Learn how to use redis, Use python The code is very simple . Focus on : It turns out that this product only has this knowledge . It is not difficult to .
The original tutorial is too redundant : Detailed tutorial
java Version tutorial :JAVA course
win7 install redis You need to download the client first : Extraction code 1234
Then decompress , Run the following server and client in the folder :
And then in python Terminal or anaconda terminal , Input :pip install redis install redis.
The following interface appears on the server , It indicates that the server has been started . The port number is 6379.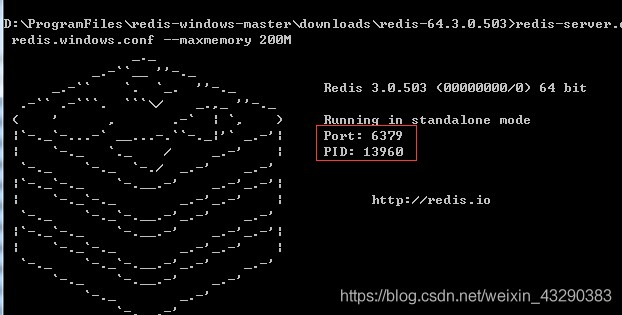
1、 build good development environment , It is enough to master the following knowledge .
import redis # Import redis modular
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
r.set('name', 'runoob') # Set up name Corresponding value
print(r.get('name')) # Remove key name Corresponding value
print(pool)
redis Most commonly used set and get The method is shown in the figure above .
Master common commands , Check again when you use it .
1.set(key, value), Just give name The assignment is value.
r.set('name', 'runoob') # Set up name Corresponding value
2.setnx(key, value)
Set the value , Only name When there is no , Perform the setup operation .
print(r.setnx('fruit1', 'banana')) # fruit1 non-existent , Output is True
3. Set multiple values at once mset, Get multiple values at once mget.
r.mset({
'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'})
print(r.mget("k1", "k2")) # Take out the values corresponding to multiple keys at a time
print(r.mget("k1"))
4、 Gets the specified sequence string getrange(key, start, end), Note the inclusion start and end, and python Medium range Different functions .
r.set("en_name","luoji") # Letter
print(r.getrange("en_name", 0, 2)) # The index number is 0-2 front 3 Bytes of bits luo Slicing operation
print(r.getrange("en_name", 0, -1)) # Take all bytes luoji Slicing operation
5. Counting function ( Add function )
increase incr(self, name, amount=1)
Same as incrbyfloat(self, name, amount=1.0).
Reduce decr(self, name, amount=1).
Suppose we count the number of page hits . If you use a relational database to store clicks , There may be a lot of row level lock contention . therefore , Increase and use of hits redis Of INCR The best order .
r.set("visit:12306:totals", 34634)
r.incr("visit:12306:totals")
r.incr("visit:12306:totals")
print(r.get("visit:12306:totals"))
Output 34636
6、append(key, value)
stay redis name The corresponding value is appended .
r.set("name","luoji") # Letter
r.append("name", "shuaige") # stay name Corresponding value luoji Append string after shuaige
print(r.get("name"))
Output :luojishuaige
1.hset(name, key,value), Just give name The assignment is value.
hget(name,key)
r.hset("hash1", "k1", "v1")
r.hset("hash1", "k2", "v2")
print(r.hkeys("hash1")) # take hash All of the key
print(r.hget("hash1", "k1")) # Single fetch hash Of key Corresponding value
print(r.hmget("hash1", "k1", "k2")) # Multiple fetch hash Of key Corresponding value
2、hgetall(name)
obtain name Corresponding hash All of the key values
print(r.hgetall("hash1"))
3、hlen(name)
obtain name Corresponding hash The number of key-value pairs .
4、hkeys(name)
obtain name Corresponding hash All of the key Value
5、hvals(name)
obtain name Corresponding hash All of the value Value
6、hexists(name, key)
Check name Corresponding hash Whether there is the current incoming key
print(r.hlen("hash1"))
print(r.hkeys("hash1"))
print(r.hvals("hash1"))
print(r.hexists("hash1", "k4")) # False non-existent
7、hdel(name,*keys)
take name Corresponding hash It is specified in key Key value pair of delete
r.hdel("hash1", "k1") # Delete a key value pair
print(r.hgetall("hash1"))
8、hincrby(name, key, amount=1)
Self increasing name Corresponding hash The specified key Value , Create if it does not exist key=amount
r.hincrby("hash1", "k4", amount=1) # If it doesn't exist ,value The default is 1
print(r.hgetall("hash1"))
9、hscan_iter(name, match=None, count=None)
Use the implementation to go in batches redis Get data in
Parameters :
match, Matching the specified key, Default None Represents all key
for item in r.hscan_iter('hash1'):
print(item)
1.lpush(listname,values)
stay listname Add the leftmost element in .
The due rpush(listname,values)
stay listname Add the rightmost element in the .
r.lpush("list1", 11, 22, 33)
print(r.lrange('list1', 0, -1)) # Output 33,22,11
r.rpush("list2", 111, 212, 313) # Operation from right to left
print(r.llen("list2")) # List length
print(r.lrange("list2", 0, 3)) # Slice extraction value , Range is index number 0-3 Output 111, 212, 313
2、r.lset(name, index, value)
Yes name Corresponding list Reassign one of the index positions in
3、 Delete ( Specify a value to delete )
r.lrem(name, value, num)
stay name Corresponding list Deletes the specified value in
Parameters :
name,redis Of name
value, The value to delete
num, num=0, Deletes all specified values from the list ;
r.lrem("list2", "22",0) # Will list all "22" Delete
4、 Value ( Take value according to index number )
lindex(name, index)
stay name The corresponding list gets the list elements by index
print(r.lindex("list2", 0))
5. Custom incremental iteration
because redis Incremental iterations of list elements are not provided in the class library , If you want to loop name All the elements of the corresponding list , So you need :
1、 obtain name All the corresponding lists
2、 Loop list
however , If the list is very large , Then it is possible to burst the memory of the program in the first step , All the functionality necessary to customize an incremental iteration :
def list_iter(name):
""" Customize redis List incremental iteration :param name: redis Medium name, namely : iteration name Corresponding list :return: yield return List elements """
list_count = r.llen(name)
for index in range(list_count):
yield r.lindex(name, index)
# Use
for item in list_iter('list2'): # Traverse the list
print(item)
1. newly added
sadd(name,values)
name Adds an element to the corresponding collection
2. Get the number of elements Be similar to len
scard(name)
obtain name The number of elements in the corresponding set
3. Get all members in the collection
smembers(name)
obtain name All members of the corresponding set
r.sadd("set1", 33, 44, 55, 66) # Add elements to a collection
print(r.scard("set1")) # The length of the set is 4
print(r.smembers("set1")) # Get all members in the collection
4、 Get all members in the collection ,sscan(name)
Returns a tuple , The second member of the tuple is list Value .
print(r.sscan("set1"))
Output :(0, [‘33’, ‘44’, ‘55’, ‘66’])
5、list Can do bad 、 hand over 、 Combine , Here you can learn about it .
Set operation ,Set A collection is a list that cannot be repeated , It's out of order .
Ordered set , On a set basis , Sort each element ; The sorting of the elements needs to be compared against another value ,
therefore , For ordered sets , Each element has two values , namely : Value and weight , Specially used for sorting .
1. newly added
zadd(name, *args, **kwargs)
stay name Adds elements to the corresponding ordered collection
2. Get the number of ordered collection elements Be similar to len
zcard(name)
obtain name The number of elements in the corresponding ordered set
3、 Get all the elements of the ordered collection
r.zrange( name, start, end,
r.zadd("zset2", {
'm1': 22, 'm2': 44})
print(r.zcard("zset2")) # Set length
print(r.zrange("zset2", 0, -1)) # Get all elements in an ordered collection
4、 Get all the elements – Sort by score by default
zscan(name)
5 Get all the elements – iterator
zscan_iter(name)
print(r.zscan("zset2"))
for i in r.zscan_iter("zset2"): # Ergodic iterator
print(i)
6、 Delete – Specified value delete
zrem(name, values)
Delete name The median of the corresponding ordered set is values Members of
r.zrem("zset2", "n3") # Delete elements in an ordered collection n3 Removing a single
1. Delete
delete(names)
According to delete redis Any data type in (string、hash、list、set、 Orderly set)
r.delete("gender") # Delete key by gender The key/value pair
2. Check if the name exists
exists(name)
testing redis Of name Whether there is , Existence is True,False non-existent
print(r.exists("zset1"))
3. Fuzzy matching
keys(pattern=’’)
Get by model redis Of name
more :
KEYS * Matches all in the database key .
print(r.keys("foo*"))
4. Access to type
type(name)
obtain name The type of the corresponding value
print(r.type("set1"))
5. View all elements
scan(cursor=0, match=None, count=None)
It needs to be classified . Note here
print(r.hscan("hash2"))
print(r.sscan("set3"))
print(r.zscan("zset2"))
6. View all elements – iterator , It needs to be classified .
scan_iter(name, count=None)
for i in r.hscan_iter("hash1"):
print(i)
for i in r.sscan_iter("set3"):
print(i)
for i in r.zscan_iter("zset3"):
print(i)
redis The default is created every time a request is executed ( Connection pool request connection ) And disconnect ( Return connection pool ) One connection operation ,
If you want to execute multiple commands in one request , You can use pipline Implement a request that specifies more than one command at a time , And next time by default pipline Atomic operations .
The Conduit (pipeline) yes redis Buffering multiple server commands in providing a single request . Reduce servers - Repeated between clients TCP Database package , Thus, the efficiency of executing batch commands is greatly improved .
import redis
import time
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
pipe = r.pipeline() # Create a pipe
pipe.set('name', 'jack')
pipe.set('role', 'sb')
pipe.sadd('faz', 'baz')
pipe.incr('num') # If num Nonexistence vaule by 1, If there is , be value Self increasing 1
pipe.execute()
print(r.get("name"))
print(r.get("role"))
print(r.get("num"))
Pipeline commands can be written together , Such as :
pipe.set('hello', 'redis').sadd('faz', 'baz').incr('num').execute()
But it's better to separate them .
(Redis) yes key-value The storage system , It's a cross platform, non relational database .
Redis Is an open source use ANSI C Language writing 、 comply with BSD agreement 、 Support network 、 Can be based on memory 、 Distributed 、 Optional persistent key value pairs (Key-Value) Storage database , And provide multilingual API.
Redis It's usually called a data structure server , Because of the value (value) Can be a string (String)、 Hash (Hash)、 list (list)、 aggregate (sets) And ordered set (sorted sets) Other types .