline.add(nvosd)
if is_aarch64():
pipeline.add(transform)
pipeline.add(sink)
print("Linking elements in the Pipeline \n")
streammux.link(queue1)
queue1.link(pgie)
pgie.link(queue2)
queue2.link(tiler)
tiler.link(queue3)
queue3.link(nvvidconv)
nvvidconv.link(queue4)
queue4.link(nvosd)
if is_aarch64():
nvosd.link(queue5)
queue5.link(transform)
transform.link(sink)
else:
nvosd.link(queue5)
queue5.link(sink)
# create an event loop and feed gstreamer bus mesages to it
loop = GObject.MainLoop()
bus = pipeline.get_bus()
bus.add_signal_watch()
bus.connect ("message", bus_call, loop)
tiler_src_pad=pgie.get_static_pad("src")
Gst.debug_bin_to_dot_file(pipeline, Gst.DebugGraphDetails.ALL, "pipeline")
if not tiler_src_pad:
sys.stderr.write(" Unable to get src pad \n")
else:
tiler_src_pad.add_probe(Gst.PadProbeType.BUFFER, tiler_src_pad_buffer_probe, 0)
# List the sources
print("Now playing...")
for i, source in enumerate(args):
if (i != 0):
print(i, ": ", source)
print("Starting pipeline \n")
# start play back and listed to events
pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.PLAYING)
try:
loop.run()
except:
pass
# cleanup
print("Exiting app\n")
pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.NULL)
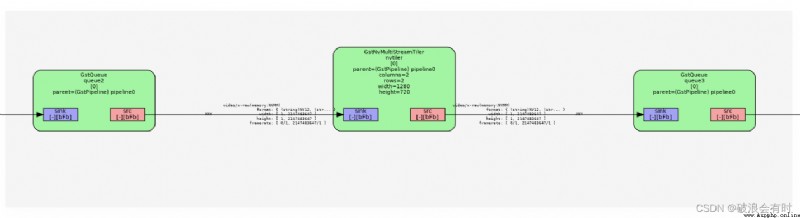
We go through graphviz Print out pipeline Visualization of , as follows :

We can zoom in locally , Here's the picture . We found that , In the original pipeline On the basis of , Between every two modules , We all added one queue modular . And this queue The input and output of the module are shown in the figure Any, explain queue The effect of is independent of input and output changes .
We see the Gstreamer Its official website , In Chapter When would you want to force a thread? The use of queue Causes and functions of :
We have seen that threads are created by elements but it is also possible to insert elements in the pipeline for the sole purpose of forcing a new thread in the pipeline. ( We have seen that the thread is composed of element Created , But it is also possible to force in pipeline Using a new thread in pipeline Insert element.)
There are several reasons to force the use of threads. However, for performance reasons, you never want to use one thread for every element out there, since that will create some overhead. Let’s now list some situations where threads can be particularly useful:( There are several reasons to force the use of threads . however , For performance reasons , You never want to be there for everyone element All use one thread , Because there will be some overhead . Now let's list some situations where threads are particularly useful :)
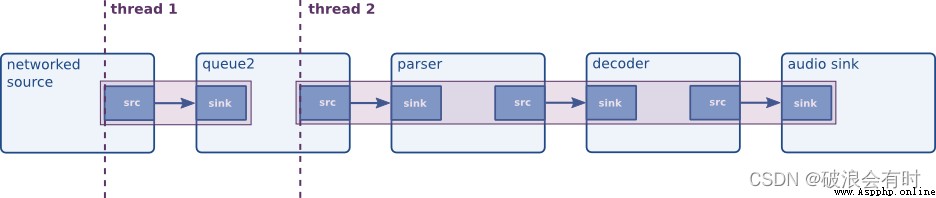
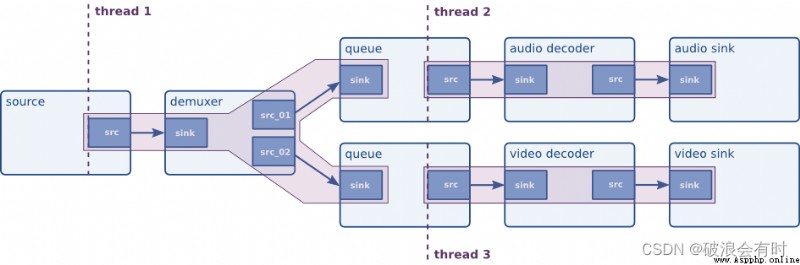
So ,queue The function of the module is to force pipeline A module in the open thread . stay Deepstream Python In the course of using , Personally, I think some can be set queue As a data buffer .