Archetypal model (Prototype Pattern) It's a creative design pattern , Enables you to copy existing objects , And you don't have to make your code depend on the class they belong to . Prototype pattern allows us to create objects based on existing objects by using cloning technology .
Speaking of cloning , A famous non-technical example is the sheep named Dolly , It was created by Scottish researchers by cloning a cell from the breast .

many Python Applications all use prototype patterns , But it is rarely called a prototype , Because cloning objects is a built-in feature of the language .
The idea of the prototype pattern is to use a copy of the complete structure of the object to generate a new object . We will see , This is in Python It is almost natural , Because we have a copy function , It is very helpful to use this technology . In the general case of creating a copy of an object , What happens is that you make a new reference to the same object , This method is called shallow copy . But if you need to copy objects , That is, the prototype , You need to make a deep copy .
The prototype pattern suggests creating an interface to create a clone of an existing object . Objects that any customer can rely on .Python Can be instantiated through classes :
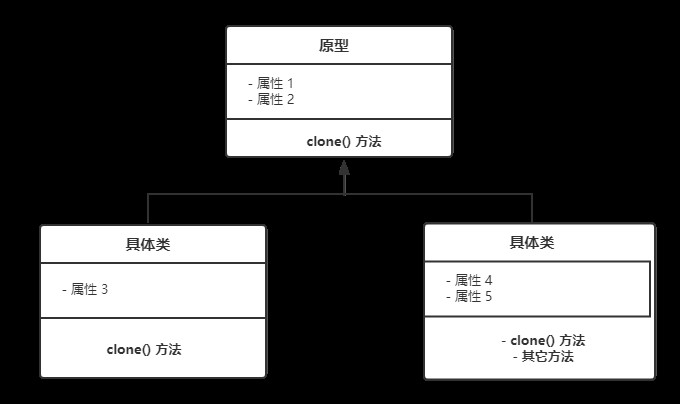
Prototype class : A superclass , It will contain all the necessary properties and methods that an object clone will have . Besides ,Prototype There is an abstract clone() Method , It must be implemented by all subclasses .
concrete class : Once we create the prototype superclass , We can start defining concrete classes based on superclasses . Concrete classes are optional , Can be defined in the application .
Concrete classes can have their own properties and methods , But they always have original archetypal properties and are overwritten clone() edition .
stay Python in , Consider for Car Object to create a prototype . Let's create an interface for the car :
class Car: def __init__(self, engine="1500cc", color="D-white", seats=7): self.engine = engine self.color = color self.seats = seats def __str__(self): return f"{self.engine} | {self.color} | {self.seats}"Prototype class :
The prototype interface has a dictionary data structure to store all cloned objects .
RegisterObject Method to add an element to the dictionary , Take the name of the new object as the key , Take existing objects as values .
DeregisterObject Method to delete an entry from the dictionary .
also , Finally through Clone Method to copy an existing object . The cloning method uses data from Copy Modular deepcopy() Method to clone an object .
import copyclass Prototype: def __init__(self): """Dictionary that will stores cloned objects.""" self._ClonedObjects = {} def RegisterObject(self, name, obj): """Method to store all clones of the existion objects.""" self._ClonedObjects[name] = obj def DeregisterObject(self, name): """Method to delete the cloned object from the dictionary.""" del self._ClonedObjects[name] def Clone(self, name, **kwargs): """Method to clone the object.""" clonedObject = copy.deepcopy(self._ClonedObjects.get(name)) clonedObject.__dict__.update(kwargs) return clonedObject Last , We make use of main Function to test :
if __name__ == "__main__": """The object that will be cloned.""" defaultCar = Car() prototype = Prototype() """The object that will be cloned.""" CarType1 = Car("1000cc", "Red", 4) """Registering the defaultCar in dictionary with its key as 'basicCar'""" prototype.RegisterObject('BasicCar', defaultCar) prototype.RegisterObject('Type-1', CarType1) carOne = prototype.Clone('BasicCar', color = "Lake side brown") carTwo = prototype.Clone('Type-1',color = "Red") carThree = prototype.Clone('Type-1', color = "Moon Dust Silver") print("Details of the default-car:", defaultCar) print("Details of car-One:", carOne) print("Details of car-Two:", carTwo) print("Details of car-Three:", carThree) Operation output :
$ python protype.py Details of the default-car: 1500cc | D-white | 7Details of car-One: 1500cc | Lake side brown | 7 Details of car-Two: 1000cc | Red | 4Details of car-Three: 1000cc | Moon Dust Silver | 4Prototype It's a creative design pattern , Enables you to copy objects , Even complex objects , And you don't have to make your code depend on the class they belong to .
All prototype classes must have a common interface , It makes it possible to copy an object even if its specific class is unknown . Prototype objects can make full copies of themselves , Because objects of the same class can access each other's private member variables .
The prototype pattern reduces the number of subclasses , Hides the complexity of creating objects , And make it easy to add or delete objects at run time .
Reference link :
Deep into design patterns : Archetypal model
The Prototype Pattern
The Prototype Design Pattern in Python