“C位打多了, 你就知道~老抗壓怪了~---凱凱不哭~凱凱堅強
”
我直接寫完語法集合,
然後補一些python語法點~就開第三方庫~~這樣有意思些
哪怕復習一遍學術名詞拼寫,也有意義.
關於語句的最後分號加不加
格式化工具 即可~ Python 是縮進嚴格的語言~ 一定注意不要隨意空格 tab 其實直接理解字面量不好理解~我是反過來理解的
所有的可以自主命名---函數名, 類名, 變量名都屬於標識符identifier
變量值的類型~也就是字面量的種類~
python中整數的大小沒有限制,可以是無限大的整數c = 123_456_789 # 下劃線位置隨便添加
輸入的內容無法識別會報 invalid token
其他進制的數字(不咋用了解下)
語句和表達式
浮點數(小數), 在Python中所有的小數都是float類型
對浮點數進行運算時, 可能會得到一個不精確的結果(很有意思哦)
a1 = 0.1
a2 = 0.2
print(a1+a2) # 0.30000000000000004
#### 字符串
文本信息吧~字符串就是用來表示'文本信息'的
要用引號包裹
- 雙引號內還需要使用引號要用單引號---` 相同引號不能相鄰嵌套`
```python
a1 = '鋤禾日當午,\
汗滴禾下土,\
誰知盤中餐,\
粒粒皆辛苦,\
'
print(a1) # 結果一行
a2 = '''鋤禾日當午,\
汗滴禾下土,\
誰知盤中餐,\
粒粒皆辛苦,\
'''
print(a2) # 不分行
a3 = '''鋤禾日當午,
汗滴禾下土,
誰知盤中餐,
粒粒皆辛苦,
'''
print(a3) # 分行
通過上面內容可以發現, 這個反斜槓的作用類似一個"軟換行"
就是告訴解釋器, 後面的換行不要當做換行/內容連接起來
“實際上叫做 續行符~ 也是一種
”轉義字符
“確實有一些做網頁不方便~因為不是必然的單一為網頁而生~比如格式保留. 需要不停地寫轉義符
C在這方面更離譜
”
寫一個有意思的 \u0040可以顯示一個@符號
\u之後跟unicode編碼 4位
“沒啥用...編輯器出不來結果 你敢直接用在浏覽器?
”
intro = '你好'
name = 'Shinkai'
# 同字符串類型可以相加
print(intro + name) # 你好Shinkai
# 下面這種寫法在python中並不常見
print(intro + name + "!!!!!") # 你好Shinkai!!!!!
# 一般寫成這樣子
print(intro+name, "!!!!!") # 你好Shinkai !!!!!
str = 'hello %s' % '孫悟空' # %s 是 string的簡寫
print(str) # hello 孫悟空
str1 = 'hello %s 你好 %s' % ('monkey', '孫悟空')
print(str1) # hello monkey 你好 孫悟空
str2 = 'hello %3s' % 'ab' # 字符串長度最少3
print(str2) # hello ab
str3 = 'hello %3.5s' % 'abcdef' # 字符串長度在3-5
print(str3) # hello abcde
%f 是浮點數占位符
%d 是整數占位符, 只是捨去小數部分
“只是使用不用這麼細~我就是學的時候知道一下~
”
res = 'res'
print('res = %s' % res) # res = res
intro = 'hello'
name = 'Shinkai'
res = f'{intro} {name}'
print(res) # hello Shinkai
“想玩的花的自己看報錯好吧.. 不模擬所有情況了
”
總結一下字符串拼接方式4種(實際兩種)
“python獨有的,字符串*n會將字符串重復n次返回
”
name = 'Shinkai' * 2
print('hello ' + name) # hello ShinkaiShinkai
print('hello', name)
print('hello %s ' % name)
print(f'hello {name} ')
邏輯判斷
布爾值實際也是整型, True是1, False是0
print(1 + True) # 2
print(1 + False) # 1
print(1 * False) # 0
None表示不存在 別跟null搞混了不存在null類型但是有None類型
目前提到的內容above, 有字符串, 數值,空值
數值包含: 整型(包含布爾), 浮點, 復數
str = '123'
num = 123
print(str) # 123
print(num) # 123
可以看到 不同類型的內容 打印出來都是123 不知道類型~
“實際上pycharm指針放變量上面就顯示了~
”
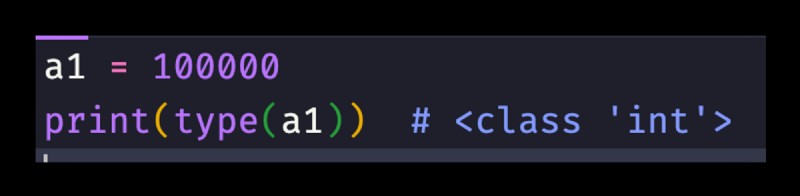
print(type(num)) # <class 'str'>
print(type(str)) # <class 'int'>
所有類型檢查
# 類型檢查
print(type('123')) # <class 'str'>
print(type(123)) # <class 'int'>
print(type(123.123)) # <class 'float'>
print(type(True)) # <class 'bool'>
print(type(None)) # <class 'NoneType'>
python是面向對象的語言~
“說白了現在的都是面向對象,面向對象只要有語法包含聲明式表達就叫面向對象.....
”

“重學還能學到好多東西~ 這是操作系統的內容
調度算法~雖然咱不用~但是備一個影響不大
這塊區別有一個靜態數據區 靜態變量是放在這裡的.
”
這裡不寫~ 內容太多了....
每個對象都會存一個id, type, value
“我們下載的官方版本的python,也就是沒有前綴的python解釋器~因此就是Cpython, Cpython的id就是變量存儲的內存地址
”
# 對象結構
name = 'Shinkai'
print(id(name)) # 4313468016, 4443786352
print(type(name)) # <class 'str'>
print(name) # Shinkai
對象實際上沒有直接存在變量中, 實際上存儲的是對象在內存中的地址
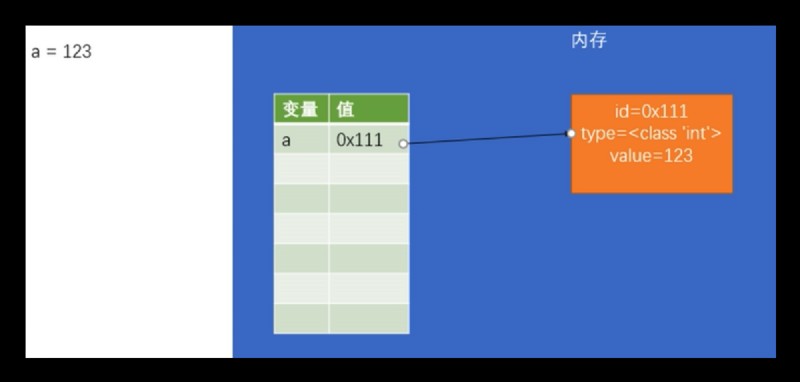
test = 123
test2 = test
test3 = 123
print(test == test2) # True
print(test == test3) # True
# 這樣寫也是相同的
test = {"key": "value"}
test2 = test
test3 = {"key": "value"}
print(test == test2) # True
print(test == test3) # True
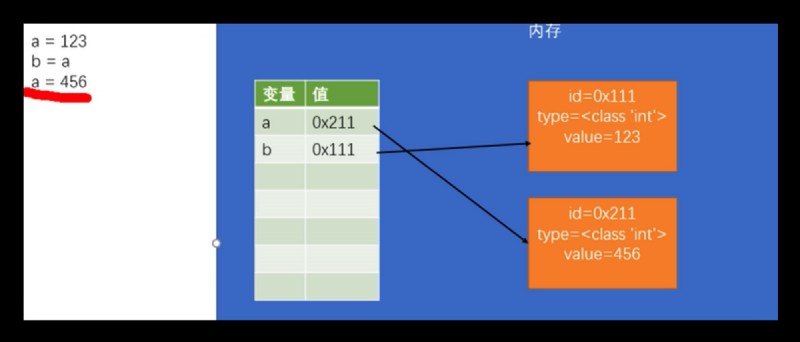
Python是強類型, 不可以對原來已經聲明的變量產生影響,並且不可以隱式轉換~但是可以強行轉換後把內容賦值給原來的變量~
變量是可以無限次賦值的~
“解釋一下就是比如int(a), 實際上是吧 a的類型改成int 然後把其他內容復制,然後把這個地址給a.
”
類似int(),但是是小數形式
Ture->'True'
False->'False'
123->'123'
...
a=True
0,None,''空字符串都是False
# +加法運算符(如果是兩個字符串之間進行加法運算,則會進行拼串操作)
# -減法運算符
# *乘法運算符(如果將字符串和數字相乘,則會對字符串進行復制操作,將字符串重復指定次數)
# / 除法運算符,運算時結果總會返回一個浮點類型
# //整除,只會保留計算後的整數位
# ** 冪運算
# % 模余運算 結果是余數
=就是簡單的右側值賦給左側
print('2'>'11') # true
實際上字符串比較比較的是unicode編碼~ 每一位的unicode. 第一位大於就是true
“js一樣
”
可以推測出
'a'>'b' # false
'ab' > 'b' # false
“沒啥用就是有意思.
”
邏輯非 not
邏輯與 and
邏輯或 or
False and print(a) # 不打印
True and print(a) # 打印
False or print(a) # 打印
True or print(a) # 不打印
把每個值轉換為布爾值運算
res = 1 and 2 # 第一個為true,返回第二個
res = 1 and 0
res = 0 and 1 # 第一個為false 短路 直接返回false
or一樣~
語法: 語句1 if 表達式 else 語句2
print('1') if True else print('2')
一般這樣用
max = a if a > b else b
就是max是ab中大的一個數
自己先建議加括號
做題看優先級表格, 太離譜的別理他 怼他,你看不懂都可以diss他
代碼塊 a = 2
if a == 1:
print('1')
print('2')
print('3') # 3
input() 函數可以暫時阻止程序結束~輸入隨機字符後結束~
if- elif -else
# # 偶數奇數判斷
# num = int(input('隨便輸入一個數'))
# print('偶數' if num % 2 == 0 else '奇數')
# # 閏年判斷
# year = int(input('隨便輸入一個年份'))
# print('閏年' if ((year % 100 != 0 and year % 4 == 0) or (year % 100 == 0))else '非閏年')
# # 狗子相當於人年齡判斷
# dog_age = int(input('請輸入你家狗年齡'))
# if dog_age <= 0:
# print('騙誰呢')
# elif dog_age <= 2:
# person_age = dog_age * 10.5
# print(f'狗的年齡相當於人的{person_age}')
# else:
# person_age = (dog_age - 2) * 4 + 21
# print(f'狗的年齡相當於人的{person_age}')
# 根據得分, 給獎勵
# score = int(input('請輸入你的得分'))
# if score == 100:
# print('niubi666')
# elif 80 <= score <= 99:
# print('還行')
# elif 60 <= score <= 79:
# print('屁股開花')
# else:
# print('no 獎勵')
# print(bool(0))
# print(bool('0'))
# 嫁不嫁判斷~
# question1 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 有房?'))
# question2 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 有車?'))
# question3 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 帥麼?'))
# if question1 or question2 or question3:
# if question1 and question2 and question3:
# print('嫁了嫁了')
# else:
# print('湊活一下也能過')
# else:
# print('你是來搞笑的吧')
# a1 = '鋤禾日當午,\
# 汗滴禾下土,\
# 誰知盤中餐,\
# 粒粒皆辛苦,\
# '
# print(a1) # 結果一行
# a2 = '''鋤禾日當午,\
# 汗滴禾下土,\
# 誰知盤中餐,\
# 粒粒皆辛苦,\
# '''
# print(a2) # 不分行
# a3 = '''鋤禾日當午,
# 汗滴禾下土,
# 誰知盤中餐,
# 粒粒皆辛苦,
# '''
# print(a3) # 分行
# intro = '你好'
# name = 'Shinkai'
# # 同字符串類型可以相加
# print(intro + name) # 你好Shinkai
# # 下面這種寫法在python中並不常見
# print(intro + name + "!!!!!") # 你好Shinkai!!!!!
# # 一般寫成這樣子
# print(intro+name, "!!!!!") # 你好Shinkai !!!!!
# str = 'hello %s' % '孫悟空' # %s 是 string的簡寫
# print(str) # hello 孫悟空
# str1 = 'hello %s 你好 %s' % ('monkey', '孫悟空')
# print(str1) # hello monkey 你好 孫悟空
# str2 = 'hello %3s' % 'ab' # 字符串長度最少3
# print(str2) # hello ab
# str3 = 'hello %3.5s' % 'abcdef' # 字符串長度在3-5
# print(str3) # hello abcde
# res = 'res'
# print('res = %s' % res) # res = res
# # 更優的寫法
# intro = 'hello'
# name = 'Shinkai'
# res = f'{intro} {name}'
# print(res) # hello Shinkai
# assignment
# name = 'Shinkai' * 2
# print('hello ' + name) # hello ShinkaiShinkai
# print('hello', name)
# print('hello %s ' % name)
# print(f'hello {name} ')
# print(1 + True) # 2
# print(1 + False) # 1
# print(1 * False) # 0
# str = '123'
# num = 123
# print(str) # 123
# print(num) # 123
# print(type(num)) # <class 'str'>
# print(type(str)) # <class 'int'>
# # 類型檢查
# print(type('123')) # <class 'str'>
# print(type(123)) # <class 'int'>
# print(type(123.123)) # <class 'float'>
# print(type(True)) # <class 'bool'>
# print(type(None)) # <class 'NoneType'>
# # 對象結構
# name = 'Shinkai'
# print(id(name)) # 4313468016, 4443786352
# print(type(name)) # <class 'str'>
# print(name) # Shinkai
# test = {"key": "value"}
# test2 = test
# test3 = {"key": "value"}
# print(test == test2) # True
# print(test == test3) # True
# # 類型轉換
# a = True
# a = int(a)
# print(a)
# a = 2**2
# print(a)
# obj1 = {'a': 123}
# obj2 = {'a': 123}
# print(obj1 is obj2)
# a = 0
# a = not a
# print(a)
# a = 0
# False and print(a) # 不打印
# True and print(a) # 打印
# False or print(a) # 打印
# True or print(a) # 不打印
# print('1') if True else print('2')
# if 1 == 1:
# print('1')
# print('1')
# a = 2
# if a == 1:
# print('1')
# print('2')
# print('3')
# a = input('請輸入1-100一個數字')
# if a == '123':
# print('回答正確')
# else:
# print('回答錯誤, 你的答案是', a)
# age = int(input('請輸入你的年齡:'))
# if age > 18:
# print('你已經成年')
# elif age > 10:
# print('你上小學了')
# elif age <= 3:
# print('你還是小孩')
# else:
# print('奇怪的年齡')
# # 偶數奇數判斷
# num = int(input('隨便輸入一個數'))
# print('偶數' if num % 2 == 0 else '奇數')
# # 閏年判斷
# year = int(input('隨便輸入一個年份'))
# print('閏年' if ((year % 100 != 0 and year % 4 == 0) or (year % 100 == 0))else '非閏年')
# dog_age = int(input('請輸入你家狗年齡'))
# if dog_age <= 0:
# print('騙誰呢')
# elif dog_age <= 2:
# person_age = dog_age * 10.5
# print(f'狗的年齡相當於人的{person_age}')
# else:
# person_age = (dog_age - 2) * 4 + 21
# print(f'狗的年齡相當於人的{person_age}')
# score = int(input('請輸入你的得分'))
# if score == 100:
# print('niubi666')
# elif 80 <= score <= 99:
# print('還行')
# elif 60 <= score <= 79:
# print('屁股開花')
# else:
# print('no 獎勵')
# print(bool(0))
# print(bool('0'))
# question1 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 有房?'))
# question2 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 有車?'))
# question3 = bool(input('1為是,不填為否, 帥麼?'))
# if question1 or question2 or question3:
# if question1 and question2 and question3:
# print('嫁了嫁了')
# else:
# print('湊活一下也能過')
# else:
# print('你是來搞笑的吧')
command + / 注釋
shift+回車 光標跳轉到下一行開頭
option+command + L 格式化代碼
shift+command+上下 可以上下移動當前行所有內容
“好多區別....js把能捨的都捨了
js根本沒有'靜態資源區域'或者說靜態資源被存在棧裡.看理解吧沒人問的
”
“js不能打印 內存地址, 這個比較麻煩只能通過雙等和三等判斷
js偏底層的api很多都沒有拋出來
”
python沒有三等
不比較地址~畢竟可以看內存地址~
js對象內容一樣,但是內存地址不一樣比較會顯示false
js中==兩個對象實際上比較內存地址~so不可能相同除非指向同一個
python用 is 和 is not來比較 內存地址也就是id 類似js===
可以用來比較是否是同一個對象
python不區分引用數據類型和基本數據類型,區分的是可變不可變數據類型
python不合法字符串轉數值,會報錯 js不報錯有個NaN類型~
python多一個整除運算// 以及乘以字符串~
python和js一樣有短路操作
python可以鏈式比較 1<score<100
js的'0'轉布爾是false js隱式轉換傾向於數值 '0'為0 0是false
python的'0'轉布爾是true.